|
Algebraic Graph Theory
Algebraic graph theory is a branch of mathematics in which algebraic methods are applied to problems about graphs. This is in contrast to geometric, combinatoric, or algorithmic approaches. There are three main branches of algebraic graph theory, involving the use of linear algebra, the use of group theory, and the study of graph invariants. Branches of algebraic graph theory Using linear algebra The first branch of algebraic graph theory involves the study of graphs in connection with linear algebra. Especially, it studies the spectrum of the adjacency matrix, or the Laplacian matrix of a graph (this part of algebraic graph theory is also called spectral graph theory). For the Petersen graph, for example, the spectrum of the adjacency matrix is (−2, −2, −2, −2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3). Several theorems relate properties of the spectrum to other graph properties. As a simple example, a connected graph with diameter ''D'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance (graph Theory)
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the distance between two vertices in a graph is the number of edges in a shortest path (also called a graph geodesic) connecting them. This is also known as the geodesic distance or shortest-path distance. Notice that there may be more than one shortest path between two vertices. If there is no path connecting the two vertices, i.e., if they belong to different connected components, then conventionally the distance is defined as infinite. In the case of a directed graph the distance between two vertices and is defined as the length of a shortest directed path from to consisting of arcs, provided at least one such path exists. Notice that, in contrast with the case of undirected graphs, does not necessarily coincide with —so it is just a quasi-metric, and it might be the case that one is defined while the other is not. Related concepts A metric space defined over a set of points in terms of distances in a graph defined over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
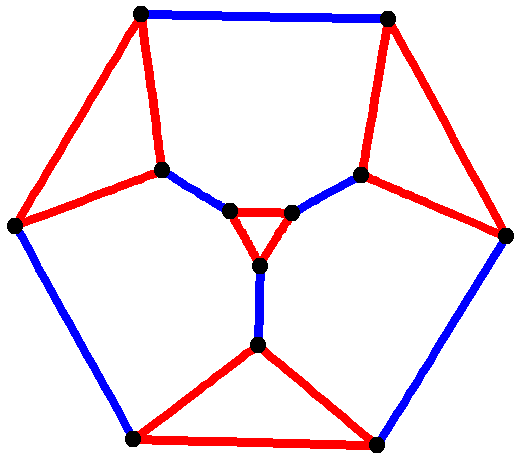
Foster Census
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a graph is symmetric (or arc-transitive) if, given any two pairs of adjacent vertices and of , there is an automorphism :f : V(G) \rightarrow V(G) such that :f(u_1) = u_2 and f(v_1) = v_2. In other words, a graph is symmetric if its automorphism group acts transitively on ordered pairs of adjacent vertices (that is, upon edges considered as having a direction). Such a graph is sometimes also called -transitive or flag-transitive. By definition (ignoring and ), a symmetric graph without isolated vertices must also be vertex-transitive. Since the definition above maps one edge to another, a symmetric graph must also be edge-transitive. However, an edge-transitive graph need not be symmetric, since might map to , but not to . Star graphs are a simple example of being edge-transitive without being vertex-transitive or symmetric. As a further example, semi-symmetric graphs are edge-transitive and regular, but not vertex-transi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongly Regular Graph
In graph theory, a strongly regular graph (SRG) is defined as follows. Let be a regular graph with vertices and degree . is said to be strongly regular if there are also integers and such that: * Every two adjacent vertices have common neighbours. * Every two non-adjacent vertices have common neighbours. The complement of an is also strongly regular. It is a . A strongly regular graph is a distance-regular graph with diameter 2 whenever μ is non-zero. It is a locally linear graph whenever . Etymology A strongly regular graph is denoted an srg(''v'', ''k'', λ, μ) in the literature. By convention, graphs which satisfy the definition trivially are excluded from detailed studies and lists of strongly regular graphs. These include the disjoint union of one or more equal-sized complete graphs, and their complements, the complete multipartite graphs with equal-sized independent sets. Andries Brouwer and Hendrik van Maldeghem (see #References) use an alternate but fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance-regular Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a distance-regular graph is a regular graph such that for any two vertices and , the number of vertices at distance from and at distance from depends only upon , , and the distance between and . Every distance-transitive graph is distance-regular. Indeed, distance-regular graphs were introduced as a combinatorial generalization of distance-transitive graphs, having the numerical regularity properties of the latter without necessarily having a large automorphism group. Intersection arrays It turns out that a graph G of diameter d is distance-regular if and only if there is an array of integers \ such that for all 1 \leq j \leq d , b_j gives the number of neighbours of u at distance j+1 from v and c_j gives the number of neighbours of u at distance j - 1 from v for any pair of vertices u and v at distance j on G . The array of integers characterizing a distance-regular graph is known as its intersection array. Cos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distance-transitive Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a distance-transitive graph is a graph such that, given any two vertices and at any distance , and any other two vertices and at the same distance, there is an automorphism of the graph that carries to and to . Distance-transitive graphs were first defined in 1971 by Norman L. Biggs and D. H. Smith. A distance-transitive graph is interesting partly because it has a large automorphism group. Some interesting finite groups are the automorphism groups of distance-transitive graphs, especially of those whose diameter is 2. Examples Some first examples of families of distance-transitive graphs include: * The Johnson graphs. * The Grassmann graphs. * The Hamming Graphs. * The folded cube graphs. * The square rook's graphs. * The hypercube graphs. * The Livingstone graph. Classification of cubic distance-transitive graphs After introducing them in 1971, Biggs and Smith showed that there are only 12 finite trivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge-transitive Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, an edge-transitive graph is a graph such that, given any two edges and of , there is an automorphism of that maps to . In other words, a graph is edge-transitive if its automorphism group acts transitively on its edges. Examples and properties The number of connected simple edge-transitive graphs on n vertices is 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 8, 9, 13, 7, 19, 10, 16, 25, 26, 12, 28 ... Edge-transitive graphs include all symmetric graph, such as the vertices and edges of the cube. Symmetric graphs are also vertex-transitive (if they are connected), but in general edge-transitive graphs need not be vertex-transitive. Every connected edge-transitive graph that is not vertex-transitive must be bipartite, (and hence can be colored with only two colors), and either semi-symmetric or biregular.. Examples of edge but not vertex transitive graphs include the complete bipartite graphs K_ where m ≠ n, which includes the star graphs K_. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex-transitive Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a vertex-transitive graph is a graph in which, given any two vertices and of , there is some automorphism :f : G \to G\ such that :f(v_1) = v_2.\ In other words, a graph is vertex-transitive if its automorphism group acts transitively on its vertices.. A graph is vertex-transitive if and only if its graph complement is, since the group actions are identical. Every symmetric graph without isolated vertices is vertex-transitive, and every vertex-transitive graph is regular. However, not all vertex-transitive graphs are symmetric (for example, the edges of the truncated tetrahedron), and not all regular graphs are vertex-transitive (for example, the Frucht graph and Tietze's graph). Finite examples Finite vertex-transitive graphs include the symmetric graphs (such as the Petersen graph, the Heawood graph and the vertices and edges of the Platonic solids). The finite Cayley graphs (such as cube-connected cycles) are also ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a graph is symmetric (or arc-transitive) if, given any two pairs of adjacent vertices and of , there is an automorphism :f : V(G) \rightarrow V(G) such that :f(u_1) = u_2 and f(v_1) = v_2. In other words, a graph is symmetric if its automorphism group acts transitively on ordered pairs of adjacent vertices (that is, upon edges considered as having a direction). Such a graph is sometimes also called -transitive or flag-transitive. By definition (ignoring and ), a symmetric graph without isolated vertices must also be vertex-transitive. Since the definition above maps one edge to another, a symmetric graph must also be edge-transitive. However, an edge-transitive graph need not be symmetric, since might map to , but not to . Star graphs are a simple example of being edge-transitive without being vertex-transitive or symmetric. As a further example, semi-symmetric graphs are edge-transitive and regular, but not vertex-transitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definition, and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations; including translation, reflection, rotation or scaling. Although these two meanings of "symmetry" can sometimes be told apart, they are intricately related, and hence are discussed together in this article. Mathematical symmetry may be observed with respect to the passage of time; as a spatial relationship; through geometric transformations; through other kinds of functional transformations; and as an aspect of abstract objects, including theoretic models, language, and music. This article describes symmetry from three perspectives: in mathematics, including geometry, the most familiar type of symmetry for many people; in science and nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
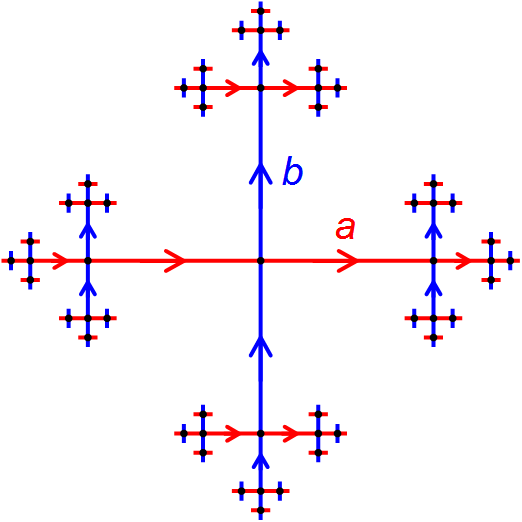
Geometric Group Theory
Geometric group theory is an area in mathematics devoted to the study of finitely generated groups via exploring the connections between algebraic properties of such group (mathematics), groups and topology, topological and geometry, geometric properties of spaces on which these groups Group action (mathematics), act (that is, when the groups in question are realized as geometric symmetries or continuous transformations of some spaces). Another important idea in geometric group theory is to consider finitely generated groups themselves as geometric objects. This is usually done by studying the Cayley graphs of groups, which, in addition to the graph (discrete mathematics), graph structure, are endowed with the structure of a metric space, given by the so-called word metric. Geometric group theory, as a distinct area, is relatively new, and became a clearly identifiable branch of mathematics in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Geometric group theory closely interacts with low-dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Automorphism
In the mathematical field of graph theory, an automorphism of a graph is a form of symmetry in which the graph is mapped onto itself while preserving the edge–vertex connectivity. Formally, an automorphism of a graph is a permutation of the vertex set , such that the pair of vertices form an edge if and only if the pair also form an edge. That is, it is a graph isomorphism from to itself. Automorphisms may be defined in this way both for directed graphs and for undirected graphs. The composition of two automorphisms is another automorphism, and the set of automorphisms of a given graph, under the composition operation, forms a group, the automorphism group of the graph. In the opposite direction, by Frucht's theorem, all groups can be represented as the automorphism group of a connected graph – indeed, of a cubic graph. Computational complexity Constructing the automorphism group is at least as difficult (in terms of its computational complexity) as solving the graph is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |