|
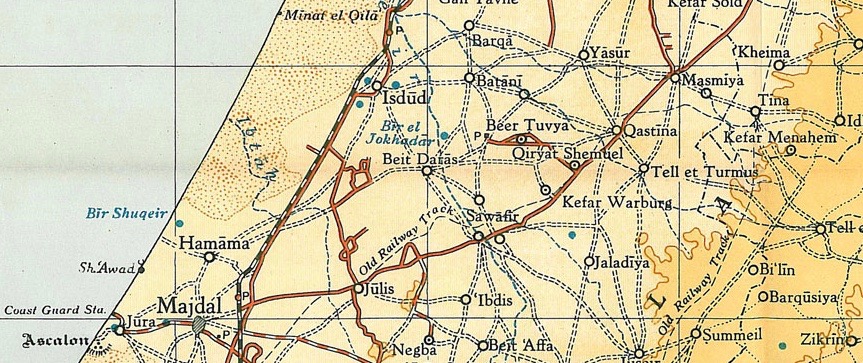
Al-Sawafir Al-Shamaliyya
Al-Sawafir al-Shamaliyya ( ar, السوافير الشمالية) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza situated along the southern coastal plain of Palestine above sea level. It was one of three namesake villages, alongside Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya and Al-Sawafir al-Gharbiyya. It had a population of 680 in 1945. Al-Sawafir al-Shamaliyya was depopulated in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.Khalidi, 1992, pp. 133-134. History The village was possibly located at the site of the biblical Shafir, mentioned by Eusibius as a "beautiful town" between Ascalon and Bayt Jibrin. Most modern scholars, however, located Shafir at Khirbat al-Qawm. The Crusader name of the village was Zeophir. They recorded that it was the property of Bishop of Jerusalem in the early 12th century. However, it is not clear which village of three Sawafirs these records pertain to. Ottoman era Incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517 with the rest of Palestine, Al-Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Further complicating the issue was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koubbeh
A ''qubba'' ( ar, قُبَّة, translit=qubba(t), pl. ''qubāb''), also transliterated as ḳubba, kubbet and koubba, is a cupola or domed structure, typically a tomb or shrine in Islamic architecture. In many regions, such as North Africa, the term ''qubba'' commonly the tomb of a local ''wali'' (local Muslim saint) or marabout, and usually consists of a chamber covered by a dome or pyramidal cupola. Etymology The Arabic word qubba was originally used to mean a tent of hides, or generally the assembly of a material such as cloth into a circle. It's likely that this original meaning was extended to denote domed buildings after the latter had developed in Islamic architecture. It is now also used generally for tomb sites if they are places of pilgrimage. In Turkish and Persian the word ''kümbet'', ''kumbad'', or ''gunbād'' has a similar meaning for dome or domed tomb. Historical development A well-known example of an Islamic domed shrine is the Dome of the Rock, known in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. Marble is commonly used for Marble sculpture, sculpture and as a building material. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shining stone", perhaps from the verb (), "to flash, sparkle, gleam"; Robert S. P. Beekes, R. S. P. Beekes has suggested that a "Pre-Greek origin is probable". This Stem (linguistics), stem is also the ancestor of the English language, English word "marmoreal," meaning "marble-like." While the English term "marble" resembles the French language, French , most other European languages (with words like "marmoreal") more closely resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term ''column'' applies especially to a large round support (the shaft of the column) with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a ''post''. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called ''piers''. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces. Other compression members are often termed "columns" because of the similar stress conditions. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest. In architecture, "column" refers to such a structural element that also has certain proportional and decorative featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Minor, North Africa, Lebanon, Syria and Palestine. Biography Guérin, a devout Catholic, graduated from the ''École normale supérieure'' in Paris in 1840. After graduation, he began working as a teacher of rhetoric and member of faculty in various colleges and high schools in France, then in Algeria in 1850, and 1852 he became a member of the French School of Athens. While exploring Samos, he identified the spring that feeds the Tunnel of Eupalinos and the beginnings of the channel. His doctoral thesis of 1856 dealt with the coastal region of Palestine, from Khan Yunis to Mount Carmel. With the financial help of Honoré Théodoric d'Albert de Luynes he was able to explore Greece and its islands, Asia Minor, Egypt, Nubia, Tunisia, and the Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waqf
A waqf ( ar, وَقْف; ), also known as hubous () or '' mortmain'' property is an inalienable charitable endowment under Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot of land or other assets for Muslim religious or charitable purposes with no intention of reclaiming the assets. A charitable trust may hold the donated assets. The person making such dedication is known as a ''waqif'' (a donor). In Ottoman Turkish law, and later under the British Mandate of Palestine, a ''waqf'' was defined as usufruct state land (or property) from which the state revenues are assured to pious foundations. Although the ''waqf'' system depended on several hadiths and presented elements similar to practices from pre-Islamic cultures, it seems that the specific full-fledged Islamic legal form of endowment called ''waqf'' dates from the 9th century AD (see below). Terminology In Sunni jurisprudence, ''waqf'', also spelled ''wakf'' ( ar, وَقْف; plural , ''awqāf''; tr, vak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akçe
The ''akçe'' or ''akça'' (also spelled ''akche'', ''akcheh''; ota, آقچه; ) refers to a silver coin which was the chief monetary unit of the Ottoman Empire. The word itself evolved from the word "silver or silver money", this word is derived from the Turkish ''ak'' ("white") and the diminutive suffix -''ça''. Three ''akçe''s were equal to one ''para''. One-hundred and twenty ''akçe''s equalled one ''kuruş''. Later after 1687 the ''kuruş'' became the main unit of account, replacing the ''akçe''. In 1843, the silver ''kuruş'' was joined by the gold lira in a bimetallic system. Its weight fluctuated, one source estimates it is between 1.15 and 1.18 grams. The name ''akçe'' originally referred to a silver coin but later the meaning changed and it became a synonym for money. The mint in Novo Brdo, a fortified mining town in the Serbian Despotate rich with gold and silver mines, began to strike ''akçe'' in 1441 when it was captured by the Ottoman forces for the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Sawafir Al-Shamaliyya
Al-Sawafir al-Shamaliyya ( ar, السوافير الشمالية) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza situated along the southern coastal plain of Palestine above sea level. It was one of three namesake villages, alongside Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya and Al-Sawafir al-Gharbiyya. It had a population of 680 in 1945. Al-Sawafir al-Shamaliyya was depopulated in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.Khalidi, 1992, pp. 133-134. History The village was possibly located at the site of the biblical Shafir, mentioned by Eusibius as a "beautiful town" between Ascalon and Bayt Jibrin. Most modern scholars, however, located Shafir at Khirbat al-Qawm. The Crusader name of the village was Zeophir. They recorded that it was the property of Bishop of Jerusalem in the early 12th century. However, it is not clear which village of three Sawafirs these records pertain to. Ottoman era Incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1517 with the rest of Palestine, Al-Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liwa Of Gaza
Gaza Sanjak ( ar, سنجق غزة) was a sanjak of the Damascus Eyalet, Ottoman Empire centered in Gaza. In the 16th century it was divided into ''nawahi'' (singular: ''nahiya''; third-level subdivisions): Gaza in the south and Ramla in the north. List of settlements In the 1596- daftar, the sanjak contained the following nahiyah and villages/town Gaza Nahiyah *Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya, Bayt Tima, Hamama,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 142 Al-Tina, Yibna, Isdud, Arab Suqrir,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 143 Deir al-Balah, Burayr, Jabalia, Beit Lahia, Al-Majdal, Askalan, Bayt 'Affa, Najd, Ni'ilya,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 144 Bayt Jirja, Hiribya, Qatra, Iraq Suwaydan, Kawkaba, Beit Jimal Monastery, Al-Batani al-Sharqi,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 145 Al-Qubayba, Al-Faluja, Bayt Daras, Al-Maghar,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 146 Hatta, Jusayr, Zikrin, Zayta, Barqa, Beit Hanoun, Dayr Sunayd, Simsim,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |