|
Aricia (mythology)
Aricia ( grc, Ἀρικία, ''Arikía'') is a name appearing in Virgil's ''Aeneid'' in a context that makes it possible for it to be interpreted as referring to a mythical personage: Ibat et Hippolyti proles pulcherrima bello, Virbius, insignem quem mater Aricia misit... (Rough translation: "To the war also came the most fair offspring of Hippolytus, Virbius, whom, distinguished, mother Aricia sent...") It may appear from the quoted passage that Aricia is the mother of Virbius by Hippolytus. Yet Virbius is commonly the name by which Hippolytus himself was known after he was brought back to life on the request of Artemis. As for Aricia, Servius in his commentary on the lines in question explained that Virgil had been referring to the town Aricia, using the epithet "mother" with the town's name in honor of Octavian Augustus whose mother was a native of Aricia. Indeed, Aricia was a location holy to Diana (equated with Artemis) near Rome where Egeria, the spirit of a nearby stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salle De Diane (Louvre) - Diane Rendant à Aricie Hippolyte Ressuscité Par Esculape
Salle is the French word for 'hall', 'room' or 'auditorium', as in: *Salle des Concerts Herz, a former Paris concert hall *Salle Favart, theatre of the Paris Opéra-Comique *Salle Le Peletier, former home of the Paris Opéra *Salle Pleyel, a Paris concert hall *Salle Ventadour, a former Paris theatre *Salle Wilfrid-Pelletier, a multipurpose venue in Montréal It may also refer to: Places: *Salle, Norfolk, a village and civil parish in England, pronounced "Saul" *Salle, Abruzzo, Italy *Salle, Nepal People: *Abraham Salle (1670–1719), Huguenot ancestor, immigrant, and colonist *Alexander Östlund, Swedish football player, nicknamed "Salle" *Auguste Sallé French traveller and entomologist *David Salle, American painter *Fred Salle, English long jumper *Jérôme Salle, French film director *Johan Sälle, Swedish ice hockey player *Mary Lou Sallee, American politician from Missouri See also * La Salle (other) (including LaSalle) * Sal (other) Sal, SAL, or S.A.L. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diana Nemorensis
Diana Nemorensis ("Diana of Nemi"), also known as " Diana of the Wood", was an Italic form of the goddess who became Hellenised during the fourth century BC and conflated with Artemis. Her sanctuary was to be found on the northern shore of Lake Nemi beneath the cliffs of the modern city Nemi (Latin ''nemus Aricinum''). This lake is referred to by poets as ''speculum Dianae'' – "Diana's Mirror"; by the town of Aricia which was situated about three miles off, at the foot of the ''Albanus Mons'', the Alban Mount, and separated by a steep descent from the lake, which lies in a small crater-like hollow on the mountainside. Origin of the legend According to one of several Hellenising foundation myths, the worship of Diana at Nemi would have been instituted by Orestes, who, after killing Thoas, king in the Tauric Chersonesus (the Crimea), fled with his sister Iphigenia to Italy, bringing with him the image of the Tauric Diana hidden in a mound of sticks. After his death, the myth h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallas (son Of Pandion)
Pallas may refer to: Astronomy * 2 Pallas asteroid ** Pallas family, a group of asteroids that includes 2 Pallas * Pallas (crater), a crater on Earth's moon Mythology * Pallas (Giant), a son of Uranus and Gaia, killed and flayed by Athena * Pallas (son of Evander), a prominent character in the ''Aeneid'' * Pallas (son of Lycaon), a teacher of Athena * Pallas (son of Pandion), the father of the 50 Pallantides * Pallas (Titan), the son of Crius and Eurybia, brother of Astraeus and Perses, and husband of Styx * Pallas (daughter of Triton) * Pallas, an epithet of Athena * Pallas, the father of Euryalus by Diomede People * Pallas (freedman) or Marcus Antonius Pallas, a freedman and favorite of Emperor Claudius * Pallas, a secondary wife of Herod the Great; her origins and fate are unknown. People with the surname * David Pallas (born 1980), Swiss footballer * Janette Pallas * José Ignacio Pallas (born 1983), Uruguayan football defender * Maria Pallas (born 1993), Estonian swimm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phèdre
''Phèdre'' (; originally ''Phèdre et Hippolyte'') is a French dramatic tragedy in five acts written in alexandrine verse by Jean Racine, first performed in 1677 at the theatre of the Hôtel de Bourgogne in Paris. Composition and premiere With ''Phèdre'', Racine chose once more a subject from Greek mythology, already treated by Greek and Roman tragic poets, notably by Euripides in '' Hippolytus'' and Seneca in ''Phaedra''. As a result of an intrigue by the Duchess of Bouillon and other friends of the aging Pierre Corneille, the play was not a success at its première on 1 January 1677 at the Hôtel de Bourgogne, home of the royal troupe of actors in Paris. Indeed, a rival group staged a play by the now forgotten playwright Nicolas Pradon on an almost identical theme. After ''Phèdre'', Racine ceased writing plays on secular themes and devoted himself to the service of religion and the king until 1689, when he was commissioned to write ''Esther'' by Madame de Maintenon, the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Racine
Jean-Baptiste Racine ( , ) (; 22 December 163921 April 1699) was a French dramatist, one of the three great playwrights of 17th-century France, along with Molière and Corneille as well as an important literary figure in the Western tradition and world literature. Racine was primarily a tragedian, producing such "examples of neoclassical perfection" as ''Phèdre'', ''Andromaque'', and ''Athalie''. He did write one comedy, '' Les Plaideurs'', and a muted tragedy, ''Esther'' for the young. Racine's plays displayed his mastery of the dodecasyllabic (12 syllable) French alexandrine. His writing is renowned for its elegance, purity, speed, and fury, and for what American poet Robert Lowell described as a "diamond-edge", and the "glory of its hard, electric rage". Racine's dramaturgy is marked by his psychological insight, the prevailing passion of his characters, and the nakedness of both plot and stage. Biography Racine was born on 21 December 1639 in La Ferté-Milon ( Aisne) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodontius
Theodontius was the author of a now lost Latin work on mythology. He was extensively quoted in Giovanni Boccaccio's ''Genealogia Deorum Gentilium'', but is otherwise almost unknown. Boccaccio says that he knew Theodontius's work through the ''Collections'' of Paul of Perugia, which Paul's wife burnt after his death (''Genealogiae'' XV 6). In telling the legend of Bathyllus, however, Boccaccio complains that Theodontius was illegible except for Bathyllus's birth, from Phorcys and a marine monster (''Genealogiae'' X 7), so he may have seen some of Theodontius's own writings; sources disagree on this. Some authorities think Boccaccio invented him. Outside Boccaccio, there was a Theodontius, who wrote on the wars of Troy, and is quoted by Servius on ''Aeneid'', I, 28; and the fourteenth century author Domenico Bandini, who made an index for the ''Genealogiae'', calls him "''Teodontius Campanus diligens investigator poetici figmenti''". Carlo Landi argued in his 1930 monograph ''D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogia Deorum Gentilium
''Genealogia deorum gentilium'', known in English as ''On the Genealogy of the Gods of the Gentiles'', is a mythography or encyclopedic compilation of the tangled family relationships of the classical pantheons of Ancient Greece and Rome, written in Latin prose from 1360 onwards by the Italian author and poet Giovanni Boccaccio. The work is "humanist in spirit and medieval in structure". According to the Preface Boccaccio undertook the project at the request of Hugh IV of Cyprus. The first version was completed in 1360, and he continuously corrected and revised the work until his death in 1374, so that various redactions of the works were copied in different manuscript traditions. In his lifetime and for two centuries afterwards it was considered his most important work. The full range of genealogies of the classical Gods are described in the fifteen books, drawing on the standard earlier works, especially the '' Liber imaginum deorum'', a 12th-century treatise by the othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
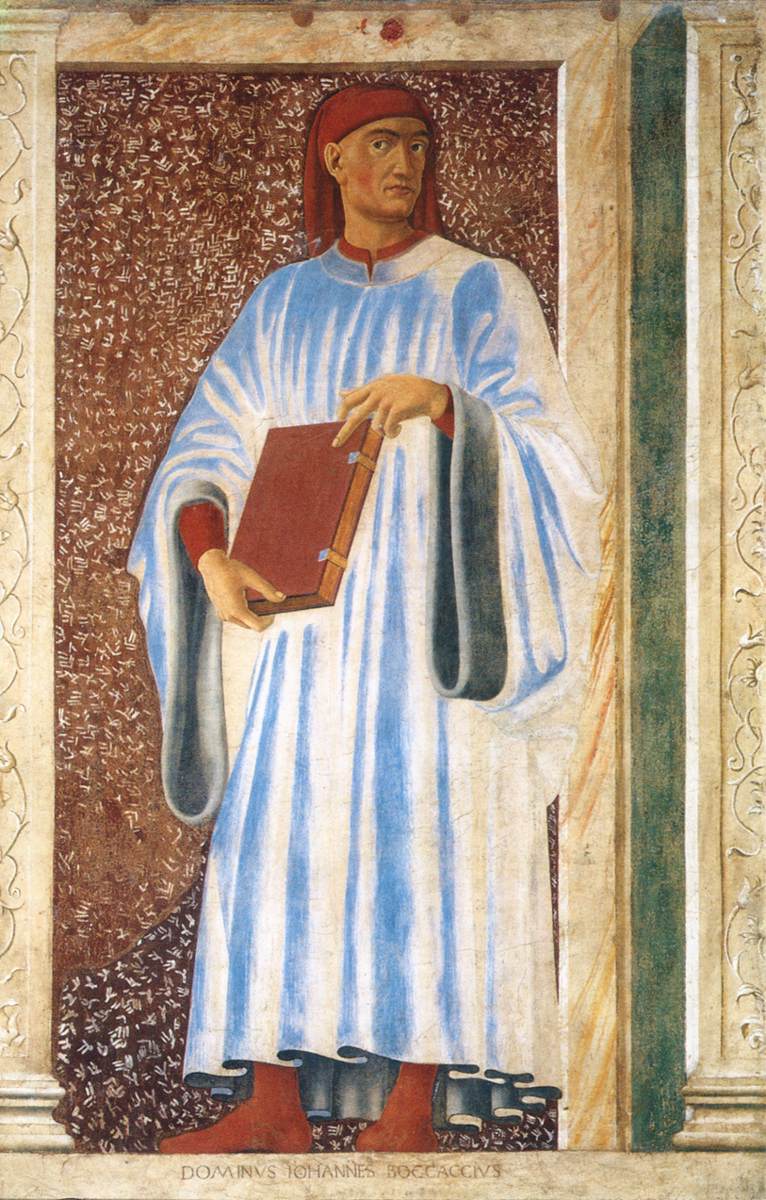
Giovanni Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so well known as a writer that he was sometimes simply known as "the Certaldese" and one of the most important figures in the European literary panorama of the fourteenth century. Some scholars (including Vittore Branca) define him as the greatest European prose writer of his time, a versatile writer who amalgamated different literary trends and genres, making them converge in original works, thanks to a creative activity exercised under the banner of experimentalism. His most notable works are ''The Decameron'', a collection of short stories which in the following centuries was a determining element for the Italian literary tradition, especially after Pietro Bembo elevated the Boccaccian style to a model of Italian prose in the sixteenth century, and ''On Famous Women''. He wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egeria (mythology)
Egeria (, grc, Ἠγερία) was a nymph attributed a legendary role in the early history of Rome as a divine consort and counselor of Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, to whom she imparted laws and rituals pertaining to ancient Roman religion. Her name is used as an eponym for a female advisor or counselor. Origin and etymology Egeria may predate Roman myth: she could have been of Italic origin in the sacred forest of Aricia in Latium, her immemorial site, which was equally the grove of Diana Nemorensis ("Diana of Nemi"). At Aricia there was also a Manius Egerius, a male counterpart of Egeria. The name ''Egeria'' has been diversely interpreted. Georges Dumézil proposed it came from ''ē-gerere'' ("bear out"), suggesting an origin from her childbirth role. It may mean "of the black poplar" (Greek αἴγειρος, ''aigeiros''). Her role as prophetess and author of "sacred books" would compare her to the Etruscan figure of Vegoia (alleged author among other thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the ''Eclogues'' (or ''Bucolics''), the ''Georgics'', and the epic ''Aeneid''. A number of minor poems, collected in the ''Appendix Vergiliana'', were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars consider his authorship of these poems as dubious. Virgil's work has had wide and deep influence on Western literature, most notably Dante's ''Divine Comedy'', in which Virgil appears as the author's guide through Hell and Purgatory. Virgil has been traditionally ranked as one of Rome's greatest poets. His ''Aeneid'' is also considered a national epic of ancient Rome, a title held since composition. Life and works Birth and biographical tradition Virgil's biographical tradition is thought to depend on a lost biography by the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diana (mythology)
Diana is a goddess in Roman and Hellenistic religion, primarily considered a patroness of the countryside, hunters, crossroads, and the Moon. She is equated with the Greek goddess Artemis, and absorbed much of Artemis' mythology early in Roman history, including a birth on the island of Delos to parents Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter and Latona, and a twin brother, Apollo,''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. though she had Diana Nemorensis, an independent origin in Italy. Diana is considered a virgin goddess and protector of childbirth. Historically, Diana made up a triad with two other Roman deities: Egeria (mythology), Egeria the water nymph, her servant and assistant midwife; and Virbius, the woodland god. Diana is revered in modern neopagan religions including Roman polytheistic reconstructionism, Roman neopaganism, Stregheria, and Wicca. In the ancient, medieval, and modern periods, Diana has been considered a triple deity, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_School_-_Boccaccio_(1313–1375)_(Giovanni_Boccaccio)_-_355512_-_National_Trust.jpg)