|
Ahes
Dahut, also called Ahes, is a princess in Breton legend and literature, associated with the legend of the drowned city of Ys. Etymology Amy Varin suggests that Dahut was given the name Ahes due to confusion with "alc'huez" (key). Legend of Ys Dating to the 15th century, the earliest mentions of Ys and its king, Gradlon, do not mention Gradlon's daughter Dahut, and the king himself is to blame for the destruction of the city. Dahut was first mentioned in the third edition of Albert Le Grand's ''Vie des Saincts de la Bretagne Armorique'' (1680). In this early version, the "shameless" Dahut intends to kill her father and steals the key which symbolizes his royalty. Her wickedness causes a storm which floods Ys, and she dies in the destruction. In most retellings, the city of Ys is protected from floods by a dike, with King Gradlon possessing the keys to its gate. His daughter, Dahut, is a wicked and lustful young woman. In some versions she has many lovers, whom she murders, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgan Le Fay
Morgan le Fay (, meaning 'Morgan the Fairy'), alternatively known as Morgan ''n''a, Morgain ''a/e Morg ''a''ne, Morgant ''e Morge ''i''n, and Morgue ''inamong other names and spellings ( cy, Morgên y Dylwythen Deg, kw, Morgen an Spyrys), is a powerful and ambiguous enchantress from the legend of King Arthur, in which most often she and he are siblings. Early appearances of Morgan in Arthurian literature do not elaborate her character beyond her role as a goddess, a fay, a witch, or a sorceress, generally benevolent and connected to Arthur as his magical saviour and protector. Her prominence increased as legends developed over time, as did her moral ambivalence, and in some texts there is an evolutionary transformation of her to an antagonist, particularly as portrayed in cyclical prose such as the ''Lancelot-Grail'' and the Post-Vulgate Cycle. A significant aspect in many of Morgan's medieval and later iterations is the unpredictable duality of her nature, with potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgen (mythological Creature)
Morgens, morgans, or mari-morgans are Welsh and Breton water spirits that drown men. Etymology The name may derive from Mori-genos or Mori-gena, meaning "sea-born. The name has also been rendered as Muri-gena or Murigen. The name may also be cognate with the Irish ''Muirgen'', an alternate name of Lí Ban, a princess who was transformed into a mermaid when her city was flooded. The Cornish term for a mermaid is usually ''Morvoren'', as in the Mermaid of Zennor. Welsh and English legend The oldest occurrence of the name is in Geoffrey of Monmouth's ''Vita Merlini'', where the ruler of Avalon is referred to as "Morgen". As such, the origin of Morgan le Fay may be connected to these Breton myths. The medievalist Lucy Allen Paton argues against this, stating that the Welsh name Morgen was pronounced "Morien" in the twelfth century, and that aside from living on an island, Morgan le Fay was not associated with the sea until later literature. Controversial English folklorist Ruth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carhaix-Plouguer
Carhaix-Plouguer (; br, Karaez-Plougêr ), commonly known as just Carhaix (), is a commune in the French department of Finistère, region of Brittany, France.Commune de Carhaix-Plouguer (29024) INSEE The commune was created in 1957 by the merger of the former communes Carhaix and Plouguer. Geography 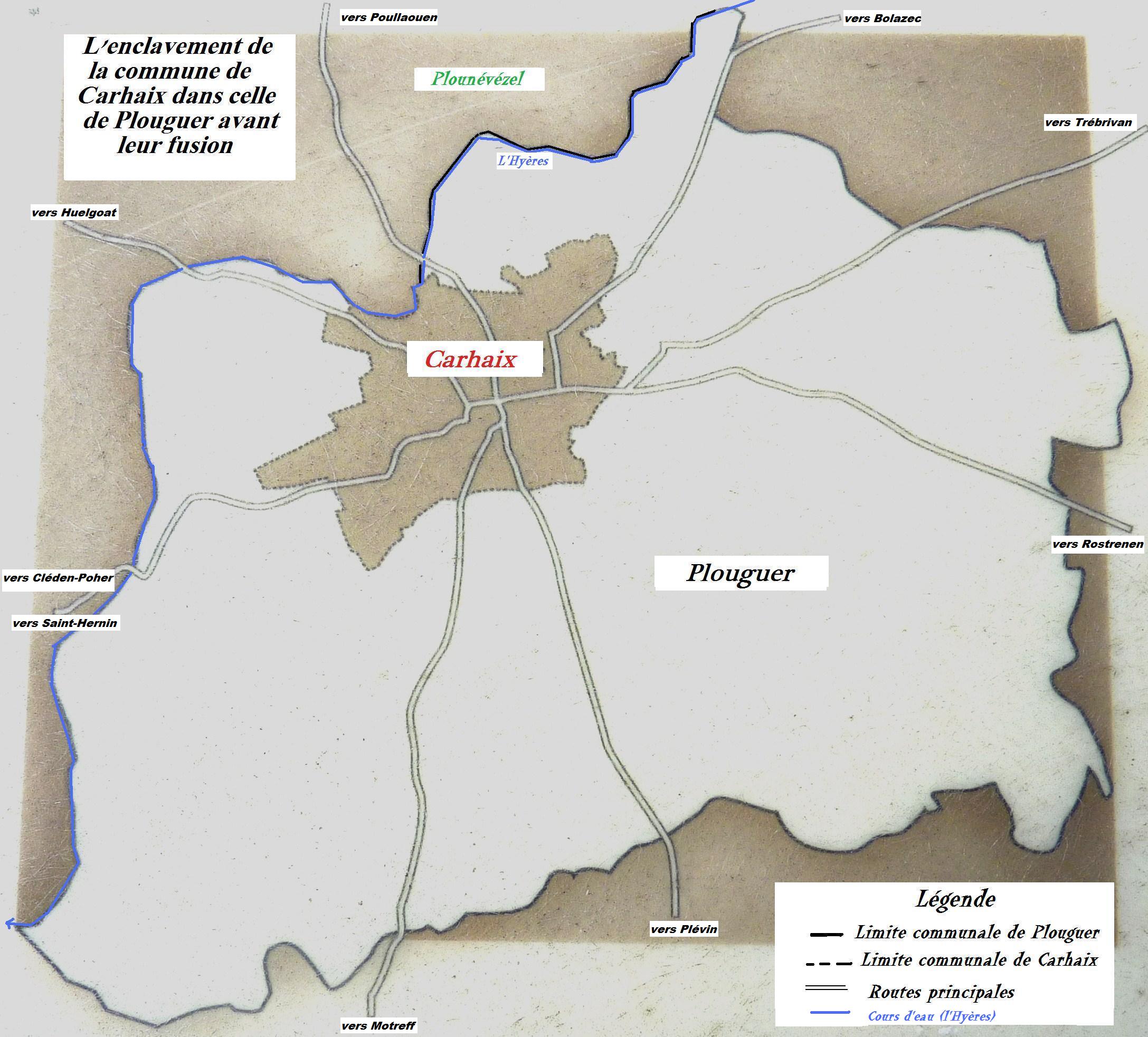 Carhaix is located in the Poher, an important territory of Brittany, sandwiched between the Arrée Mountains to ...
Carhaix is located in the Poher, an important territory of Brittany, sandwiched between the Arrée Mountains to ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictional Characters Who Use Magic
Fiction is any creative work, chiefly any narrative work, portraying individuals, events, or places that are imaginary, or in ways that are imaginary. Fictional portrayals are thus inconsistent with history, fact, or plausibility. In a traditional narrow sense, "fiction" refers to written narratives in prose often referring specifically to novels, novellas, and short stories. More broadly, however, fiction encompasses imaginary narratives expressed in any medium, including not just writings but also live theatrical performances, films, television programs, radio dramas, comics, role-playing games, and video games. Definition Typically, the fictionality of a work is publicly marketed and so the audience expects the work to deviate in some ways from the real world rather than presenting, for instance, only factually accurate portrayals or characters who are actual people. Because fiction is generally understood to not fully adhere to the real world, the themes and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breton Mythology And Folklore
Breton most often refers to: *anything associated with Brittany, and generally **Breton people **Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany **Breton (horse), a breed ** Galette or Breton galette or crêpe, a thin buckwheat flour pancake popular in Brittany ** Breton (hat) headgear with upturned brim, said to be based on designs once worn by Breton agricultural workers Breton may also refer to: *Breton (surname) *Breton (band), a South London-based music group *Breton (Elder Scrolls), a race in ''The Elder Scrolls'' game series who are descendants of men and Elves *Breton, an alternative name for these wine grapes: **Cabernet Franc **Béquignol noir *Breton (company) *Breton, Alberta, village in Alberta, Canada See also *''Bretonne'', 2010 album by Nolwenn Leroy *Briton (other) *Brereton (other) *Bretton (other) Bretton may refer to: Places England *Bretton, Derbyshire *Bretton, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruonto
Peruonto is an Italian literary fairy tale written by Giambattista Basile in his 1634 work, the ''Pentamerone''. Synopsis A widow named Ceccarella had a stupid son named Peruonto, as ugly as an ogre. One day, she sent him to gather wood. He saw three men sleeping in the sunlight and made them a shelter of branches. They woke, and being the sons of a fairy, gave him a charm that whatever he asked for would be done. As he was carrying the wood back, he wished that it would carry him, and he rode it back like a horse. The king's daughter Vastolla, who never laughed, saw it and burst out laughing. Peruonto wished she would marry him and he would cure her of her laughing. A marriage was arranged for Vastolla with a prince, but Vastolla refused, because she would marry only the man who rode the wood. The king proposed putting her to death. His councilors advised him to go after the man instead. The king had a banquet with all the nobles and lords, thinking Vastolla would betray whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lí Ban (mermaid)
Lí Ban or Liban (, hence 'paragon of women'), in the legend surrounding the formation of Lough Neagh, was a woman turned mermaid who inhabited the area before the great lake gushed up on dry land. Her family was drowned, but she survived in an underwater chamber in the lake for a year, after which she was transformed into a being who was half-human, half-salmon. In her mermaid form, she was spotted by the ship carrying a messenger sent by St. Comgall to Rome. She promised to meet at the seaport inlet of Inbhear nOllarbha (Larne Lough) in Ireland after one year, and was captured in a fishnet. There she was baptised by Comgall, and given the Christened name Muirgein ("sea-born") or Muirgeilt ("sea-wander"). She appears canonised as St. Muirgen in genealogies of Irish saints, her feast day assigned to 27 January. The mermaid figure may ultimately derive from another Lí Ban, Sister of Fand, in Irish mythology. Legend Liban, a mermaid (''muirgelt'') who was the daughter of Eoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantre'r Gwaelod
, also known as or ( en, The Lowland Hundred), is a legendary ancient sunken kingdom said to have occupied a tract of fertile land lying between Ramsey Island and Bardsey Island in what is now Cardigan Bay to the west of Wales. It has been described as a "Welsh Atlantis" and has featured in folklore, literature, and song. The legend Cantre'r Gwaelod was an area of land which, according to legend, was located in an area west of present-day Wales which is now under the waters of Cardigan Bay. Accounts variously suggest the tract of land extended from Bardsey Island to Cardigan or as far south as Ramsey Island. Legends of the land suggest that it may have extended 20 miles west of the present coast. Rachel Bromwich questions this identification, saying that "There is no certainty, however, that in twelfth century tradition Maes Gwyddneu did represent the submerged land in Cardigan Bay." She also links Gwyddno Garanhir with the Hen Ogledd, not Wales. There are several ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nolwenn Leroy
Nolwenn Le Magueresse (; born 28 September 1982), known by her stage name Nolwenn Leroy (), is a French singer-songwriter, musician and actress. Originally classically trained (violin and opera singing), she rose to fame after winning the second season of the French television music competition '' Star Academy'' in 2002. She has since recorded eight studio albums and scored two number one singles, " Cassé" and "Nolwenn Ohwo!", on the French charts. In 2012, her album '' Bretonne'' was certified two times diamond for sales exceeding one million copies. Leroy is fluent in English, having spent a year in the US as an exchange student. She sings in many languages, including French, Breton, English and Irish. Leroy has received numerous awards and nominations. In January 2015, she was ranked 17th on '' Le Journal du Dimanches 50 Most Loved Celebrities in France, making her the top female singer on the list since December 2012. She was appointed an Officer of the Order of the Arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Of Cornwall
Mark of Cornwall ( la, Marcus, kw, Margh, cy, March, br, Marc'h) was a sixth-century King of Kernow (Cornwall), possibly identical with King Conomor. He is best known for his appearance in Arthurian legend as the uncle of Tristan and the husband of Iseult who engages with Tristan in a secret liaison, giving Mark the epithet "Cuckold King". King Mark In Old Welsh records, Mark is recorded as "March son of Meirchion" of Kernow (Cornwall). He is associated with governing portions of Gwynedd and Glamorgan in Wales. Mark has been identified with Conomor, a king of Domnonea and Kernev (Domnonée and Cornouaille) in Armorica. In his ''Life of St. Pol de Leon'', Wrmonoc of Landévennec refers to a "King Marc whose other name is Quonomorus". Also rendered as ''Cunomorus'', the name means "Hound-of-the-sea".Thomas, Charles (1986). ''Celtic Britain''. London: Thames & Hudson ; p. 70 An inscription on a sixth-century gravestone near the Cornish town of Fowey memorializes (in Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




