|
Ang Eng
Ang Eng ( km, អង្គអេង ; 1773 – 5 May 1796) was King of Cambodia from 1779 to his death in 1796. He reigned under the name of Neareay Reachea III ( km, នារាយណ៍រាជាទី៣, link=no). Ang Eng was a son of Outey II. He was installed the Cambodian king by Prince Talaha (Mu) ( km, ចៅហ្វ៊ាមូ, th, เจ้าฟ้าทะละหะ (มู)) in 1780. Prince Talaha (Mu) acted as regent, and was pro- Vietnamese. Talaha rebelled against Siam, Taksin decided on an invasion of Cambodia. A Siamese army under Somdej Chao Phraya Maha Kasatsuek was dispatched to Cambodia, to crown Inthraphithak as the new king of Cambodia. However, a coup occurred in the same year. Maha Kasatsuek and Maha Surasi marched back to Siam. Later, Maha Kasatsuek was crowned as the new Siamese king and became Rama I. In 1782, the Tây Sơn dynasty of Vietnam attacked Gia Định and defeated the Nguyễn lord. The Vietnamese lost their control of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of Cambodia
The monarchy of Cambodia is the head of state of the Kingdom of Cambodia. In the contemporary period, the King's power has been limited to that of a symbolic figurehead. The monarchy had been in existence since at least 68 AD except during its abolition from 1970 to 1993. Since 1993, the King of Cambodia has been an elected monarch, making Cambodia one of the few elective monarchies of the world. The king is elected for life by the Royal Council of the Throne, which consists of several senior political and religious figures. Candidates are chosen from among male descendants of King Ang Duong who are at least 30 years old, from the two royal houses of Cambodia (the House of Norodom and the House of Sisowath). Role Cambodia's constitution, promulgated in 1993 stipulated the king's role as a mainly ceremonial one. It declared that the king "shall reign, but not govern" as well as being the "symbol of national unity and continuity". The king performs important functions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maha Sura Singhanat
Somdet Phra Bawornrajchao Maha Sura Singhanat ( th, สมเด็จพระบวรราชเจ้ามหาสุรสิงหนาท; , lit: ''His Royal Highness, Maharurasinghanat, Prince of Front Palace'') (1 November 1744 – 3 November 1803) was the younger brother of Rama I, the first monarch of the Chakri dynasty of Siam. As an Ayutthayan general, he fought alongside his brother in various campaigns against Burmese invaders and the local warlords. When his brother crowned himself as the king of Siam at Bangkok in 1781, he was appointed the Front Palace or Maha Uparaj, the title of the heir. During the reign of his brother, he was known for his important role in the campaigns against Bodawpaya of Burma. Early life Bunma was born in 1744 to Thongdee and Daoreung. His father Thongdee was the Royal Secretary of Northern Siam and Keeper of Royal Seal. As a son of aristocrat, he entered the palace and began his aristocratic life as a royal page. Thongdee was a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Cambodian Monarchs
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulletin De L'École Française D'Extrême-Orient
The French School of the Far East (french: École française d'Extrême-Orient, ), abbreviated EFEO, is an associated college of PSL University dedicated to the study of Asian societies. It was founded in 1900 with headquarters in Hanoi in what was then French Indochina. After the independence of Vietnam, its headquarters were transferred to Phnom Penh in 1957 and subsequently to Paris in 1975. Its main fields of research are archaeology, philology and the study of modern Asian societies. Since 1907, the EFEO has been in charge of conservation work at the archeological site of Angkor. EFEO romanization system A romanization system for Mandarin was developed by the EFEO. It shares a few similarities with Wade-Giles and Hanyu Pinyin. In modern times, it has been superseded by Hanyu Pinyin. The differences between the three romanization systems are shown in the following table: Directors *1900: Louis Finot *1905: Alfred Foucher *1908: Claude-Eugène Maitre *1920: Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Que Sais-je ?
