|
Anglo-Thai Peace Treaty
The Anglo-Thai Peace Treaty (long title: Formal Agreement for the Termination of the State of War between Siam and Great Britain and India) signed in Singapore on 1 January 1946 ended the state of war that had existed between Thailand and the United Kingdom since the former's declaration of war of 25 January 1942 during World War II. Although the Thais had also declared war on the United States on the same day, a U.S.–Thai peace treaty was never signed because the American government opted not to recognise the legality of the declaration in light of the Japanese invasion of Thailand on 8 December 1941. The peace treaty went into effect on the day it was signed. It was registered in the ''United Nations Treaty Series'' on 23 August 1951. Background During World War II, Thailand was an ally of the Empire of Japan. In that capacity, it gained some territories that were incorporated in Thailand in exchange for freedom for the Japanese government to establish military bases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signing Of The Anglo-Thai Peace Treaty
Signing may refer to: * Using sign language * Signature, placing one's name on a document * Signature (other) A signature is a hand-written, possibly stylized, version of someone's name, which may be used to confirm the person's identity. The writer of a signature is a signatory or signer. Signature or signatory may also refer to: Businesses and organ ... * Manual communication, signing as a form of communication using the hands in place of the voice * Digital signature, signing as a method of authenticating digital information See also * Wikipedia:Sign your posts on talk pages, the Wikipedia policy of signing Talk pages {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Thai Movement
The Free Thai Movement ( th, เสรีไทย; ) was a Thai underground resistance movement against Imperial Japan during World War II. Seri Thai were an important source of military intelligence for the Allies in the region. Background In the aftermath of the Japanese invasion of Thailand on 7–8 December 1941, the regime of Plaek Phibunsongkhram (Phibun) declared war on the United Kingdom and the United States on 25 January 1942. Seni Pramoj, the Thai ambassador in Washington, refused to deliver the declaration to the United States government. Accordingly, the United States refrained from declaring war on Thailand. Seni, a conservative aristocrat whose anti-Japanese credentials were well established, organized the Free Thai Movement with American assistance, recruiting Thai students in the United States to work with the United States Office of Strategic Services (OSS). The OSS trained Thai personnel for underground activities, and units were readied to infiltrate Thail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statute Of Westminster Adoption Act 1942
The Statute of Westminster Adoption Act 1942 is an act of the Australian Parliament that formally adopted sections 2–6 of the Statute of Westminster 1931, an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom enabling the total legislative independence of the various self-governing Dominions of the British Empire. With its enactment, Westminster relinquished nearly all of its authority to legislate for the Dominions, effectively making them ''de jure'' sovereign nations. With the enactment of the Adoption Act, the British Parliament could no longer legislate for the Commonwealth without the express request and consent of the Australian Parliament. The act received Royal Assent on 9 October 1942, but the adoption of the Statute was made retroactive to 3 September 1939, when Australia entered World War II. The Act is more important for its symbolic value than for the legal effect of its provisions. While Australia's growing independence from the United Kingdom was well accepted, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian–Thai Peace Treaty
The Australian–Thai Peace Treaty that ended World War II between Australia and Thailand was signed in Bangkok on 3 April 1946. The full title of the peace treaty is "Final Peace Agreement Between the Government of Australia and the Government of Siam". It was one of the first expressions of Australian sovereignty and independence in foreign affairs after the Statute of Westminster came into effect in 1942. Background In November 1941, as concerns about war with the Japanese in the Pacific grew, the Thai minister of justice, Thamrong Navasawat, met the Australian prime minister, Robert Gordon Menzies, in Canberra during a goodwill tour of the British Empire in Asia. This meeting was designed to assure the government of Australia of Thailand's neutrality. The British had been pressing the Australians to establish a legation in Bangkok, but the latter still preferred that their interests be represented by Westminster. On 8 December, the Japanese invaded Thailand and the Thai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquartered on international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in Geneva, Nairobi, Vienna, and The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for a conference and started drafting the UN Charter, which was adopted on 25 June 1945 and took effect on 24 October 1945, when the UN began operations. Pursuant to the Charter, the organization's objectives include maintaining internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1946 Siamese General Election
General elections were held in Siam on 6 January 1946 to elect 96 of the 192 members of the House of Representatives. The other 96 members were appointed by King Ananda Mahidol. Voter turnout was 33%.Nohlen ''et al''., p278 At the time there were no political parties, so all candidates ran as independents. Results Aftermath Following the promulgation of a new constitution later in 1946, the appointed seats were abolished and the number of elected seats expanded to 178. Elections were held in August 1946 to elect an additional 82 members and political parties were allowed to contest the elections for the first time. Supporters of Pridi Banomyong (Sahachip Party and the Constitutional Front) took 57 seats, the Democrat Party took 18 seats and seven seats went to unaffiliated representatives. References Cited works * Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz & Christof Hartmann (2001) ''Elections in Asia: A data handbook, Volume II''. {{Thai elections Siam General A general officer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pridi Banomyong
Pridi Banomyong ( th, ปรีดี พนมยงค์, , ; 11 May 1900 – 2 May 1983), also known by his noble title Luang Praditmanutham ( th, หลวงประดิษฐ์มนูธรรม) was a Thai politician and professor. As a Thai Regent, prime minister and senior statesman of Thailand, he also held multiple ministerial posts. He was a leader of the civilian wing of Khana Ratsadon, founder of University of Moral and Political Sciences and the Bank of Thailand. Born to a family of farmers in Ayutthaya Province, he nonetheless received a good education, becoming one of the nation's youngest barristers in 1919, at the age of nineteen. In 1920, he won scholarship to study in France, where he graduated from University of Caen with a master's degree, and completed his doctorate from University of Paris in 1927. In the same year, he co-founded Khana Ratsadon with like-minded Siamese overseas students. After returning to Thailand, still called Siam at the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
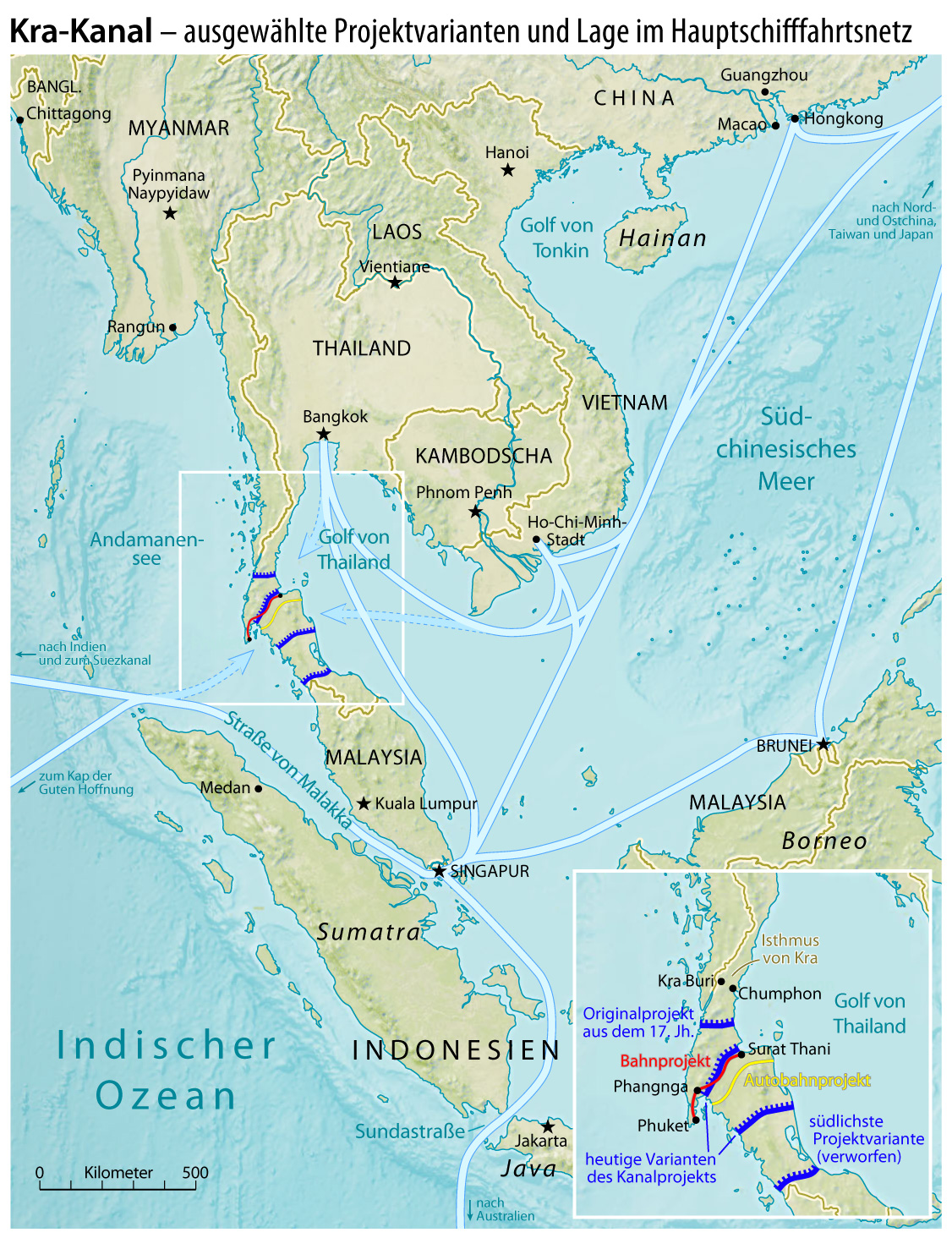
Thai Canal
The Thai Canal, also known as Kra Canal or Kra Isthmus Canal, refers to proposals for a canal that would connect the Gulf of Thailand with the Andaman Sea across the Kra Isthmus in southern Thailand. Such a canal would significantly reduce travel times through heavily-navigated trade routes. The canal would provide an alternative to transit through the Straits of Malacca and shorten transit for shipments of oil to Japan and China by 1,200 km. China refers to it as part of its 21st century maritime Silk Road. Proposals, of 2015, measure 102 kilometres long, 400 meters wide and 25 meters deep. Plans for a canal have been discussed and explored at various times. Cost, environmental concerns, and geopolitical concerns have been weighed against the potential economic and strategic benefits. In February 2018, Thailand's Prime Minister Prayut Chan-o-cha declared that the canal was not a government priority. However, on 16 January 2020, the Thai House of Representatives agreed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terengganu
Terengganu (; Terengganu Malay: ''Tranung'', Jawi: ), formerly spelled Trengganu or Tringganu, is a sultanate and constitutive state of federal Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, ''Dāru l- Īmān'' ("Abode of Faith"). The coastal city of Kuala Terengganu, which stands at the mouth of the broad Terengganu River, is both the state and royal capital as well as the largest city in Terengganu. There are many islands located close to the coast of Terengganu state, such as Perhentian Islands and Redang Island. Etymology There are several theories on the origin of the name "Terengganu". One theory attributes the name's origin to ''terang ganu'', Malay for 'bright rainbow'. Another story, said to have been originally narrated by the ninth Sultan of Terengganu, Baginda Omar, tells of a party of hunters from Pahang roving and hunting in the area of what is now southern Terengganu. One of the hunters spotted a big animal fang lying on the ground. A fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perlis
Perlis, ( Northern Malay: ''Peghelih''), also known by its honorific title Perlis Indera Kayangan, is the smallest state in Malaysia by area and population. Located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia, it borders the Thai provinces of Satun and Songkhla to the north and the Malaysian state of Kedah to the south. It was called Palit ( th, ปะลิส) by the Siamese when it was under their influence. Perlis had a population of 227,025 as of the 2010 census. The capital of Perlis is Kangar, and the royal capital is Arau. Another important town is Padang Besar, at the Malaysia–Thailand border and Kuala Perlis, the ferry town to Langkawi. The main port and ferry terminal is at the small village of Kuala Perlis, linking mostly to Langkawi Island. Another important lately developed area is Pauh Putra within subdistrict of Kurong Anai which houses the main campus of Malaysia University of Perlis and Politeknik Tuanku Syed Sirajuddin. Perlis has a famous snake far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelantan
Kelantan (; Jawi: ; Kelantanese Malay: ''Klate'') is a state in Malaysia. The capital is Kota Bharu and royal seat is Kubang Kerian. The honorific name of the state is ''Darul Naim'' (Jawi: ; "The Blissful Abode"). Kelantan is located in the north-eastern corner of the peninsula. Kelantan, which is said to translate as the "Land of Lightning" (see alternate theories below), is an agrarian state with green paddy fields, rustic fishing villages and casuarina-lined beaches. Kelantan is home to some of the most ancient archaeological discoveries in Malaysia, including several prehistoric aboriginal settlements. Due to Kelantan's relative isolation and largely rural lifestyle, Kelantanese culture differs somewhat from Malay culture in the rest of the peninsula; this is reflected in the cuisine, arts and the unique Kelantanese Malay language, which is unintelligible even for some speakers of standard Malay. Kelantan is positioned in the north-east of the Malay Peninsula. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedah
Kedah (), also known by its honorific Darul Aman and historically as Queda, is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km2, and it consists of the mainland and the Langkawi islands. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice, while Langkawi is an archipelago, most of which are uninhabited islands. Kedah was previously known as Kadaram (; ') by the ancient and medieval Tamils, Kataha or Kalahbar (; ' or ; ') by the Arabs, and '' Syburi'' ( th, ไทรบุรี; ) by the Siamese when it was under their influence. To the north, Kedah borders the state of Perlis and shares an international boundary with the Songkhla and Yala provinces of Thailand. It borders the states of Perak to the south and Penang to the southwest. The state's capital is Alor Setar and the royal seat is in Anak Bukit. Other major towns include Sungai Petani (its largest urban area by pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |