|
Alexander Duncan (army Officer)
General Alexander Duncan (1780–1859) was a Scottish officer of the East India Company army in Bengal. Early life Alexander Duncan was the third son of the physician Andrew Duncan, the elder. The family lived on Bristo Street in Edinburgh's South Side. When his father got the position as Professor of Medicine at Edinburgh University the family moved to Adam Square. Alexander attended the Edinburgh High School a short distance away to the east. He arrived in India as a cadet in 1795, and served there in the East India Company's forces until 1840, when he returned to the United Kingdom with the rank of Major-General. Military service in India In 1800 Duncan served in Awadh, and then was in the Doab of the Yamuna, in actions at Sasni and Bijai Garh. He took part in the Second Anglo-Maratha War, being present at the Battle of Laswari, and was promoted to Captain in 1805. Duncan was brigade major at Fatehgarh from 1806. In the Bundelkhand Agency, he was on active service at Kalinja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sohagpur
Sohagpur is a town and a nagar panchayat in Hoshangabad district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is one of the subdivisions and development blocks in Hoshangabad district. Sohagpur is also one of the legislative constituencies of Madhya Pradesh. Sohagpur is famour for its Betel culture, and an enormous quantity of betel is exported from here. History Sohagpur is also known as the capital of Gondvana Princely state ruled under Nawab Kavi Uz Zafar Alvi in British India. The town gets its name from Suhagpur-Sobhagyapur-Shonitpur. In ''Dvapara Yuga'', it was the capital of the kingdom ruled by Banasura, the demon king who was a devotee of Shiva. He dueled with Lord Krishna and was killed and attained moksha. Every year, the famous Mahashivratri mela is organized here with great pomp and show. Geography Sohagpur is located at . It has an average elevation of 323 metres (1059 feet). The area is generally flat terrain and full of natural sites like Madhai (मढ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gattonside House
Gattonside is a small village in the Scottish Borders. It is located north of Melrose, on the north side of the River Tweed. In 1143, the lands of Gattonside were granted to the monks of Melrose Abbey by King David I. Gattonside was the home of modernist architect Peter Womersley (1923–1993), whose self-designed house, The Rig (1956), is now a Category B listed building. The village is linked to Melrose, on the opposite side of the river, by the 19th-century Gattonside Suspension Bridge. Built in 1826, the bridge was repaired in 1992, and is protected as a Category B listed building. The plantation owner, Robert Waugh of Harmony Hall was a shareholder who on his death in 1832 left his shares to the poor of Melrose. Gattonside House Gattonside House was originally built c.1810. James Brown (died 1816), a coffee planter in Jamaica who also owned the Bryan's Hill estate at the end of his life, lived there for some years to his death. It was then sold by his sons, James Mellor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
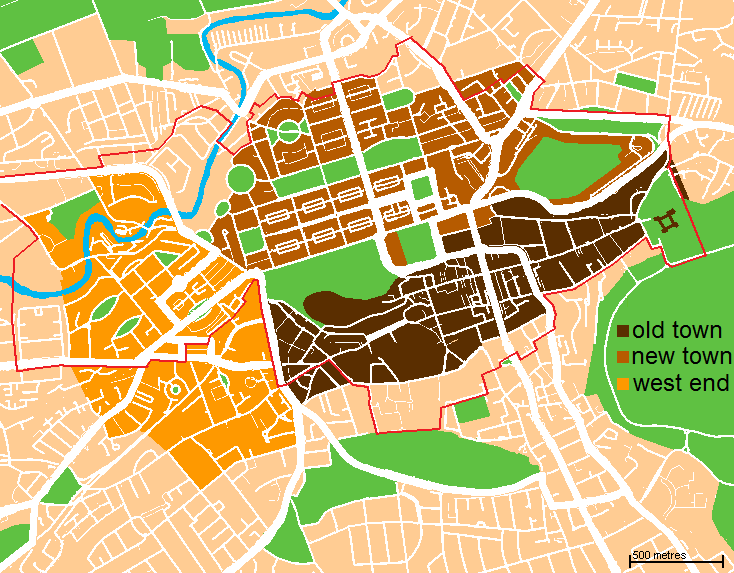
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab to the north. It shares International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province. The economy of Sindh is the second-largest in Pakistan after the province of Punjab; its provincial capital of Karachi is the most populous city in the country as well as its main financial hub. Sindh is home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolan Pass
Bolān Pass ( ur, ) is a valley and a natural gateway, through the Toba Kakar range in Balochistan province of Pakistan, south of the Afghanistan border. The pass is an stretch of the Bolan river valley from Rindli in the south to Darwāza near Kolpur in the north. It is made up of a number of narrow gorges and stretches.Bolān Pass ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' 4 October 2014. It connects with by road and railway. Strategically located, traders, invaders, and nomadic tribes have also used it as a gateway to and from South Asia. The Bolān Pass is an important pass on the Baluch frontier, connecting |
Firozpur
Firozpur, also known as Ferozepur, is a city on the banks of the Sutlej River in Firozpur District, Punjab, India. After the partition of India in 1947, it became a border town on the India–Pakistan border with memorials to soldiers who died fighting for India. History The city of Firozpur was founded by Firuz Shah Tughlaq , a ruler of the Tughluq dynasty, who reigned over the Sultanate of Delhi from 1351 to 1388. It is located on the banks of the Sutlej River on the India–Pakistan border. The nearby Firozpur Cantonment is a major cantonment of the country. British rule was first established in 1835, when, on the failure of heirs to the Sikh family who possessed it, a small escheat to the British government was formed, and the district was gradually formed around this nucleus. The strategic importance of Ferozepur (as it was spelled under the British) was at this time very great, and in 1839 it was the outpost of British India in the direction of the Sikh power. It acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Keane, 1st Baron Keane
