|
Electrophorus Electricus
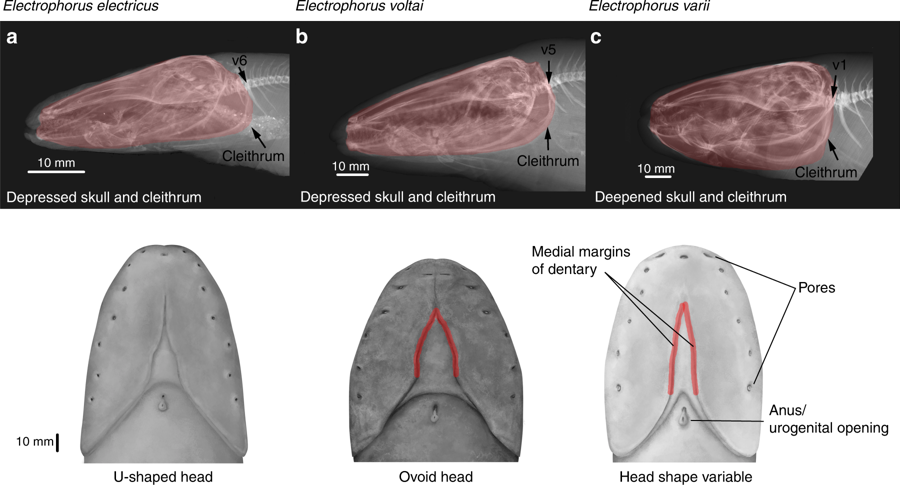
''Electrophorus electricus'' is the best-known species of electric eel. It is a South American electric fish. Until the discovery of two additional species in 2019, the genus was classified as the monotypic, with this species the only one in the genus. Despite the name, it is not an eel, but rather a knifefish. It is considered as a freshwater teleost which contains an electrogenic tissue that produces electric discharges. Taxonomic history The species has been reclassified several times. When originally described by Carl Linnaeus in 1766, he used the name ''Gymnotus electricus'', placing it in the same genus as ''Gymnotus carapo'' (banded knifefish) which he had described several years earlier. It was only about a century later, in 1864, that the electric eel was moved to its own genus ''Electrophorus'' by Theodore Gill. In September 2019, David de Santana et al. suggested the division of the genus into three species based on DNA divergence, ecology and habitat, anatomy and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Aquarium
The New England Aquarium is a public aquarium located in Boston, Massachusetts. The species exhibited include harbor and northern fur seals, California sea lions, African and southern rockhopper penguins, giant Pacific octopuses, weedy seadragons, and thousands of saltwater and freshwater fishes. In addition to the main aquarium building, attractions at Central Wharf include the Simons Theatre and the New England Aquarium Whale Watch. More than 1.3 million guests visited the aquarium each year prior to the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Anderson Cabot Center for Ocean Life at the New England Aquarium conducts long-running research on the North Atlantic right whale, and its Quincy Animal Care Center rescues and rehabilitates hundreds of sea turtles annually. History Boston has had multiple aquariums since the 1880s, the last before the New England Aquarium being the South Boston Aquarium at Marine Park, which closed its doors in the 1950s. As part of the city’s goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostariophysi
Ostariophysi is the second-largest superorder of fish. Members of this superorder are called ostariophysians. This diverse group contains 10,758 species, about 28% of known fish species in the world and 68% of freshwater species, and are present on all continents except Antarctica. They have a number of common characteristics such as an alarm substance and a Weberian apparatus. Members of this group include fish important to people for food, sport, the aquarium industry, and research. Taxonomy The superorder is divided into two series, Anotophysi and Otophysi. However, in older literature, Ostariophysi was restricted only to the fish that are currently classified under Otophysi. Otophysi was coined in 1970 by Rosen and Greenwood to separate the traditional Ostariophysians from the added Gonorynchiformes. The superorder is classified below: *Series Anotophysi ** Gonorynchiformes, about 37 species *Series Otophysi (Euostariophysi) ** Cypriniformes ( minnows and allies), about 4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Organs
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Eel
The electric eels are a genus, ''Electrophorus'', of neotropical freshwater fish from South America in the family Gymnotidae. They are known for their ability to stun their prey by generating electricity, delivering shocks at up to 860 volts. Their electrical capabilities were first studied in 1775, contributing to the invention in 1800 of the electric battery. Despite their name, electric eels are not closely related to the true eels (Anguilliformes) but are members of the electroreceptive knifefish order, Gymnotiformes. This order is more closely related to catfish. In 2019, electric eels were split into three species: for more than two centuries before that, the genus was believed to be monotypic, containing only '' Electrophorus electricus.'' They are nocturnal, obligate air-breathing animals, with poor vision complemented by electrolocation; they mainly eat fish. Electric eels grow for as long as they live, adding more vertebrae to their spinal column. Males are larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery (electricity)
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering Electricity, electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the Gibbs free energy, free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary battery, Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and disposable product, discarded, as the electrode materials are irreversibly changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere, or ''amp'', which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. The ampere (symbol: A) is an SI base unit. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter. Electric currents create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, generators, inductors, and transformers. In ordinary con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Potential
The electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as the amount of work energy needed to move a unit of electric charge from a reference point to the specific point in an electric field. More precisely, it is the energy per unit charge for a test charge that is so small that the disturbance of the field under consideration is negligible. Furthermore, the motion across the field is supposed to proceed with negligible acceleration, so as to avoid the test charge acquiring kinetic energy or producing radiation. By definition, the electric potential at the reference point is zero units. Typically, the reference point is earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. In classical electrostatics, the electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar quantity denoted by or occasionally , equal to the electric potential energy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous System
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves or '' efferent'' nerves, while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves or '' afferent''. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that serve both fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocyte
An Torpediniformes.html" ;"title="electric ray (Torpediniformes">electric ray (Torpediniformes) showing location of paired electric organs in the head, and electrocytes stacked within it In biology, the electric organ is an organ that an electric fish uses to create an electric field. Electric organs are derived from modified muscle or in some cases nerve tissue, and have evolved at least six times among the elasmobranchs and teleosts. These fish use their electric discharges for navigation, communication, mating, defence, and in strongly electric fish also for the incapacitation of prey. The electric organs of two strongly electric fish, the torpedo ray and the electric eel were first studied in the 1770s by John Walsh, Hugh Williamson, and John Hunter. Charles Darwin used them as an instance of convergent evolution in his 1859 ''On the Origin of Species''. Modern study began with Hans Lissmann's 1951 study of electroreception and electrogenesis in ''Gymnarchus''. Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Organ Discharge
An electric ray (Torpediniformes) showing location of paired electric organs in the head, and electrocytes stacked within it">Torpediniformes.html" ;"title="electric ray (Torpediniformes">electric ray (Torpediniformes) showing location of paired electric organs in the head, and electrocytes stacked within it In biology, the electric organ is an organ that an electric fish uses to create an electric field. Electric organs are derived from modified muscle or in some cases nerve tissue, and have evolved at least six times among the elasmobranchs and teleosts. These fish use their electric discharges for navigation, communication, mating, defence, and in strongly electric fish also for the incapacitation of prey. The electric organs of two strongly electric fish, the torpedo ray and the electric eel were first studied in the 1770s by John Walsh, Hugh Williamson, and John Hunter. Charles Darwin used them as an instance of convergent evolution in his 1859 ''On the Origin of Species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_IMG_0321.jpg)




