|
Anthos (play)
''Anthos'' or ''Antheus'' (''Flower'') is a play by the 5th century BCE Athenian dramatist Agathon. The play has been lost. The play is mentioned by Aristotle in his ''Poetics'' (1451b) as an example of a tragedy with a plot which gives pleasure despite the incidents and characters being entirely made up. ''Anthos'' is the only known Greek tragedy play whose plot was entirely invented by the poet. Other 5th century tragedies were based on myth Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), ..., or less frequently on actual history. References {{reflist Lost plays Ancient Greek tragedies 5th-century BC plays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathon
Agathon (; grc, Ἀγάθων; ) was an Athenian tragic poet whose works have been lost. He is best known for his appearance in Plato's ''Symposium,'' which describes the banquet given to celebrate his obtaining a prize for his first tragedy at the Lenaia in 416. He is also a prominent character in Aristophanes' comedy the ''Thesmophoriazusae''. Life and career Agathon was the son of Tisamenus, and the lover of Pausanias, with whom he appears in both the ''Symposium'' and Plato's ''Protagoras''. Together with Pausanias, he later moved to the court of Archelaus, king of Macedon, who was recruiting playwrights; it is here that he probably died around 401 BC. Agathon introduced certain innovations into the Greek theater: Aristotle tells us in the ''Poetics'' (1456a) that the characters and plot of his '' Anthos'' were original and not, following Athenian dramatic orthodoxy, borrowed from mythological or historical subjects. Agathon was also the first playwright to write choral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Athens
The city of Athens ( grc, Ἀθῆναι, ''Athênai'' .tʰɛ̂ː.nai̯ Modern Greek: Αθήναι, ''Athine'' or, more commonly and in singular, Αθήνα, ''Athina'' .'θi.na during the classical period of ancient Greece (480–323 BC) was the major urban centre of the notable ''polis'' (city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC (aftermath of Lamian War). The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles. In the classical period, Athens was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum, Athens was also the birthplace of Socrates, Plato, Pericles, Ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragedy
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsis, or a "pain hatawakens pleasure", for the audience. While many cultures have developed forms that provoke this paradoxical response, the term ''tragedy'' often refers to a specific tradition of drama that has played a unique and important role historically in the self-definition of Western civilization. That tradition has been multiple and discontinuous, yet the term has often been used to invoke a powerful effect of cultural identity and historical continuity—"the Greeks and the Elizabethans, in one cultural form; Hellenes and Christians, in a common activity," as Raymond Williams puts it. From its origins in the theatre of ancient Greece 2500 years ago, from which there survives only a fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy within the Lyceum and the wider Aristotelian tradition. His writings cover many subjects including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theatre, music, rhetoric, psychology, linguistics, economics, politics, meteorology, geology, and government. Aristotle provided a complex synthesis of the various philosophies existing prior to him. It was above all from his teachings that the West inherited its intellectual lexicon, as well as problems and methods of inquiry. As a result, his philosophy has exerted a unique influence on almost every form of knowledge in the West and it continues to be a subject of contemporary philosophical discussion. Little is known about his life. Aristotle was born in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetics (Aristotle)
Aristotle's ''Poetics'' ( grc-gre, Περὶ ποιητικῆς ''Peri poietikês''; la, De Poetica; c. 335 BCDukore (1974, 31).) is the earliest surviving work of Greek dramatic theory and first extant philosophical treatise to focus on literary theory. In this text Aristotle offers an account of ποιητική, which refers to poetry and more literally "the poetic art," deriving from the term for "poet; author; maker," ποιητής. Aristotle divides the art of poetry into verse drama (to include comedy, tragedy, and the satyr play), lyric poetry, and epic. The genres all share the function of mimesis, or imitation of life, but differ in three ways that Aristotle describes: # Differences in music rhythm, harmony, meter and melody. # Difference of goodness in the characters. # Difference in how the narrative is presented: telling a story or acting it out. The surviving book of ''Poetics'' is primarily concerned with drama, and the analysis of tragedy constitutes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
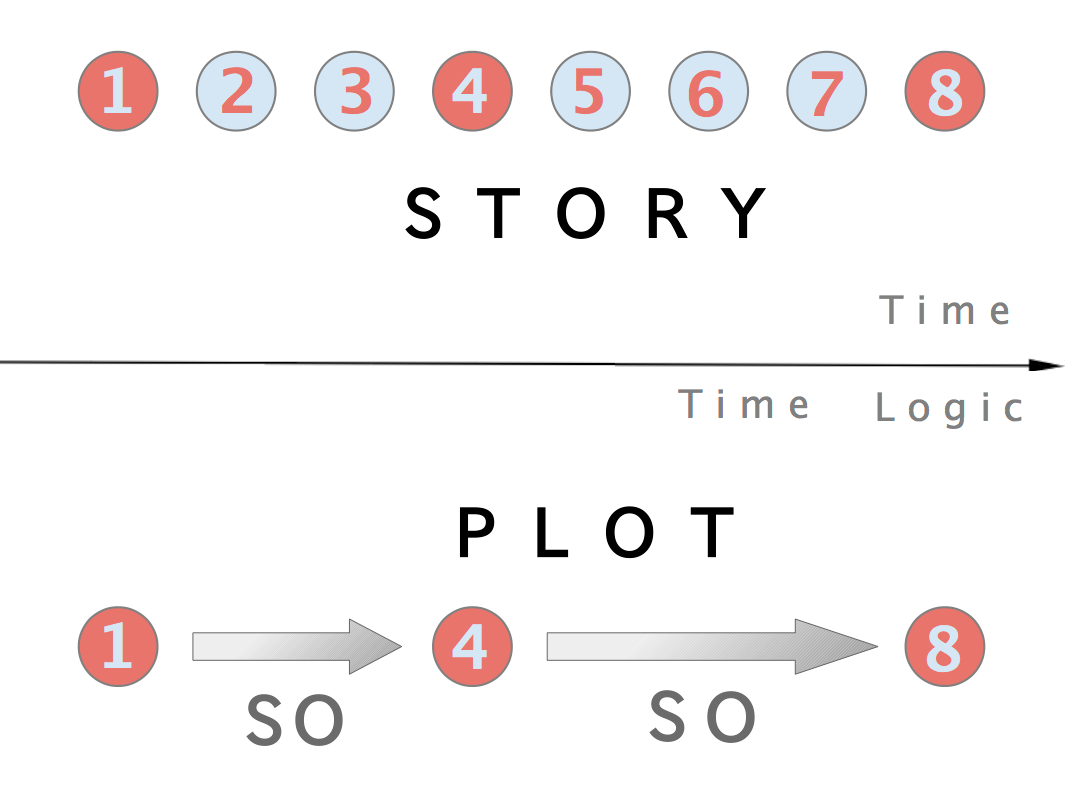
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the sequence of events in which each event affects the next one through the principle of cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a series of events linked by the connector "and so". Plots can vary from the simple—such as in a traditional ballad—to forming complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot or ''imbroglio''. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The term ''plot'' can also serve as a verb, referring to either the writer's crafting of a plot (devising and ordering story events), or else to a character's planning of future actions in the story. The term ''plot'', however, in common usage (for example, a "movie plot") can mean a narrative summary or story synopsis, rather th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Tragedy
Greek tragedy is a form of theatre from Ancient Greece and Greek inhabited Anatolia. It reached its most significant form in Athens in the 5th century BC, the works of which are sometimes called Attic tragedy. Greek tragedy is widely believed to be an extension of the ancient rites carried out in honor of Dionysus, and it heavily influenced the theatre of Ancient Rome and the Renaissance. Tragic plots were most often based upon myths from the oral traditions of archaic epics. In tragic theatre, however, these narratives were presented by actors. The most acclaimed Greek tragedians are Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides. These tragedians often explored many themes around human nature, mainly as a way of connecting with the audience but also as way of bringing the audience into the play. Etymology Aristotelian hypothesis The origin of the word ''tragedy'' has been a matter of discussion from ancient times. The primary source of knowledge on the question is the ''Poetics'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), objectively true, the identification of a narrative as a myth can be highly controversial. Many adherents of religions view their own religions' stories as truth and so object to their characterization as myth, the way they see the stories of other religions. As such, some scholars label all religious narratives "myths" for practical reasons, such as to avoid depreciating any one tradition because cultures interpret each other differently relative to one another. Other scholars avoid using the term "myth" altogether and instead use different terms like "sacred history", "holy story", or simply "history" to avoid placing pejorative overtones on any sacred narrative. Myths are often endorsed by secular and religious authorities and are close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Plays
Lost may refer to getting lost, or to: Geography *Lost, Aberdeenshire, a hamlet in Scotland *Lake Okeechobee Scenic Trail, or LOST, a hiking and cycling trail in Florida, US History *Abbreviation of lost work, any work which is known to have been created but has not survived to the present day Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Lost'' (1950 film), a Mexican film directed by Fernando A. Rivero * ''Lost'' (1956 film), a British thriller starring David Farrar * ''Lost'' (1983 film), an American film directed by Al Adamson * ''Lost!'' (film), a 1986 Canadian film directed by Peter Rowe * ''Lost'' (2004 film), an American thriller starring Dean Cain * ''The Lost'' (2006 film), an American psychological horror starring Marc Senter Games *'' Lost: Via Domus'', a 2008 video game by Ubisoft based on the ''Lost'' TV series * ''The Lost'' (video game), a 2002 vaporware game by Irrational Games Literature * ''Lost'' (Maguire novel), a 2001 horror/mystery novel by Gregory Maguire * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Tragedies
Greek tragedy is a form of theatre from Ancient Greece and Greek inhabited Anatolia. It reached its most significant form in Athens in the 5th century BC, the works of which are sometimes called Attic tragedy. Greek tragedy is widely believed to be an extension of the ancient rites carried out in honor of Dionysus, and it heavily influenced the theatre of Ancient Rome and the Renaissance. Tragic plots were most often based upon myths from the oral traditions of archaic epics. In tragic theatre, however, these narratives were presented by actors. The most acclaimed Greek tragedians are Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides. These tragedians often explored many themes around human nature, mainly as a way of connecting with the audience but also as way of bringing the audience into the play. Etymology Aristotelian hypothesis The origin of the word ''tragedy'' has been a matter of discussion from ancient times. The primary source of knowledge on the question is the ''Poetics'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |