Anguilliform Motion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Fish locomotion is the various types of
Fish locomotion is the various types of
 Consider the
Consider the  The backbone is flexible, allowing muscles to contract and relax rhythmically and bring about undulating movement. A
The backbone is flexible, allowing muscles to contract and relax rhythmically and bring about undulating movement. A
 In the anguilliform group, containing some long, slender fish such as
In the anguilliform group, containing some long, slender fish such as
 The thunniform group contains high-speed long-distance swimmers, and is characteristic of
The thunniform group contains high-speed long-distance swimmers, and is characteristic of
 Not all fish fit comfortably in the above groups.
Not all fish fit comfortably in the above groups.
 Diodontiform locomotion propels the fish propagating undulations along large pectoral fins, as seen in the porcupinefish ( Diodontidae).
Diodontiform locomotion propels the fish propagating undulations along large pectoral fins, as seen in the porcupinefish ( Diodontidae).
 Gymnotiform locomotion consists of undulations of a long anal fin, essentially upside down amiiform, seen in the South American knifefish ''
Gymnotiform locomotion consists of undulations of a long anal fin, essentially upside down amiiform, seen in the South American knifefish ''


 There are some species of fish that can "walk" along the sea floor but not on land; one such animal is the flying gurnard (it does not actually fly, and should not be confused with
There are some species of fish that can "walk" along the sea floor but not on land; one such animal is the flying gurnard (it does not actually fly, and should not be confused with
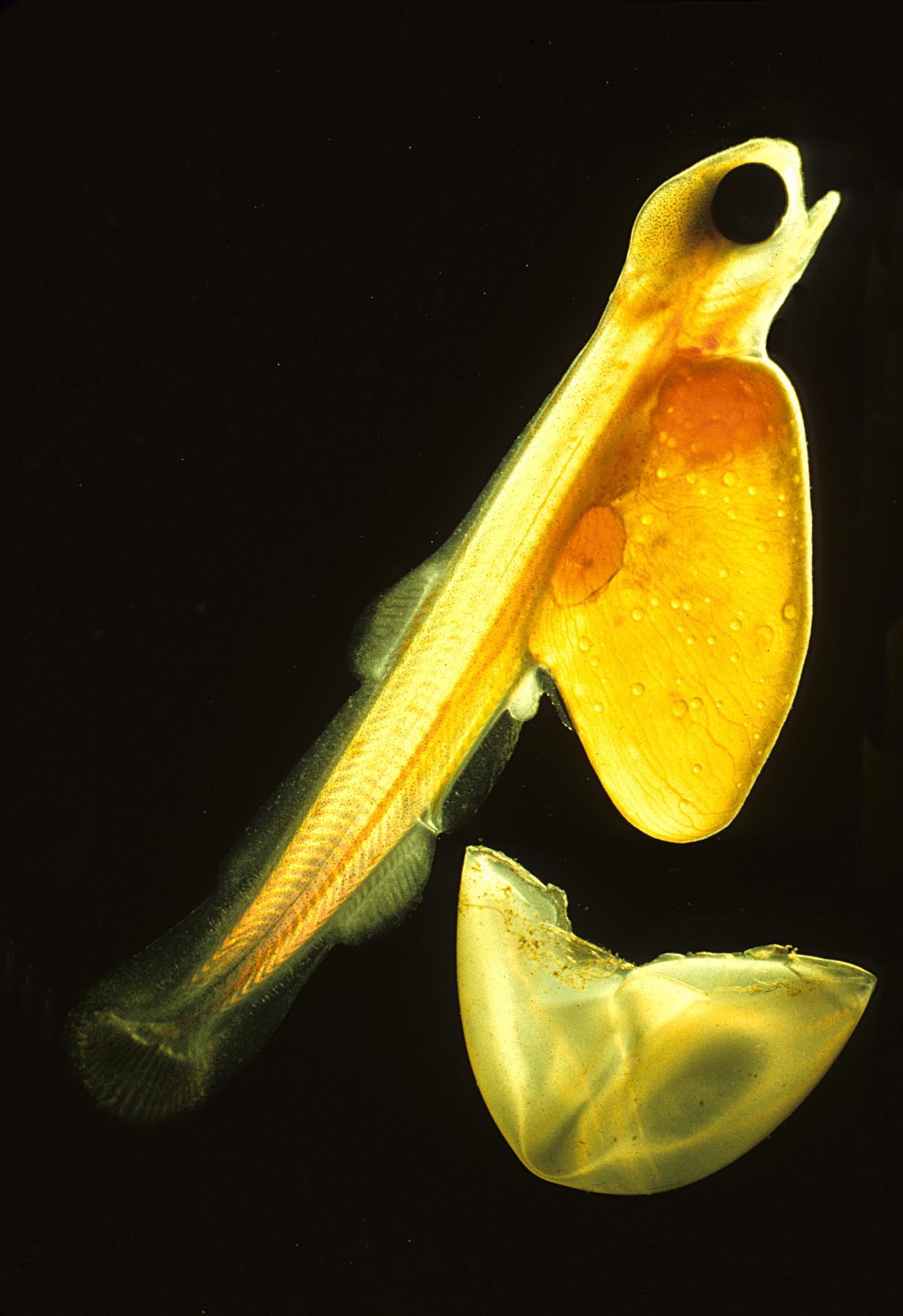 Fish larvae, like many adult fishes, swim by undulating their body. The swimming speed varies proportionally with the size of the animals, in that smaller animals tend to swim at lower speeds than larger animals. The swimming mechanism is controlled by the flow regime of the larvae.
Fish larvae, like many adult fishes, swim by undulating their body. The swimming speed varies proportionally with the size of the animals, in that smaller animals tend to swim at lower speeds than larger animals. The swimming mechanism is controlled by the flow regime of the larvae.
File:Clupeaharenguskils2.jpg,
''Fish Swimming''
Springer. . * Vogel, Steven (1994) ''Life in Moving Fluid: The Physical Biology of Flow.'' Princeton University Press. (particularly pp. 115–117 and pp. 207–216 for specific biological examples swimming and flying respectively) * Wu, Theodore, Y.-T., Brokaw, Charles J., Brennen, Christopher, Eds. (1975) ''Swimming and Flying in Nature''. Volume 2, Plenum Press. (particularly pp. 615–652 for an in depth look at fish swimming)
How fish swim: study solves muscle mystery
Simulated fish locomotion
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110724192433/http://www.geol.umd.edu/~jmerck/bsci392/lecture10/lecture10.html The biomechanics of swimming {{fins, limbs and wings Ichthyology Aquatic locomotion Animal locomotion Articles containing video clips
 Fish locomotion is the various types of
Fish locomotion is the various types of animal locomotion
In ethology, animal locomotion is any of a variety of methods that animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flight, flying, hopping, soaring and gli ...
used by fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, principally by swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, such as saltwater or freshwater environments, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Swimmers achieve locomotion by coordinating limb and body movements to achieve hydrody ...
. This is achieved in different groups of fish by a variety of mechanisms of propulsion, most often by wave-like lateral flexions of the fish's body and tail in the water, and in various specialised fish by motions of the fin
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. F ...
s. The major forms of locomotion in fish are:
* Anguilliform, in which a wave passes evenly along a long slender body;
* Sub-carangiform, in which the wave increases quickly in amplitude towards the tail;
* Carangiform, in which the wave is concentrated near the tail, which oscillates rapidly;
* Thunniform, rapid swimming with a large powerful crescent-shaped tail; and
* Ostraciiform, with almost no oscillation except of the tail fin.
More specialized fish include movement by pectoral fins with a mainly stiff body, opposed sculling with dorsal and anal fins, as in the sunfish; and movement by propagating a wave along the long fins with a motionless body, as in the knifefish or featherbacks.
In addition, some fish can variously "walk" (i.e., crawl over land using the pectoral and pelvic fins), burrow
file:Chipmunk-burrow (exits).jpg, An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of Animal lo ...
in mud, leap out of the water and even glide temporarily through the air.
Swimming
Mechanism
Fish swim by exerting force against the surrounding water. There are exceptions, but this is normally achieved by the fish contractingmuscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s on either side of its body in order to generate waves of flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used de ...
that travel the length of the body from nose to tail, generally getting larger as they go along. The vector
Vector most often refers to:
* Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
* Disease vector, an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematics a ...
force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
s exerted on the water by such motion cancel out laterally, but generate a net force backwards which in turn pushes the fish forward through the water. Most fishes generate thrust using lateral movements of their body and caudal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
, but many other species move mainly using their median and paired fins. The latter group swim slowly, but can turn rapidly, as is needed when living in coral reefs for example. But they can not swim as fast as fish using their bodies and caudal fins.
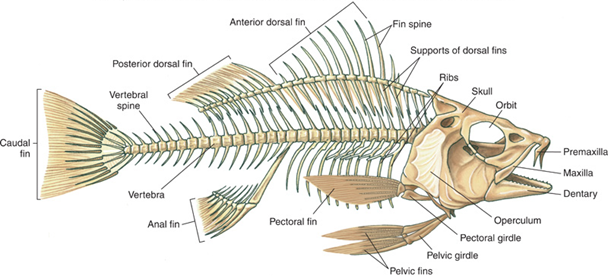
 Consider the
Consider the tilapia
Tilapia ( ) is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the coelotilapine, coptodonine, heterotilapine, oreochromine, pelmatolapiine, and tilapiine tribes (formerly all were "Tilapiini"), with the economically mos ...
shown in the diagram. Like most fish, the tilapia has a streamlined body shape reducing water resistance to movement and enabling the tilapia to cut easily through water. Its head is inflexible, which helps it maintain forward thrust. Its scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
overlap and point backwards, allowing water to pass over the fish without unnecessary obstruction. Water friction is further reduced by mucus which tilapia secrete over their body.
 The backbone is flexible, allowing muscles to contract and relax rhythmically and bring about undulating movement. A
The backbone is flexible, allowing muscles to contract and relax rhythmically and bring about undulating movement. A swim bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ (anatomy), organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift ...
provides buoyancy which helps the fish adjust its vertical position in the water column
The (oceanic) water column is a concept used in oceanography to describe the physical (temperature, salinity, light penetration) and chemical ( pH, dissolved oxygen, nutrient salts) characteristics of seawater at different depths for a defined ...
. A lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelia ...
system allows it to detect vibrations and pressure changes in water, helping the fish to respond appropriately to external events.
Well developed fins are used for maintaining balance, braking and changing direction. The pectoral fins act as pivots around which the fish can turn rapidly and steer itself. The paired pectoral and pelvic fins control pitching, while the unpaired dorsal and anal fins reduce yawing and rolling
Rolling is a Motion (physics)#Types of motion, type of motion that combines rotation (commonly, of an Axial symmetry, axially symmetric object) and Translation (geometry), translation of that object with respect to a surface (either one or the ot ...
. The caudal fin provides raw power for propelling the fish forward.
Body/caudal fin propulsion
There are five groups that differ in the fraction of their body that is displaced laterally:Anguilliform
 In the anguilliform group, containing some long, slender fish such as
In the anguilliform group, containing some long, slender fish such as eel
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 20 families, 164 genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage ...
s, there is little increase in the amplitude of the flexion wave as it passes along the body.
Subcarangiform
The subcarangiform group has a more marked increase in wave amplitude along the body with the vast majority of the work being done by the rear half of the fish. In general, the fish body is stiffer, making for higher speed but reduced maneuverability.Trout
Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the ...
use sub-carangiform locomotion.
Carangiform
The carangiform group, named for theCarangidae
The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the ...
, are stiffer and faster-moving than the previous groups. The vast majority of movement is concentrated in the very rear of the body and tail. Carangiform swimmers generally have rapidly oscillating tails.
Thunniform
 The thunniform group contains high-speed long-distance swimmers, and is characteristic of
The thunniform group contains high-speed long-distance swimmers, and is characteristic of tuna
A tuna (: tunas or tuna) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae ( mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bul ...
s and is also found in several lamnid sharks. Here, virtually all the sideways movement is in the tail and the region connecting the main body to the tail (the peduncle). The tail itself tends to be large and crescent shaped.
Ostraciiform
The ostraciiform group have no appreciable body wave when they employ caudal locomotion. Only the tail fin itself oscillates (often very rapidly) to createthrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that ...
. This group includes Ostraciidae
Ostraciidae or Ostraciontidae is a family of squared, Actinopterygii, bony fish belonging to the order Tetraodontiformes, closely related to the pufferfishes and filefishes. Fish in the family are known variously as boxfishes, cofferfishes, cowfi ...
.
Median/paired fin propulsion
 Not all fish fit comfortably in the above groups.
Not all fish fit comfortably in the above groups. Ocean sunfish
The ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), also known as the common mola, is one of the largest bony fish in the world. It is the type species of the genus ''Mola'', and one of five extant species in the family Molidae. It was once misidentified as th ...
, for example, have a completely different system, the tetraodontiform mode, and many small fish use their pectoral fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column ...
s for swimming as well as for steering and dynamic lift. Fish in the order Gymnotiformes
The Gymnotiformes are an order of teleost bony fishes commonly known as Neotropical knifefish or South American knifefish. They have long bodies and swim using undulations of their elongated anal fin. Found almost exclusively in fresh water (the ...
possess electric organs along the length of their bodies and swim by undulating an elongated anal fin while keeping the body still, presumably so as not to disturb the electric field that they generate.
Many fish swim using combined behavior of their two pectoral fins
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only b ...
or both their anal
Anal may refer to:
Related to the anus
*Related to the anus of animals:
** Anal fin, in fish anatomy
** Anal vein, in insect anatomy
** Anal scale, in reptile anatomy
*Related to the human anus:
** Anal sex, a type of sexual activity involving ...
and dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
fins. Different types of Median paired fin propulsion can be achieved by preferentially using one fin pair over the other, and include rajiform, diodontiform, amiiform, gymnotiform and balistiform modes.
Rajiform
Rajiform locomotion is characteristic ofrays
Ray or RAY may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), the bony or horny spine on ray-finned fish
Science and mathematics
* Half-line (geometry) or ray, half of a line split at an ...
and skate
Skate or Skates may refer to: Fish
*Skate (fish), several genera of fish belonging to the family Rajidae
* Pygmy skates, several genera of fish belonging to the family Gurgesiellidae
* Smooth skates or leg skates, several genera of fish belongin ...
s, when thrust is produced by vertical undulations along large, well developed pectoral fins.
Diodontiform
 Diodontiform locomotion propels the fish propagating undulations along large pectoral fins, as seen in the porcupinefish ( Diodontidae).
Diodontiform locomotion propels the fish propagating undulations along large pectoral fins, as seen in the porcupinefish ( Diodontidae).
Amiiform
Amiiform locomotion consists of undulations of a long dorsal fin while the body axis is held straight and stable, as seen in thebowfin
The ruddy bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a ray-finned fish native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species ...
.
Gymnotiform
 Gymnotiform locomotion consists of undulations of a long anal fin, essentially upside down amiiform, seen in the South American knifefish ''
Gymnotiform locomotion consists of undulations of a long anal fin, essentially upside down amiiform, seen in the South American knifefish ''Gymnotiformes
The Gymnotiformes are an order of teleost bony fishes commonly known as Neotropical knifefish or South American knifefish. They have long bodies and swim using undulations of their elongated anal fin. Found almost exclusively in fresh water (the ...
''.
Balistiform
In balistiform locomotion, both anal and dorsal fins undulate. It is characteristic of the family Balistidae (triggerfishes). It may also be seen in theZeidae
The Zeidae (named after the fish ''zaeus'' from Pliny the Elder) are a family of large, showy, deep-bodied zeiform marine fish—the "true dories". Found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, the family contains just six species in ...
.
Oscillatory
Oscillation is viewed as pectoral-fin-based swimming and is best known as mobuliform locomotion. The motion can be described as the production of less than half a wave on the fin, similar to a bird wing flapping. Pelagic stingrays, such as the manta, cownose, eagle and bat rays use oscillatory locomotion.=Tetraodontiform
= In tetraodontiform locomotion, the dorsal and anal fins are flapped as a unit, either in phase or exactly opposing one another, as seen in theTetraodontiformes
Tetraodontiformes (), also known as the Plectognathi, is an order of ray-finned fishes which includes the pufferfishes and related taxa. This order has been classified as a suborder of the order Perciformes, although recent studies have found ...
(boxfish
Ostraciidae or Ostraciontidae is a family of squared, Actinopterygii, bony fish belonging to the order Tetraodontiformes, closely related to the pufferfishes and filefishes. Fish in the family are known variously as boxfishes, cofferfishes, cowfi ...
es and pufferfish
Tetraodontidae is a family of marine and freshwater fish in the order Tetraodontiformes. The family includes many familiar species variously called pufferfish, puffers, balloonfish, blowfish, blowers, blowies, bubblefish, globefish, swellfis ...
es). The ocean sunfish
The ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), also known as the common mola, is one of the largest bony fish in the world. It is the type species of the genus ''Mola'', and one of five extant species in the family Molidae. It was once misidentified as th ...
displays an extreme example of this mode.
=Labriform
= In labriform locomotion, seen in the wrasses (Labriformes
Labriformes is an Order (biology), order of ray-finned fishes within the clade Percomorpha. Some authors include the Labriformes as the clade Labroidei within the Perciformes while others include more Family (biology), families within the Labrif ...
), oscillatory movements of pectoral fins are either drag based or lift based. Propulsion is generated either as a reaction to drag produced by dragging the fins through the water in a rowing motion, or via lift mechanisms.
Dynamic lift
Bone and muscle tissues of fish are denser than water. To maintain depth, bony fish increasebuoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
by means of a gas bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift via swimming, ...
. Alternatively, some fish store oils or lipids
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins Vitamin A, A, Vitamin D, D, Vitamin E, E and Vitamin K, K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The fu ...
for this same purpose. Fish without these features use dynamic lift instead. It is done using their pectoral fins in a manner similar to the use of wings by airplane
An airplane (American English), or aeroplane (Commonwealth English), informally plane, is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a vari ...
s and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s. As these fish swim, their pectoral fins are positioned to create lift
Lift or LIFT may refer to:
Physical devices
* Elevator, or lift, a device used for raising and lowering people or goods
** Paternoster lift, a type of lift using a continuous chain of cars which do not stop
** Patient lift, or Hoyer lift, mobile ...
which allows the fish to maintain a certain depth. The two major drawbacks of this method are that these fish must stay moving to stay afloat and that they are incapable of swimming backwards or hovering.
Hydrodynamics
Similarly to the aerodynamics of flight, powered swimming requires animals to overcome drag by producing thrust. Unlike flying, however, swimming animals often do not need to supply much vertical force because the effect ofbuoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
can counter the downward pull of gravity, allowing these animals to float without much effort. While there is great diversity in fish locomotion, swimming behavior can be classified into two distinct "modes" based on the body structures involved in thrust production, Median-Paired Fin (MPF) and Body-Caudal Fin (BCF). Within each of these classifications, there are numerous specifications along a spectrum of behaviours from purely undulatory to entirely oscillatory
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
. In undulatory swimming modes, thrust is produced by wave-like movements of the propulsive structure (usually a fin or the whole body). Oscillatory modes, on the other hand, are characterized by thrust produced by swiveling of the propulsive structure on an attachment point without any wave-like motion.
Body-caudal fin
Most fish swim by generating undulatory waves that propagate down the body through thecaudal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
. This form of undulatory locomotion
Undulatory locomotion is the type of motion characterized by wave-like movement patterns that act to propel an animal forward. Examples of this type of gait include crawling in snakes, or swimming in the lamprey. Although this is typically the ...
is termed body-caudal fin (BCF) swimming on the basis of the body structures used; it includes anguilliform, sub-carangiform, carangiform, and thunniform locomotory modes, as well as the oscillatory ostraciiform mode.
Adaptation
Similar to adaptation in avian flight, swimming behaviors in fish can be thought of as a balance of stability and maneuverability. Because body-caudal fin swimming relies on morecaudal
Caudal may refer to:
Anatomy
* Caudal (anatomical term) (from Latin ''cauda''; tail), used to describe how close something is to the trailing end of an organism
* Caudal artery, the portion of the dorsal aorta of a vertebrate that passes into th ...
body structures that can direct powerful thrust only rearwards, this form of locomotion is particularly effective for accelerating quickly and cruising continuously. body-caudal fin swimming is, therefore, inherently stable and is often seen in fish with large migration patterns that must maximize efficiency over long periods. Propulsive forces in median-paired fin swimming, on the other hand, are generated by multiple fins located on either side of the body that can be coordinated to execute elaborate turns. As a result, median-paired fin swimming is well adapted for high maneuverability and is often seen in smaller fish that require elaborate escape patterns.
The habitats occupied by fishes are often related to their swimming capabilities. On coral reefs, the faster-swimming fish species typically live in wave-swept habitats subject to fast water flow speeds, while the slower fishes live in sheltered habitats with low levels of water movement.
Fish do not rely exclusively on one locomotor mode, but are rather locomotor generalists, choosing among and combining behaviors from many available behavioral techniques. Predominantly body-caudal fin swimmers often incorporate movement of their pectoral, anal, and dorsal fins as an additional stabilizing mechanism at slower speeds, but hold them close to their body at high speeds to improve streamlining and reducing drag. Zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Danionidae of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (an ...
have even been observed to alter their locomotor behavior in response to changing hydrodynamic influences throughout growth and maturation.
Flight
The transition of predominantly swimming locomotion directly to flight has evolved in a single family of marine fish, theExocoetidae
The Exocoetidae are a family of marine ray-finned fish in the order Beloniformes, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven genera. While they do not "fly" in the same way a bird does, flying fish c ...
. Flying fish are not true fliers in the sense that they do not execute powered flight. Instead, these species glide directly over the surface of the ocean water without ever flapping their "wings." Flying fish have evolved abnormally large pectoral fins that act as airfoils and provide lift when the fish launches itself out of the water. Additional forward thrust and steering forces are created by dipping the hypocaudal (i.e. bottom) lobe of their caudal fin into the water and vibrating it very quickly, in contrast to diving birds in which these forces are produced by the same locomotor module used for propulsion. Of the 64 extant species of flying fish, only two distinct body plans exist, each of which optimizes two different behaviors.Fish, F.E. (1990) Wing design and scaling of flying fish with regard to flight performance. "J. Zool. Lond." 221, 391-403.Fish, Frank. (1991) On a Fin and a Prayer. "Scholars." 3(1), 4-7.

Tradeoffs
While most fish havecaudal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
s with evenly sized lobes (i.e. homocaudal), flying fish have an enlarged ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
lobe (i.e. hypocaudal) which facilitates dipping only a portion of the tail back onto the water for additional thrust production and steering.
Because flying fish are primarily aquatic animals, their body density must be close to that of water for buoyancy stability. This primary requirement for swimming, however, means that flying fish are heavier (have a larger mass) than other habitual fliers, resulting in higher wing loading and lift to drag ratios for flying fish compared to a comparably sized bird. Differences in wing area, wing span, wing loading, and aspect ratio have been used to classify flying fish into two distinct classifications based on these different aerodynamic designs.
Biplane body plan
In thebiplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While ...
or ''Cypselurus
''Cypselurus'' is a genus of flying fish in the family Exocoetidae. They are found across Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific ...
'' body plan, both the pectoral and pelvic fins are enlarged to provide lift during flight. These fish also tend to have "flatter" bodies which increase the total lift-producing area, thus allowing them to "hang" in the air better than more streamlined shapes. As a result of this high lift production, these fish are excellent gliders and are well adapted for maximizing flight distance and duration.
Comparatively, ''Cypselurus
''Cypselurus'' is a genus of flying fish in the family Exocoetidae. They are found across Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific ...
'' flying fish have lower wing loading and smaller aspect ratios (i.e. broader wings) than their ''Exocoetus
''Exocoetus'' is a genus of flying fishes.
It is a bony fish.
The body is covered with cycloid scales.
The mouth is wide, and the jaws bear teeth.
It is a marine fish.
The tail has hypobatic fins as the ventral lobe.
Species
Five species in th ...
'' monoplane counterparts, which contributes to their ability to fly for longer distances than fish with this alternative body plan. Flying fish with the biplane design take advantage of their high lift production abilities when launching from the water by utilizing a "taxiing glide" in which the hypocaudal lobe remains in the water to generate thrust even after the trunk clears the water's surface and the wings are opened with a small angle of attack for lift generation.

Monoplane body plan
In the ''Exocoetus
''Exocoetus'' is a genus of flying fishes.
It is a bony fish.
The body is covered with cycloid scales.
The mouth is wide, and the jaws bear teeth.
It is a marine fish.
The tail has hypobatic fins as the ventral lobe.
Species
Five species in th ...
'' or monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple wings.
A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing con ...
body plan, only the pectoral fins are enlarged to provide lift. Fish with this body plan tend to have a more streamlined body, higher aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a geometry, geometric shape is the ratio of its sizes in different dimensions. For example, the aspect ratio of a rectangle is the ratio of its longer side to its shorter side—the ratio of width to height, when the rectangl ...
s (long, narrow wings), and higher wing loading than fish with the biplane body plan, making these fish well adapted for higher flying speeds. Flying fish with a monoplane body plan demonstrate different launching behaviors from their biplane counterparts. Instead of extending their duration of thrust production, monoplane fish launch from the water at high speeds at a large angle of attack (sometimes up to 45 degrees). In this way, monoplane fish are taking advantage of their adaptation for high flight speed, while fish with biplane designs exploit their lift production abilities during takeoff.
Walking
A "walking fish" is a fish that is able to travel overland
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of Earth not submerged by the ocean or another body of water. It makes up 29.2% of Earth's surface and includes all continents and islands. Earth's land sur ...
for extended periods of time. Some other cases of nonstandard fish locomotion include fish "walking" along the sea floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as seabeds.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
, such as the handfish or frogfish
Frogfishes are any member of the anglerfish family Antennariidae, of the order Lophiiformes. Antennariids are known as anglerfish in Australia, where the term "frogfish" refers to members of the unrelated family Batrachoididae. Frogfishes are f ...
.
Most commonly, walking fish are amphibious fish
Amphibious fish are fish that are able to leave water for extended periods of time. About 11 distantly related genera of fish are considered amphibious. This suggests that many fish genera independently evolved amphibious traits, a process know ...
. Able to spend longer times out of water, these fish may use a number of means of locomotion, including springing, snake-like lateral undulation, and tripod-like walking. The mudskipper
Mudskippers are any of the 23 extant species of amphibious fish from the subfamily Oxudercinae of the goby family (biology), family Oxudercidae. They are known for their unusual body shapes, preferences for semiaquatic habitats, limited terrestria ...
s are probably the best land-adapted of contemporary fish and are able to spend days moving about out of water and can even climb mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s, although to only modest heights. The Climbing gourami
The Anabantidae are a family of ray-finned fish within the order Anabantiformes commonly called the climbing gouramies or climbing perches. The family includes about 34 species. As labyrinth fishes, they possess a labyrinth organ, a structure i ...
is often specifically referred to as a "walking fish", although it does not actually "walk", but rather moves in a jerky way by supporting itself on the extended edges of its gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
plates and pushing itself by its fins and tail. Some reports indicate that it can also climb trees.
There are a number of fish that are less adept at actual walking, such as the walking catfish
The walking catfish (''Clarias batrachus'') is a species of freshwater airbreathing catfish native to Southeast Asia. It is named for its ability to "walk" and wiggle across dry land, to find food or suitable environments. While it does not tr ...
. Despite being known for "walking on land", this fish usually wriggles and may use its pectoral fins to aid in its movement. Walking Catfish have a respiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
that allows them to live out of water for several days. Some are invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
. A notorious case in the United States is the Northern snakehead
The northern snakehead (''Channa argus'') is a species of snakehead fish native to temperate East Asia, in China, Russia, North Korea, and South Korea. Their natural range goes from the Amur River watershed in Siberia and Manchuria down to Hainan ...
. Polypterids have rudimentary lungs and can also move about on land, though rather clumsily. The Mangrove rivulus
The mangrove rivulus or mangrove killifish, ''Kryptolebias marmoratus'' (syn. ''Rivulus marmoratus''), is a species of killifish in the Family (biology), family Rivulidae. It lives in brackish and marine waters (less frequently in fresh water) a ...
can survive for months out of water and can move to places like hollow logs.
 There are some species of fish that can "walk" along the sea floor but not on land; one such animal is the flying gurnard (it does not actually fly, and should not be confused with
There are some species of fish that can "walk" along the sea floor but not on land; one such animal is the flying gurnard (it does not actually fly, and should not be confused with flying fish
The Exocoetidae are a family (biology), family of Saltwater fish, marine Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish in the order (biology), order Beloniformes, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven genus, ge ...
). The batfishes of the family Ogcocephalidae
Ogcocephalidae is a family of anglerfish specifically adapted for a benthic lifestyle of crawling about on the seafloor. Ogcocephalid anglerfish are sometimes referred to as batfishes,Ephippidae
Ephippidae is a family of percomorph fishes, the spadefishes, in the order Moroniformes. These fishes are found in the tropical and temperate oceans of the world, except for the central Pacific.
Taxonomy
Ephippidae was first proposed as a fami ...
) are also capable of walking along the sea floor. ''Bathypterois grallator
The tripod fish or tripod spiderfish, ''Bathypterois grallator'', is a deep-sea benthic fish in the family Ipnopidae found at lower latitudes. It is now an iconic deep-sea fish, being observed and photographed by submersibles, using elongate ...
'', also known as a "tripodfish", stands on its three fins on the bottom of the ocean and hunts for food. The African lungfish (''P. annectens'') can use its fins to ''"walk"'' along the bottom of its tank in a manner similar to the way amphibians and land vertebrates use their limbs on land.
Burrowing
Many fishes, particularly eel-shaped fishes such as true eels,moray eels
Moray eels, or Muraenidae (), are a family of eels whose members are found worldwide. There are approximately 200 species in 15 genera which are almost exclusively marine, but several species are regularly seen in brackish water, an ...
, and spiny eel
The name spiny eel is used to describe members of two different families of fish: the freshwater Mastacembelidae of Asia and Africa, and the marine (and generally deep sea) Notacanthidae. Both are so-named because of their eel-like shape and sturdy ...
s, are capable of burrow
file:Chipmunk-burrow (exits).jpg, An eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow
A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of Animal lo ...
ing through sand or mud. Ophichthids, the snake eels, are capable of burrowing either forwards or backwards.
In larvae
Swimming
 Fish larvae, like many adult fishes, swim by undulating their body. The swimming speed varies proportionally with the size of the animals, in that smaller animals tend to swim at lower speeds than larger animals. The swimming mechanism is controlled by the flow regime of the larvae.
Fish larvae, like many adult fishes, swim by undulating their body. The swimming speed varies proportionally with the size of the animals, in that smaller animals tend to swim at lower speeds than larger animals. The swimming mechanism is controlled by the flow regime of the larvae. Reynolds number
In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between Inertia, inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to ...
(Re) is defined as the ratio of inertial force
A fictitious force, also known as an inertial force or pseudo-force, is a force that appears to act on an object when its motion is described or experienced from a non-inertial frame of reference. Unlike real forces, which result from physical ...
to viscous force
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup h ...
. Smaller organisms are affected more by viscous forces, like friction, and swim at a smaller Reynolds number. Larger organisms use a larger proportion of inertial forces, like pressure, to swim, at a higher Reynolds number.‘Flow Patterns Of Larval Fish: Undulatory Swimming in the Intermediate Flow Regime’ by Ulrike K. Müller, Jos G. M. van den Boogaart and Johan L. van Leeuwen. Journal of Experimental Biology 2008 211: 196–205; doi: 10.1242/jeb.005629
The larvae of ray finned fishes, the Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built ...
, swim at a quite large range of Reynolds number (Re ≈10 to 900). This puts them in an intermediate flow regime where both inertial and viscous forces play an important role. As the size of the larvae increases, the use of pressure forces to swim at higher Reynolds number increases.
Undulatory swimmers generally shed at least two types of wake: Carangiform swimmers shed connected vortex loops and Anguilliform swimmers shed individual vortex rings. These vortex rings depend upon the shape and arrangement of the trailing edge from which the vortices are shed. These patterns depend upon the swimming speed, ratio of swimming speed to body wave speed and the shape of body wave.
A spontaneous bout of swimming has three phases. The first phase is the start or acceleration phase: In this phase the larva tends to rotate its body to make a 'C' shape which is termed the preparatory stroke. It then pushes in the opposite direction to straighten its body, which is called a propulsive stroke, or a power stroke, which powers the larva to move forward. The second phase is cyclic swimming. In this phase, the larva swims with an approximately constant speed. The last phase is deceleration. In this phase, the swimming speed of the larva gradually slows down to a complete stop. In the preparatory stroke, due to the bending of the body, the larva creates 4 vortices around its body, and 2 of those are shed in the propulsive stroke. Similar phenomena can be seen in the deceleration phase. However, in the vortices of the deceleration phase, a large area of elevated vorticity can be seen compared to the starting phase.
The swimming abilities of larval fishes are important for survival. This is particularly true for the larval fishes with higher metabolic rate and smaller size which makes them more susceptible to predators. The swimming ability of a reef fish larva helps it to settle at a suitable reef and for locating its home as it is often isolated from its home reef in search of food. Hence the swimming speed of reef fish larvae are quite high (≈12 cm/s - 100 cm/s) compared to other larvae."Critical Swimming Speeds of Late-Stage Coral Reef Fish Larvae: Variation within Species, Among Species and Between Locations" by Fisher, R., Leis, J.M., Clark, D.L.in Marine Biology (2005) 147: 1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0001-x, The swimming speeds of larvae from the same families at the two locations are relatively similar. However, the variation among individuals is quite large. At the species level, length is significantly related to swimming ability. However, at the family level, only 16% of variation in swimming ability can be explained by length. There is also a negative correlation between the fineness ratio
In naval architecture and aerospace engineering, the fineness ratio is the ratio of the length of a body to its maximum width. Shapes that are short and wide have a low fineness ratio, those that are long and narrow have high fineness ratios. Air ...
(length of body to maximum width) and the swimming ability of reef fish larvae. This suggests a minimization of overall drag and maximization of volume. Reef fish larvae differ significantly in their critical swimming speed abilities among taxa which leads to high variability in sustainable swimming speed. This again leads to sustainable variability in their ability to alter dispersal patterns, overall dispersal distances and control their temporal and spatial patterns of settlement.
Hydrodynamics
Small undulatory swimmers such as fish larvae experience both inertial and viscous forces, the relative importance of which is indicated by Reynolds number (Re). Reynolds number is proportional to body size and swimming speed. The swimming performance of a larva increases between 2–5 days post fertilization. Compared with adults, larval fish experience relatively high viscous force. To enhance thrust to an equal level with the adults, it increases its tail beat frequency and thus amplitude. In zebrafish, tail beat frequency increases over larval age to 95 Hz in 3 days post fertilization from 80 Hz in 2 days post fertilization. This higher frequency leads to higher swimming speed, thus reducing predation and increasing prey catching ability when they start feeding at around 5 days post fertilization. The vortex shedding mechanics changes with the flow regime in an inverse non-linear way. Strouhal number is a design parameter for the vortex shedding mechanism. It can be defined as a ratio of the product of tail beat frequency with amplitude with the mean swimming speed. Reynolds number (Re) is the main deciding criteria of a flow regime. It has been observed over different type of larval experiments that, slow larvae swims at higher Strouhal number but lower Reynolds number. However, the faster larvae swims distinctively at opposite conditions, that is, at lower Strouhal number but higher Reynolds number. Strouhal number is constant over similar speed ranged adult fishes. Strouhal number does not only depend on the small size of the swimmers, but also dependent to the flow regime. As in fishes which swim in viscous or high-friction flow regime, would create high body drag which will lead to higher Strouhal number. Whereas, in high viscous regime, the adults swim at lower stride length which leads to lower tail beat frequency and lower amplitude. This leads to higher thrust for same displacement or higher propulsive force, which unanimously reduces the Reynolds number.'How body torque and Strouhal number change with swimming speed and developmental stage in larval zebrafish' by Johan L. van Leeuwen, Cees J. Voesenek and Ulrike K. Müller in J. R. Soc. Interface 2015 12 20150479; DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2015.0479. 6 September 2015 Larval fishes start feeding at 5–7 days post fertilization. And they experience extreme mortality rate (≈99%) in the few days after feeding starts. The reason for this 'Critical Period' (Hjort-1914) is mainly hydrodynamic constraints. Larval fish fail to eat even if there are enough prey encounters. One of the primary determinants of feeding success is the size of larval body. The smaller larvae function in a lower Reynolds number (Re) regime. As the age increases, the size of the larvae increases, which leads to higher swimming speed and increased Reynolds number. It has been observed through many experiments that the Reynolds number of successful strikes (Re~200) is much higher than the Reynolds number of failed strikes (Re~20). Numerical analysis of suction feeding at a low Reynolds number concluded that around 40% energy invested in mouth opening is lost to frictional forces rather than contributing to accelerating the fluid towards mouth. Ontogenetic improvement in the sensory system, coordination and experiences are non-significant relationship while determining feeding success of larvae A successful strike positively depends upon the peak flow speed or the speed of larvae at the time of strike. The peak flow speed is also dependent on the gape speed or the speed of opening the buccal cavity to capture food. As the larva ages, its body size increase and its gape speed also increase, which cumulatively increase the successful strike outcomes. The ability of a larval prey to survive an encounter with predator totally depends on its ability to sense and evade the strike. Adult fishes exhibit rapid suction feeding strikes as compared to larval fishes. Sensitivity of larval fish to velocity and flow fields provides the larvae a critical defense against predation. Though many prey use their visual system to detect and evade predators when there is light, it is hard for the prey to detect predators at night, which leads to a delayed response to the attack. There is a mechano-sensory system in fishes to identify the different flow generated by different motion surrounding the water and between the bodies called as lateral line system. After detecting a predator, a larva evades its strike by 'fast start' or 'C' response. A swimming fish disturbs a volume of water ahead of its body with a flow velocity that increases with the proximity to the body. This particular phenomenon is sometimes called abow wave
A bow wave is the wave that forms at the bow (watercraft), bow of a ship when it moves through the water. As the bow wave spreads out, it defines the outer limits of a ship's Wake (physics), wake. A large bow wave slows the ship down, is a risk t ...
. The timing of the 'C' start response affects escape probability inversely. Escape probability increases with the distance from the predator at the time of strike. In general, prey successfully evade a predator strike from an intermediate distance (3–6 mm) from the predator.
Atlantic herring
Atlantic herring (''Clupea harengus'') is a herring in the family Clupeidae. It is one of the most abundant fish species in the world. Atlantic herrings can be found on both sides of the northern Atlantic Ocean, congregating in large schools. ...
eggs, with a newly hatched larva
File:Clupealarvamatchkils.jpg, Freshly hatched herring larva in a drop of water compared to a match head.
File:Lanternfish larva.jpg, Late stage lanternfish
Lanternfish (or myctophids, from the Greek language, Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family (biology), family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, ...
larva
File:Arnoglossus laterna larva.jpg, A 9mm long late stage scaldfish
The scaldfishes comprise a genus, ''Arnoglossus'', of lefteye flounders. They are found in the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans, including the Mediterranean and Black Sea. They are entirely absent from most of the Americas; the only exceptions ...
larva
File:LeptocephalusConger.jpg, Larva of a conger eel, 7.6 cm
File:Larval stage of bluefin tuna.jpg, Bluefin tuna Bluefin tuna is a common name used to refer to several species of tuna of the genus ''Thunnus''.
{{Animal common name
Commercial fish
Thunnus
Fish common names ...
larva
File:Pacific cod larvae.jpg, Pacific cod
The Pacific cod (''Gadus macrocephalus)'' is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gadidae. It is a bottom-dwelling fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean, mainly on the continental shelf and upper slopes, to depths of about . It can grow ...
larva
File:Walleye larva (8740460659).jpg, Walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', Synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the walleyed pike, yellow pike, yellow pikeperch or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern ...
larva
File:Common sturgeon larva.jpg, Common sturgeon larva
File:FMIB 47039 Ostracion hoops.jpeg, Boxfish
Ostraciidae or Ostraciontidae is a family of squared, Actinopterygii, bony fish belonging to the order Tetraodontiformes, closely related to the pufferfishes and filefishes. Fish in the family are known variously as boxfishes, cofferfishes, cowfi ...
larva
File:Molalavdj.jpg, Ocean sunfish
The ocean sunfish (''Mola mola''), also known as the common mola, is one of the largest bony fish in the world. It is the type species of the genus ''Mola'', and one of five extant species in the family Molidae. It was once misidentified as th ...
larva, 2.7mm
Behavior
Objective quantification is complicated in higher vertebrates by the complex and diverse locomotor repertoire and neural system. However, the relative simplicity of a juvenile brain and simple nervous system of fishes with fundamental neuronal pathways allows zebrafish larvae to be an apt model to study the interconnection between locomotor repertoire and neuronal system of a vertebrate. Behavior represents the unique interface between intrinsic and extrinsic forces that determine an organism's health and survival.‘Locomotion In Larval Zebrafish: Influence of Time of Day, Lighting and Ethanol’ by R.C. MacPhail, J. Brooks, D.L. Hunter, B. Padnos a, T.D. Irons, S. Padilla in Neurotoxicology. 30. 52-8. 10.1016/j.neuro.2008.09.011. Larval zebrafish perform many locomotor behavior such as escape response, prey tracking, optomotor response etc. These behaviors can be categorized with respect to body position as ‘C’-starts, ‘J’-turns, slow scoots, routine turns etc. Fish larvae respond to abrupt changes in illumination with distinct locomotor behavior. The larvae show high locomotor activity during periods of bright light compared to dark. This behavior can direct towards the idea of searching food in light whereas the larvae do not feed in dark.‘Modulation of Locomotor Activity in Larval Zebrafish During Light Adaptation’ by Harold A. Burgess and Michael Granato. In Journal of Experimental Biology 2007 210: 2526–2539; doi: 10.1242/jeb.003939 Also light exposure directly manipulates the locomotor activities of larvae throughout circadian period of light and dark with higher locomotor activity in light condition than in dark condition which is very similar as seen in mammals. Following the onset of darkness, larvae shows hyperactive scoot motion prior to a gradual drop off. This behavior could possibly be linked to find a shelter before nightfall. Also larvae can treat this sudden nightfall as under debris and the hyperactivity can be explained as the larvae navigation back to illuminated areas. Prolonged dark period can reduce the light-dark responsiveness of larvae. Following light extinction, larvae execute large angle turns towards the vanished light source, which explains the navigational response of a larva. Acute ethanol exposure reduce visual sensitivity of larvae causing a latency to respond in light and dark period change.See also
* *Microswimmer
A microswimmer is a microscopic object with the ability to move in a fluid environment. #Natural microswimmers, Natural microswimmers are found everywhere in the natural world as biological microorganisms, such as bacteria, archaea, protists, spe ...
*
*
*
References
Further reading
* Alexander, R. McNeill (2003) ''Principles of Animal Locomotion.'' Princeton University Press. . * * * Videler JJ (1993''Fish Swimming''
Springer. . * Vogel, Steven (1994) ''Life in Moving Fluid: The Physical Biology of Flow.'' Princeton University Press. (particularly pp. 115–117 and pp. 207–216 for specific biological examples swimming and flying respectively) * Wu, Theodore, Y.-T., Brokaw, Charles J., Brennen, Christopher, Eds. (1975) ''Swimming and Flying in Nature''. Volume 2, Plenum Press. (particularly pp. 615–652 for an in depth look at fish swimming)
External links
How fish swim: study solves muscle mystery
Simulated fish locomotion
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110724192433/http://www.geol.umd.edu/~jmerck/bsci392/lecture10/lecture10.html The biomechanics of swimming {{fins, limbs and wings Ichthyology Aquatic locomotion Animal locomotion Articles containing video clips