"Que sais-je?" (QSJ) (; Literally: "What do I know?", ) is an editorial collection published by the Presses universitaires de France (PUF). The aim of the series is to provide the lay reader with an accessible introduction to a field of study written by an expert in the field. As such, they are a good example of ''haute vulgarisation'' (high popularization). The sentence "Que sais-je?" is taken from the works of French essayist Michel de Montaigne. Started in 1941 by Paul Angoulvent (1899–1976), founder of the Presses Universitaires de France, the series now numbers over 3,900 titles by more than 2,500 authors, and translated in more than 43 languages. Somes titles have sold more than 300,000 copies (namely by Piaget). Each year, 50 to 60 new titles are added to the collection, which comprises ten different series. As such, it easily constitutes the world's largest running 'encyclopedia' in paperback format. The range of subjects is truly encyclopedic, covering everything f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achille Dauphin-Meunier
Achille Dauphin-Meunier (1906–1984) was a French economist. He wrote on US-Laotian relations. He was a member of the Club de l'horloge The Carrefour de l'Horloge (literally ''The Clock Crossroad''), formerly Club de l'Horloge (1974–2015), is a French far-right national liberal think tank founded in 1974 and presided by Henry de Lesquen. The organization promotes an "integral .... References Carrefour de l'horloge people 1906 births 1984 deaths 20th-century French economists {{France-economist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siem Reap
Siem Reap ( km, សៀមរាប, ) is the second-largest city of Cambodia, as well as the capital and largest city of Siem Reap Province in northwestern Cambodia. Siem Reap has French colonial and Chinese-style architecture in the Old French Quarter and around the Old Market. In the city, there are museums, traditional Apsara dance performances, a Cambodian cultural village, souvenir and handicraft shops, silk farms, rice paddies in the countryside, fishing villages and a bird sanctuary near Tonlé Sap, and a cosmopolitan drinking and dining scene. Cambodia’s Siem Reap city, home to the famous Angkor Wat temples, was crowned the ASEAN City of Culture for the period 2021–2022 at the 9th Meeting of the ASEAN Ministers Responsible for Culture and Arts (AMCA) organised on Oct 22, 2020. Siem Reap today—being a popular tourist destination—has many hotels, resorts, and restaurants. This owes much to its proximity to the Angkor Wat temples, Cambodia's most popular tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battambang
Battambang ( km, បាត់ដំបង, Romanization of Khmer#UNGEGN, UNGEGN: ) is the capital of Battambang Province and the third largest city in Cambodia. Founded in the 11th century by the Khmer Empire, Battambang is the leading rice-producing province of the country. For nearly 100 years it was a major commercial hub and provincial capital of Siamese province of Inner Cambodia (1795-1907), though it was always populated by Khmer, with some ethnic Vietnamese, Lao, Thai and Chinese. Battambang remains the hub of Cambodia's northwest, connecting the region with Phnom Penh and Thailand. The city is situated on the Sangkae River, a tranquil, small body of water that winds its way picturesquely through Battambang Province. As with much of Cambodia, French Colonial architecture is a notable aspect of the city, with some of the best-preserved examples in the country. Now the government and Ministry of Culture and Fine Art are preparing documents to nominate The Old Town of Batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phnom Penh
Phnom Penh (; km, ភ្នំពេញ, ) is the capital and most populous city of Cambodia. It has been the national capital since the French protectorate of Cambodia and has grown to become the nation's primate city and its economic, industrial, and cultural centre. Phnom Penh succeeded Angkor Thom as the capital of the Khmer nation but was abandoned several times before being reestablished in 1865 by King Norodom. The city formerly functioned as a processing center, with textiles, pharmaceuticals, machine manufacturing, and rice milling. Its chief assets, however, were cultural. Institutions of higher learning included the Royal University of Phnom Penh (established in 1960 as Royal Khmer University), with schools of engineering, fine arts, technology, and agricultural sciences, the latter at Chamkar Daung, a suburb. Also located in Phnom Penh were the Royal University of Agronomic Sciences and the Agricultural School of Prek Leap. The city was nicknamed the "Pearl of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chams
The Cham ( Cham: ''Čaṃ'') or Champa people ( Cham: , ''Urang Campa''; vi, Người Chăm or ; km, ជនជាតិចាម, ) are an Austronesian ethnic group. From the 2nd century to 1832 the Cham populated Champa, a contiguous territory of independent principalities in central and southern Vietnam. They spoke the Cham language and the Tsat language (the former is still spoken by the Cham, and the latter is spoken by their Utsul descendants, on China’s Hainan Island), two Chamic languages from the Malayo-Polynesian group of the Austronesian family. Chams and Malays are the only sizable Austronesian peoples that settled in Iron Age mainland Southeast Asia among the more ancient Austroasiatic inhabitants. History For a long time, researchers believed that the Chams had arrived by sea in the first millennium BC from Sumatra, Borneo and the Malay Peninsula, eventually settling in central modern Vietnam. The original Cham are therefore the likely heirs of Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Lord
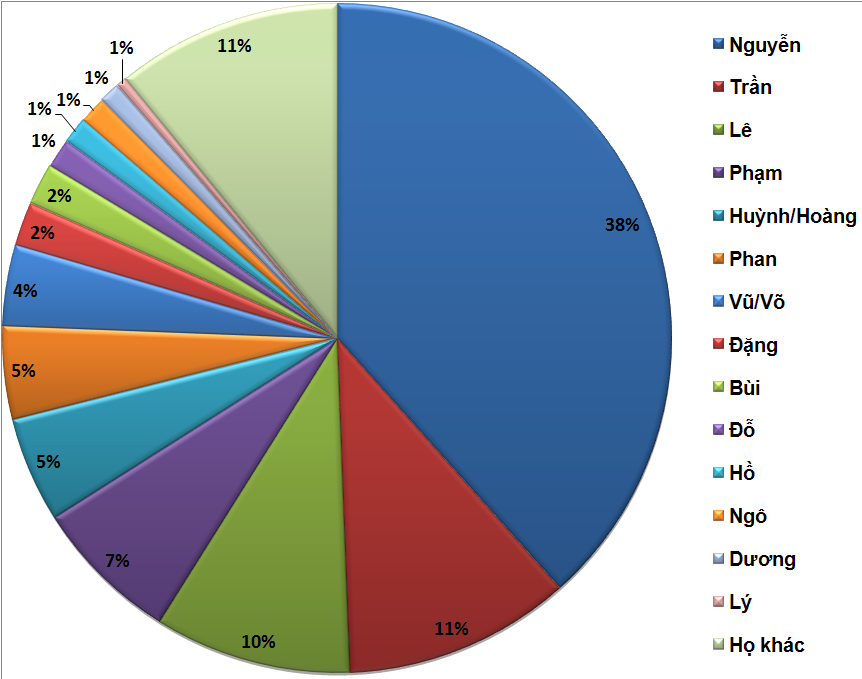
Nguyễn () is the most common Vietnamese surname. Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as Nguyen. Nguyên (元)is a different word and surname. By some estimates 39 percent of Vietnamese people bear this surname.Lê Trung Hoa, ''Họ và tên người Việt Nam'', NXB Khoa học - Xã hội, 2005 Origin and usage "Nguyễn" is the spelling of the Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation of the Han character 阮 (, ). The same Han character is often romanized as ''Ruǎn'' in Mandarin, ''Yuen'' in Cantonese, ''Gnieuh'' or ''Nyoe¹'' in Wu Chinese, or ''Nguang'' in Hokchew. . Hanja reading (Korean) is 완 (''Wan'') or 원 (''Won'') and in Hiragana, it is げん (''Gen''), old reading as け゚ん (Ngen). The first recorded mention of a person surnamed Nguyen is a 317 CE description of a journey to Giao Châu undertaken by Eastern Jin dynasty (, ) officer and his family. Many events in Vietnamese history have contributed to the name's prominence. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ho Chi Minh City
, population_density_km2 = 4,292 , population_density_metro_km2 = 697.2 , population_demonym = Saigonese , blank_name = GRP (Nominal) , blank_info = 2019 , blank1_name = – Total , blank1_info = US$61.7 billion , blank2_name = – Per capita , blank2_info = US$6,862 , blank3_name = GRP ( PPP) , blank3_info = 2019 , blank4_name = – Total , blank4_info = US$190.3 billion , blank5_name = – Per capita , blank5_info = US$21,163 , blank6_name = HDI (2020) , blank6_info = 0.795 ( 2nd) , area_code = 28 , area_code_type = Area codes , website = , timezone = ICT , utc_offset = +07:00 , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = 700000–740000 , iso_code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)