Lieutenant-General John Keane, 1st Baron Keane (6 February 1781 – 24 August 1844) was an Irish soldier in the British Army. Early life John Keane was born in Waterford, Ireland, on 6 February 1781; he was the second son of John Keane and Sarah Keiley. Keane's father would be created a baronet in 1801. He was the younger brother of the future Lieutenant-Colonel Sir Richard Keane, 2nd Baronet and the elder of Colonel Edward Keane. Military service French Revolutionary Wars While there is some confusion as to when this occurred, Keane most likely joined the British Army on 11 October 1794, becoming an ensign in the 122nd Regiment of Foot. He was quickly promoted, becoming a lieutenant on 30 October. With the speed of Keane's promotions, it is likely that he never actually reported for duty with the 122nd. His father then purchased his promotion to captain in the 124th Regiment of Foot on 12 November. The 124th was disbanded in May 1795 but some time before this Keane tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willoughby Cotton
Lieutenant General Sir Willoughby Cotton (1783 – 4 May 1860) was a British soldier. Family Willoughby Cotton was born in 1783, to Vice-Admiral Rowland Cotton and Elizabeth Aston. They also had a daughter, Sydney Arabella Cotton. Rowland Cotton was from a well-established Chester family, was the second son of Sir Lynch Cotton, 4th Baronet, while Elizabeth was the eldest daughter of Sir Willoughby Aston, 5th Baronet Aston, of Aston, Chester. Cotton married Lady Augusta Maria Coventry on 16 May 1806 in Marylebone, London. They had three children together, Augusta Mary Cotton, Willoughby Cotton and Maj.-Gen. Corbet Cotton. School years Willoughby Cotton entered Rugby School at the age of 12 in 1795. Cotton, aged 14, was a ringleader in the " Great Rebellion" of November 1797. Aggrieved by the attitude of the Head Master, Dr. Henry Ingles (1794–1806), following the breaking of a window, students blew his classroom door off with gunpowder and followed this by burning desks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Fane (British Army Officer)
General Sir Henry Fane (26 November 177824 March 1840) commanded brigades under Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington during several battles during the Peninsular War, and served both as a member of Parliament and Commander-in-Chief of India. Origins He was the eldest son of Hon. Henry Fane (d.1802), of Fulbeck Hall, Lincolnshire, younger son of Thomas Fane, 8th Earl of Westmorland. Military career Fane joined the 6th Dragoon Guards as a cornet in 1792 and served as '' aide-de-camp'' to the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, John Fane, before obtaining a Lieutenancy in the 55th Regiment of Foot. He was promoted to Captain-lieutenant in the 4th Dragoons in 1795; to Major the following year and to Lieutenant-colonel in 1797, subsequently serving throughout the rebellion that year. On 1January 1805, following his removal to the Lieutenant-colonency of the 1st King's Dragoon Guards, he was appointed ''aide-de-camp'' to King George III, which made him a Colonel in the army. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War ( fa, جنگ اول افغان و انگلیس) was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking sides in a war of succession, succession dispute between emir Dost Mohammad Khan (Emir of Afghanistan), Dost Mohammad (Barakzai dynasty, Barakzai) and former emir Shah Shujah Durrani, Shah Shujah (Durrani dynasty, Durrani), whom they reinstalled upon occupying Kabul in August 1839. The main British Indian force occupied Kabul and endured harsh winters. The force and its camp followers were almost completely massacred during the 1842 retreat from Kabul. The British then sent an Kabul Expedition (1842), ''Army of Retribution'' to Kabul to avenge the destruction of the previous forces. After recovering prisoners, they left Afghanistan by the end of the year. Dost Mohammed returned from exile in India to resume his rule. It was one of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Jat Light Infantry
The6th Jat Light Infantry were an infantry regiment of the Bengal Army, later of the united British Indian Army. They could trace their origins to 1803, when they were the 1st Battalion, 22nd Bengal Native Infantry. Over the years they were known by a number of different names the 43rd Bengal Native Infantry 1824–1842, the 43rd Bengal Native (Light) Infantry 1842–1861, the 6th Bengal Native (Light) Infantry 1861– after the Kitchener reforms of the Indian Army the 6th Jat Bengal (Light) Infantry. The regiment was involved in the First Anglo-Afghan War, the First Anglo-Sikh War, the Second Anglo-Afghan War, the Boxer Rebellion and World War I. After World War I the Indian Government reformed the army moving from single battalion regiments to multi battalion regiments.Sumner, p.15 The 6th Jat Light Infantry became the new 1st Battalion, 9th Jat Regiment. After India gained independence they were one of the regiments allocated to the Indian Army. See also * Jat people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |