|
Alfred Makower
Alfred Jacques Makower (9 May 1876 in London – 1 February 1941) was electrical engineer and community activist. He was head of the Electrical Engineering Department of Chelsea Polytechnic, South-Western Polytechnic. Alfred was the son of a German silk merchant. He attended University College School from 1884, the University College itself in 1894, then Trinity College, Cambridge, in 1895. Here he took the Mathematical Tripos, before moving on to the Technische Hochschule in Charlottenburg (now Technische Universität Berlin), in 1898. Then in 1900 he was given a job by Union-Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft (UEG), a subsidiary of the Thomson-Houston Electric Company. He then returned to England to work for British Thomson-Houston Company in 1902. In 1904 he was appointed head of the Electrical Engineering Department of South-Western Polytechnic. In 1913 he became a founding director Mossay and Co., a company established by Paul Mossay, along with A. Berkeley and Alfred Mays-Smith. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
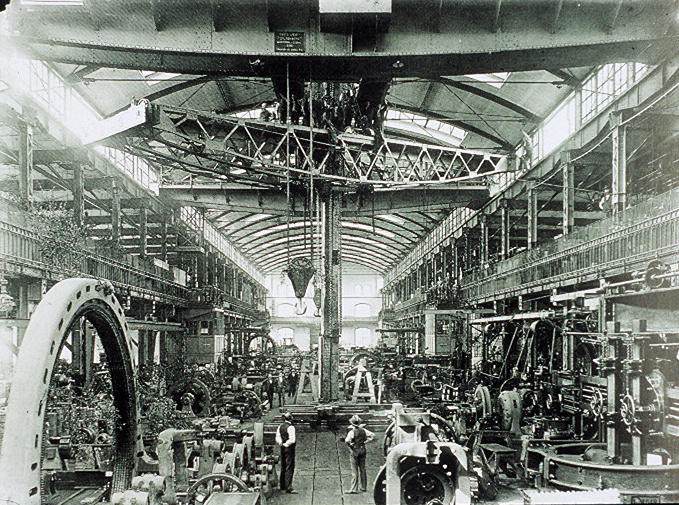
AEG Turbinenfabrik Huttenstrasse Turbinenhalle Foto Um 1900 Vogt Arnold 92526368
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AG (AEG; ) was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in Berlin as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität'' in 1883 by Emil Rathenau. During the Second World War, AEG worked with the Nazi Party and benefited from forced labour from concentration camps. After World War II, its headquarters moved to Frankfurt am Main. In 1967, AEG joined with its subsidiary Telefunken, Telefunken AG, creating ''Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AEG-Telefunken''. In 1985, Daimler-Benz purchased the ''AEG-Telefunken Aktiengesellschaft'' (which was renamed to ''AEG Aktiengesellschaft'') and wholly integrated the company in 1996 into Daimler-Benz AG (1998: Daimler AG, DaimlerChrysler). The remains of AEG became part of Adtranz (later Bombardier Transportation) and DaimlerChrysler Aerospace, Deutsche Aerospace (1998: DASA, today part of Airbus, Airbus SE). After acquiring the AEG household subsidiary AEG Hausgeräte GmbH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsidiary
A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company or holding company. Two or more subsidiaries that either belong to the same parent company or having a same management being substantially controlled by same entity/group are called sister companies. The subsidiary can be a company (usually with limited liability) and may be a government- or state-owned enterprise. They are a common feature of modern business life, and most multinational corporations organize their operations in this way. Examples of holding companies are Berkshire Hathaway, Jefferies Financial Group, The Walt Disney Company, Warner Bros. Discovery, or Citigroup; as well as more focused companies such as IBM, Xerox, and Microsoft. These, and others, organize their businesses into national and functional subsidiaries, often with multiple levels of subsidiaries. Details Subsidiaries are separate, distinct legal entities f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1941 Deaths
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January–August – 10,072 men, women and children with mental and physical disabilities are asphyxiated with carbon monoxide in a gas chamber, at Hadamar Euthanasia Centre in Germany, in the first phase of mass killings under the Action T4 program here. * January 1 – Thailand's Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram decrees January 1 as the official start of the Thai solar calendar new year (thus the previous year that began April 1 had only 9 months). * January 3 – A decree (''Normalschrifterlass'') promulgated in Germany by Martin Bormann, on behalf of Adolf Hitler, requires replacement of blackletter typefaces by Antiqua. * January 4 – The short subject ''Elmer's Pet Rabbit'' is released, marking the second appearance of Bugs Bunny, and also the first to have his name on a title card. * January 5 – WWII: Battle of Bardia in Libya: Australian and British troops de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1876 Births
Events January–March * January 1 ** The Reichsbank opens in Berlin. ** The Bass Brewery Red Triangle becomes the world's first registered trademark symbol. * February 2 – The National League of Professional Base Ball Clubs is formed at a meeting in Chicago; it replaces the National Association of Professional Base Ball Players. Morgan Bulkeley of the Hartford Dark Blues is selected as the league's first president. * February 2 – Third Carlist War – Battle of Montejurra: The new commander General Fernando Primo de Rivera marches on the remaining Carlist stronghold at Estella, where he meets a force of about 1,600 men under General Carlos Calderón, at nearby Montejurra. After a courageous and costly defence, Calderón is forced to withdraw. * February 14 – Alexander Graham Bell applies for a patent for the telephone, as does Elisha Gray. * February 19 – Third Carlist War: Government troops under General Primo de Rivera drive throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Board Of Guardians (United Kingdom)
The Board of Guardians for the Relief of the Jewish Poor or, as it is most generally known, the Jewish Board of Guardians, was a charity established by the upper class Jewish community in the East End of London in 1859. The board sought to provide relief for Jewish immigrants and soon became the central provider of relief for the Jewish poor in London. After an amalgamation with other charities in the 1990s, the Jewish Board of Guardians became Jewish Care, an organization that still exists today. Early history and foundation The Jewish Board of Guardians was a charity established in the East End of London by members of the Jewish community in 1859. The situation of the Jewish poor in London was increasingly problematic by the late 19th century. Christian missionaries and conversionists targeted the Jewish poor, which became a concern for their co-religionists. Members of the Jewish community deemed existing methods of relief for the Jewish poor in London as insufficient. The Board ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Mays-Smith
Sir Alfred Samuel Mays-Smith was an English car manufacturer. From 1920 to 1922 he was chairman of the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders. In the 1922 New Year Honours, Mays-Smith was knighted in recognition for important services to the Disposal and Liquidation Commission. In 1913 Mays-Smith was a director of Mossay and Co. alongside Alfred Makower, Paul Mossay Paul Alphonse Hubert Mossay (1877- 25 June 1963, Knutsford) was a Belgian electrical engineer involved in the development of electric vehicles. Mossay attended grammar school in Verviers and then went to University of Liège, where he gained a deg ... and A. Berkeley. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Mays-Smith, Alfred English industrialists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Mossay
Paul Alphonse Hubert Mossay (1877- 25 June 1963, Knutsford) was a Belgian electrical engineer involved in the development of electric vehicles. Mossay attended grammar school in Verviers and then went to University of Liège, where he gained a degree in Electrical Engineering. Mossay worked for British Thomson-Houston from 1902 until 1906. Then he worked for British Westinghouse before moving on to North German Automobile and Engine in Bremen in 1907. Here he was responsible for designing both the engines and the electric vehicles themselves. He then returned to Belgium, where he worked for Ateliers Germain in Monceau-sur-Sambre on petrol powered vehicles. However, he then went back to England and established Mossay and Co. as a consultancy company which worked with Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies Ransomes, Sims and Jefferies Limited was a major British agricultural machinery maker also producing a wide range of general engineering products in Ipswich, Suffolk including traction engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Thomson-Houston
British Thomson-Houston (BTH) was a British engineering and heavy industrial company, based at Rugby, Warwickshire, England, and founded as a subsidiary of the General Electric Company (GE) of Schenectady, New York, United States. They were known primarily for their electrical systems and steam turbines. BTH was taken into British ownership and amalgamated with the similar Metropolitan-Vickers company in 1928 to form Associated Electrical Industries (AEI), but the two brand identities were maintained until 1960. The holding company, AEI, later merged with GEC. In the 1960s AEI's apprenticeships were highly thought-of, both by the apprentices themselves and by their future employers, because they gave the participants valuable experience in the design, production and overall industrial management of a very wide range of electrical products. Over a hundred of the apprentices - who came to Rugby from all over the UK, and a few from abroad - lodged in the nearby Apprentices' Host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson-Houston Electric Company
The Thomson-Houston Electric Company was a manufacturing company which was one of the precursors of the General Electric company. History The Thomson-Houston Electric Company was formed in 1882 in the United States when a group of Lynn, Massachusetts investors led by Charles A. Coffin bought out Elihu Thomson and Edwin Houston's American Electric Company from their New Britain, Connecticut, investors. The company moved its operations to a new building on Western Ave. in Lynn, Massachusetts, because many of the investors were shoe manufacturers from Lynn. Elihu Thomson Papers at the American Philosophical Society Charles A. Coffin led the company and organized its finances, marketing, and sales operations. Elwin W. Rice organized the manufacturing facilities, and Elihu Thomson ran the Model Room which was a precursor to the industrial research lab. With their leadership, the company grew into an enterprise with sales of and 4000 employees by 1892. In 1884 Thomson-Houston I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union-Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft
Union-Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft (UEG) was a German subsidiary of the American Thomson-Houston Electric Company. The subsidiary was established to represent the parent company's interests in Germany, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Russia and Turkey."Aus sechs wird eins" in: ''Straßenbahn Magazin'' 9/2019, p. 60 ff. The company was founded in 1882 and existed as an independent company until it was absorbed by the AEG on February 27, 1904. Work completed In the twelve years between 1892 and 1904, the UEG built a further 2400 kilometers of electric railways, principally in Europe, and delivered 5285 tramcars to over seventy tram companies. These included: * 1892 Bremen * 1894 Brussels, Gotha * 1895 Munich * 1896 Liège, Cairo * 1897 Aachen, Bergen * 1899 Batavia Batavia may refer to: Historical places * Batavia (region), a land inhabited by the Batavian people during the Roman Empire, today part of the Netherlands * Batavia, Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |