|
Artabazos II Of Phrygia
Artabazos II (in Greek Ἀρτάβαζος) (fl. 389 – 328 BC) was a Persian general and satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of the Persian satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia Pharnabazus II, and younger kinsman (most probably nephew) of Ariobarzanes of Phrygia who revolted against Artaxerxes II around 356 BC. His first wife was an unnamed Greek woman from Rhodes, sister of the two mercenaries Mentor of Rhodes and Memnon of Rhodes. Towards the end of his life, he became satrap of Bactria for Alexander the Great. Revolt of Datames In 362 BC, Artabazos was sent by Artaxerxes II to capture Datames, the satrap of Cappadocia, who had joined in the Satraps' revolt in which Artabazus' brother, Ariobarzanes, was a participant. However, Artabazos was defeated by Datames. Artaxerxes II ultimately prevailed, and Ariobarzanes was crucified and Datames assassinated. Rebellion against Artaxerxes III Following the capture and death of his brother, Artabazos was ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes. The city of Rhodes had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022 the island has population of 124,851 people. It is located northeast of Crete, southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522. Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Medieval Old Town of the City of Rhodes has been declared a World Heritage Site. Today, it is one of the most popular tourist dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pammenes Of Thebes
Pammenes ( grc-gre, Παμμένης) was a Theban general of considerable fame who lived during the 4th century BC. He was connected with Epaminondas by political ties and ties of friendship. When Philip, the future king of Macedonia, was sent as a hostage to Thebes, he was placed under the care of Pammenes. In 369 BC, when Megalopolis was founded, there was a concern that the Spartans would attack those engaged in establishing the community, Epaminondas sent Pammenes at the head of 1000 specially picked soldiers to defend the community. In 362 BC, some of Megalopolitan colonists were in favour of dissolving the community, and returning to their own lands, and called upon the Mantineans and other Peloponnesians, for aid. The Megalopolitan settlers who opposed the dissolution of their community called for help to the Thebans, who sent Pammenes with 3000 foot soldiers and 300 cavalry to their assistance. With this force Pammenes overcame all resistance, and compelled those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orontes I
Orontes I (Old Persian: ''*Arvanta-''; died 344 BC) was a Bactrian nobleman, who served as a military officer of the Achaemenid Empire in the first half of the 4th-century BC. He first appears in 401 BC as the satrap of the satrapy of Armenia. There he participated in the Battle of Cunaxa, where he harassed the Ten Thousand following their retreat. In the same year, he married Rhodogune, a daughter of the King of Kings Artaxerxes II (). In the 380s BC, Orontes along with the satrap Tiribazus were assigned to lead the campaign against Evagoras I (), the king of Salamis in Cyprus. The campaign was initially successful, with Evagoras offering to make peace. However, after the negotiations between him and Tiribazus failed, Orontes accused the latter of deliberately prolonging the war and planning to declare independence. This led to Tiribazus' dismissal and imprisonment. This was followed by a chain of events which ultimately weakened the Persian forces, forcing Orontes to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
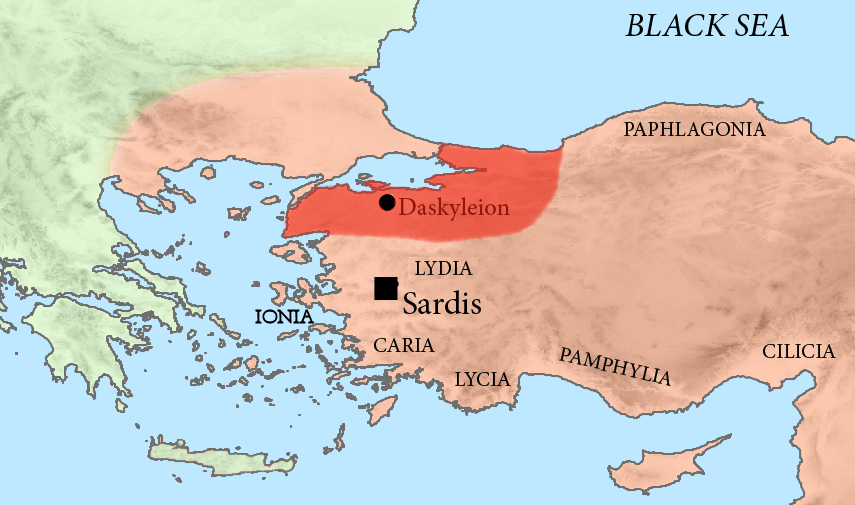
Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lydia on the south, Aeolis on the southwest, Troad on the west, and the Propontis on the north. In ancient times it was inhabited by the Mysians, Phrygians, Aeolian Greeks and other groups. Geography The precise limits of Mysia are difficult to assign. The Phrygian frontier was fluctuating, while in the northwest the Troad was only sometimes included in Mysia. The northern portion was known as "Lesser Phrygia" or ( grc, μικρὰ Φρυγία, mikra Phrygia; la, Phrygia Minor), while the southern was called "Greater Phrygia" or "Pergamene Phrygia". Mysia was in later times also known as Hellespontine Phrygia ( grc, Ἑλλησποντιακὴ Φρυγία, Hellespontiake Phrygia; la, Phrycia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List of urban areas in the European Union, largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful Greek city-state, city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum (classical), Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of civilization, cradle of Western culture, Western civilization and the democracy#History, birthplace of democracy, larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chares Of Athens
Chares of Athens () was a 4th-century BC Athenian military commander (Strategos), who for a number of years was one of Athens's foremost commanders. He was also a well connected politician enabling him to procure the commands he desired, commands he primarily used to enrich himself and his adherents. First campaigns Chares is first mentioned in historical records in 367 BC, when he was sent to the aid of the city of Phlius. The city was hard pressed by the Arcadians and Argives, assisted by the Theban commander at Sicyon. His forces were successful in relieving the city. (It was during this campaign that Aeschines, the orator, first distinguished himself.) After his successful campaign, Chares was recalled to take the command against Oropus; and the recovery of their harbour by the Sicyonians from the Spartan garrison, immediately on his departure, shows how important his presence had been for the support of the Spartan cause in the north of the Peloponnese. In 361 BC, Chares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes III Of Persia
Ochus ( grc-gre, wikt:Ὦχος, Ὦχος ), known by his dynastic name Artaxerxes III ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, wikt:Ἀρταξέρξης, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 359/58 to 338 BC. He was the son and successor of Artaxerxes II and his mother was Stateira (wife of Artaxerxes II), Stateira. Before ascending the throne Artaxerxes was a satrap and commander of his father's army. Artaxerxes came to power after one of his brothers was executed, another committed suicide, the last murdered and his father, Artaxerxes II died. Soon after becoming king, Artaxerxes murdered all of the royal family to secure his place as king. He started two major campaigns against Egypt. The first campaign failed, and was followed up by rebellions throughout the western part of his empire. During the second, Artaxerxes finally defeated Nectanebo II, the Pharaoh of Egypt, bringing the country back into the Persian fold after six decades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolt Of The Satraps
The Great Satraps' Revolt, or the Revolt of the Satraps (366-360 BC), was a rebellion in the Achaemenid Empire of several satraps against the authority of the Great King Artaxerxes II Mnemon. The Satraps who revolted were Datames, Ariobarzanes and Orontes of Armenia. Mausolus the Dynast of Caria participated in the Revolt of the Satraps, both on his nominal sovereign Artaxerxes Mnemon's side and (briefly) against him. They were supported by the pharaohs of Egypt, Nectanebo I, Teos, and Nectanebo II, to whom was sent Rheomithres who came back with 50 ships and 500 talents, and all joined forces against Artaxerxes II. Revolt of Datames (372-362 BC) Datames, the satrap of Cappadocia and a talented military commander, had inherited his satrapy from his father Camissares after 384 BC but later problems with the court led him to revolt in 372 BC. The court commanded the neighboring satraps, Autophradates of Lydia and Artumpara of Lycia, to crush the rebellion but Datames success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Revolt (499 BC), the Cappadocians were reported as occupying a region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine (Black Sea). Cappadocia, in this sense, was bounded in the south by the chain of the Taurus Mountains that separate it from Cilicia, to the east by the upper Euphrates, to the north by Pontus, and to the west by Lycaonia and eastern Galatia. Van Dam, R. ''Kingdom of Snow: Roman rule and Greek culture in Cappadocia.'' Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2002, p.13 The name, traditionally used in Christian sources throughout history, continues in use as an international Tourism in Turkey, tourism concept to define a region of exceptional natural wonders, in particular characterized by fairy chimneys and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)





.jpg)