|
Anguilliformity
Anguilliformity is a morphological pattern in fishes, named for and typified by the eels. Anguilliform fish have a long, slender body, and travel by anguilliform motion. The caudal fin is often emphasized, with the other fins reduced, absent, or fused with the caudal fin. Anguilliformity has evolved independently in many groups, including among others: * Anguilliformes, the eels * Synbranchiformes, the swamp eels * Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes * Dipnoi, the lungfishes * Cobitidae, the loaches * Gymnotidae, the knifefishes, including the electric eel ''Electrophorus electricus ''Electrophorus electricus'' is the best-known species of electric eel. It is a South American electric fish. Until the discovery of two additional species in 2019, the genus was classified as the monotypic, with this species the only one in the ...'' References Fish anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguilliform Motion
Fish locomotion is the various types of animal locomotion used by fish, principally by swimming. This is achieved in different groups of fish by a variety of mechanisms of propulsion, most often by wave-like lateral flexions of the fish's body and tail in water, and in various specialised fish by motions of the fins. The major forms of locomotion in fish are: * Anguilliform, in which a wave passes evenly along a long slender body; * Sub-carangiform, in which the wave increases quickly in amplitude towards the tail; * Carangiform, in which the wave is concentrated near the tail, which oscillates rapidly; * Thunniform, rapid swimming with a large powerful crescent-shaped tail; and * Ostraciiform, with almost no oscillation except of the tail fin. More specialized fish include movement by pectoral fins with a mainly stiff body, opposed sculling with dorsal and anal fins, as in the sunfish; and movement by propagating a wave along the long fins with a motionless body, as in the knif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguilliformes
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators. The term "eel" is also used for some other eel-shaped fish, such as electric eels (genus ''Electrophorus''), spiny eels (family Mastacembelidae), swamp eels (family Synbranchidae), and deep-sea spiny eels (family Notacanthidae). However, these other clades evolved their eel-like shapes independently from the true eels. Eels live both in salt and fresh water, and some species are catadromous. Description Eels are elongated fish, ranging in length from in the one-jawed eel (''Monognathus ahlstromi'') to in the slender giant moray. Adults range in weight from to well over . They possess no pelvic fins, and many species also lack pectoral fins. The dorsal and anal fins are fused with the caudal fin, forming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synbranchiformes
Synbranchiformes, often called swamp eels, is an order of ray-finned fishes that are eel-like but have spiny rays, indicating that they belong to the superorder Acanthopterygii. Taxonomy No synbrachiform fossil is known. The Mastacembeloidei were removed from the Perciformes and added to the Synbranchiformes after a phylogenetic analysis by Johnson and Patterson. These authors consider the Synbranchiformes to be part of a monophyletic group called Smegmamorpha, also containing Mugilimorpha, Atherinomorpha, Gasterosteiformes, and Elassomatidae. Later authors have proposed that the Synbranchiformes along with the Anabantiformes, Carangiformes, Istiophoriformes and Pleuronectiformes form a sister clade to the Ovalentaria which has been called the “Carangimorpharia” but in the 5th Edition of Fishes of the World this clade remained unnamed and unranked. There are a total of about 99 species divided over 15 genera in three families. There are two suborders: Synbranchoidei and Mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipnoi
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobitidae
Cobitidae, also known as the True loaches, is a family of Old World freshwater fish. They occur throughout Eurasia and in Morocco, and inhabit riverine ecosystems. Today, most "loaches" are placed in other families (see below). The family includes about 260 described species. New species are being described regularly.Perdices, A., Bohlen, J., Šlechtová, V. & Doadrio, I. (2016): Molecular Evidence for Multiple Origins of the European Spined Loaches (Teleostei, Cobitidae). ''PLoS ONE, 11 (1): e0144628.'' Description and ecology The body forms of the Cobitidae tend to be vermiform – worm-shaped, long and thin. Most true loaches do not have true scales, and like many other Cypriniformes or catfishes, they have barbels at their mouths (usually three to six pairs). Some other traits typically found in this family are a small bottom-facing mouth suited to their scavenging benthic lifestyle, an erectile spine below the eye, and a single row of pharyngeal (throat) teeth. True ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
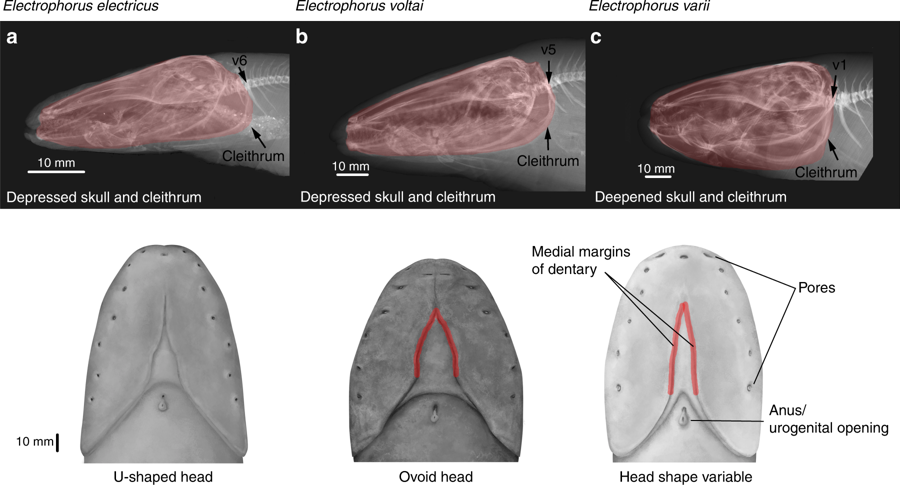
Electrophorus Electricus
''Electrophorus electricus'' is the best-known species of electric eel. It is a South American electric fish. Until the discovery of two additional species in 2019, the genus was classified as the monotypic, with this species the only one in the genus. Despite the name, it is not an eel, but rather a knifefish. It is considered as a freshwater teleost which contains an electrogenic tissue that produces electric discharges. Taxonomic history The species has been reclassified several times. When originally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1766, he used the name ''Gymnotus electricus'', placing it in the same genus as ''Gymnotus carapo'' (banded knifefish) which he had described several years earlier. It was only about a century later, in 1864, that the electric eel was moved to its own genus ''Electrophorus'' by Theodore Gill. In September 2019, David de Santana et al. suggested the division of the genus into three species based on DNA divergence, ecology and habitat, anatomy and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |