|
Agordat
Agordat; also Akordat or Ak'ordat) is a city in Gash-Barka, Eritrea. It was the capital of the former Barka province, which was situated between the present-day Gash-Barka and Anseba regions. History Excavations in Agordat uncovered pottery related to the C-Group (Temehu) pastoral culture, which inhabited the Nile Valley between 2500 and 1500 BC. Sherds akin to those of the Kerma culture, another community that flourished in the Nile Valley around the same period, were also found at other local archaeological sites in the Barka valley belonging to the Gash Group. Agordat was the last major town along the Eritrean Railway to Massawa through Asmara. The line continued on through to Bishia, its terminus. The local economy is reliant on passing traders moving between Asmara and Kessela in Sudan. Overview Agordat lies in the western part of the country on the Barka River. An important market town and it also home to a large mosque. Agordat has many restaurants, as well as a hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
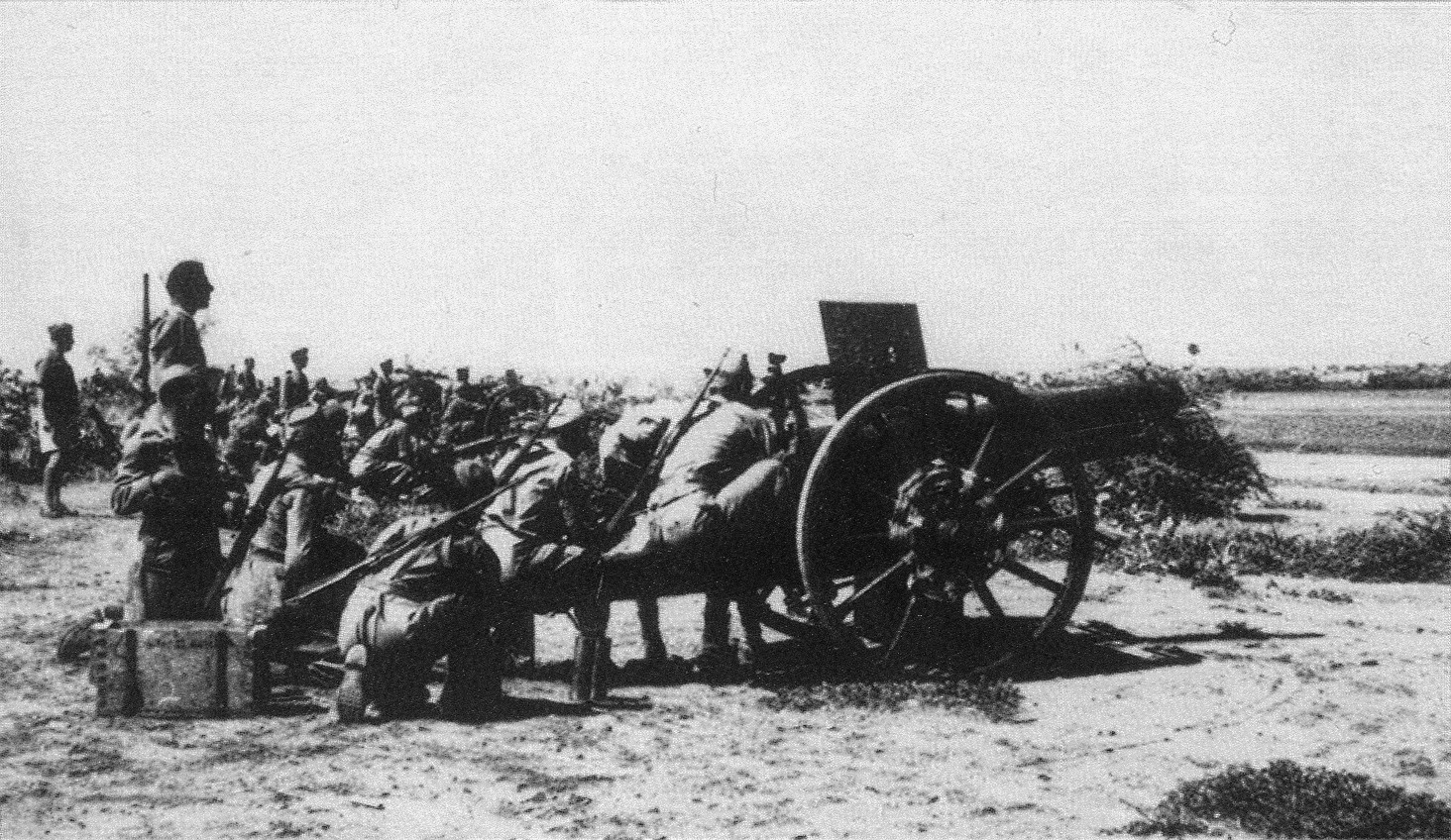
Battle Of Agordat (1941)
The Battle of Agordat was fought near Agordat in Eritrea from 26 to 31 January 1941, by the Kingdom of Italy, Italian army and Royal Corps of Colonial Troops against British, Commonwealth and Indian forces, during the East African Campaign (World War II), East African Campaign of the Second World War. The British had the advantage of breaking Italian codes and cyphers before the offensive and received copious amounts of information from Italian sources on the order of battle and plans of the (Italian Royal Air Force) and the Italian army. After the garrison of Italian and colonial troops at Kassala in Sudan was ordered to withdraw in mid-January, the British offensive into Eritrea due in February 1941 began in mid-January instead. Agordat was an excellent defensive position and the British advance was slowed by delaying actions and mined roads but the attack began on 28 January on the left (northern) flank, which was repulsed. Determined fighting took place on the hills and plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Cruiser Agordat
''Agordat'' was a torpedo cruiser of the Italian ''Regia Marina'' built in the late 1890s. She was the lead ship of the , which had one other member, . The ship, which was armed with twelve guns and two torpedo tubes, was too slow and short-ranged to be able to scout effectively for the fleet, so her career was limited. She saw action during the Italo-Turkish War in 1911–12, where she provided gunfire support to Italian troops in North Africa. She assisted in the occupation of Constantinople in the aftermath of World War I, and in 1919 she was reclassified as a gunboat. In January 1923, ''Agordat'' was sold for scrapping. Design ''Agordat'' was long overall and had a beam of and a draft of . She displaced up to at full load. Her propulsion system consisted of a pair of horizontal triple-expansion steam engines each driving a single screw propeller, with steam supplied by eight Blechynden water-tube boilers. Her engines were rated at and produced a top speed of . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Agordat
The Second Battle of Agordat was fought in late December 1893, between Italian colonial troops and Mahdists from the Sudan. Emir Ahmed Ali campaigned against the Italian forces in eastern Sudan and led about 10–12,000 men east from Kassala. This force encountered 2,400 Italians and their Eritrean askaris at Agordat, west of Asmara, commanded by Colonel Arimondi. Over 1,000 Dervishes, including the Emir, were killed in severe fighting. The outcome of the battle constituted: A year later, Italian colonial forces seized Kassala. Sources {{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 1893 in Sudan 1893 in the Italian Empire Agordat Agordat Agordat Agordat Agordat; also Akordat or Ak'ordat) is a city in Gash-Barka, Eritrea. It was the capital of the former Barka province, which was situated between the present-day Gash-Barka and Anseba regions. History Excavations in Agordat uncovered pottery re ... December 1893 events Italian Eritrea fr:Combat d'Agordat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Agordat
The First Battle of Agordat, the first battle between Italy and Mahdist Sudan, took place on June 27, 1890. Violence began when a force of one-thousand Mahdists attacked tribes that had signed protectorates with the Kingdom of Italy." After that, the Sudanese continued on to the wells at Agordat, where they were met by two companies of Italian-led ascari. The battle that ensued was an Italian victory, with 250 Mahdists being killed. Italian losses were three dead and eight wounded. Author Sean McLachlan blames the Mahdists' "inferior weaponry and fire discipline" for their defeat at Agordat and the upcoming Battle of Serobeti (1892). References {{coord missing, Eritrea 1890 in Sudan 1890 in the Italian Empire Agordat Agordat Agordat Agordat Agordat Agordat; also Akordat or Ak'ordat) is a city in Gash-Barka, Eritrea. It was the capital of the former Barka province, which was situated between the present-day Gash-Barka and Anseba regions. History Excavations in Agordat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eritrean Railway
The Eritrean Railway is the only railway system in Eritrea. It was constructed between 1887 and 1932 during the Italian Eritrea colony and connects the port of Massawa with Asmara. Originally it also connected to Bishia. The line was partly damaged by warfare in subsequent decades, but was rebuilt in the 1990s. Vintage equipment is still used on the line. Main railway line Characteristics The railway was built during Italian Eritrea in order to connect Massawa and Asmara, the main cities of Eritrea. In the 1930s Italian leader Benito Mussolini wanted to reach Kassala in Sudan, but his war to conquer Ethiopia and create the Italian Empire stopped the enlargement to Agordat and Bishia. After damage suffered by the railway during World War II, the section between Massawa and Asmara was dismantled partially and was only rebuilt in the 1990s by the Eritrean authorities. The railway is narrow gauge and is being rebuilt after the devastation wreaked upon it by the war of independen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gash-Barka Region
Gash-Barka ( ti, ጋሽ-ባርካ, it, Regione di Gasc-Barca) is an Regions of Eritrea, administrative region of Eritrea. It is situated in the south-west of the country, bordering the Anseba region to the north, and the Maekel Region, Maekel (Central) and Debub Region, Debub (Southern) regions to the east; the country of Sudan lies to the west and Ethiopia to the south. The capital of Gash-Barka is Barentu, Eritrea, Barentu. Other towns include Agordat (the former capital), Molki, Sebderat and Teseney. As of 2005, the region had a population of 708,800 compared to a population of 625,100 in 2001. The net growth rate was 11.81 per cent. The total area of the province was 33,200 km2 and the density was 21.35 persons per km2., making up roughly one-third of Eritrea. The region is dubbed as the "breadbasket" of the country as it is rich in agriculture. The region is also rich in marble, and other important minerals, including gold. In Ougaro, there are some old mining, mineshaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the south, Sudan in the west, and Djibouti in the southeast. The northeastern and eastern parts of Eritrea have an extensive coastline along the Red Sea. The nation has a total area of approximately , and includes the Dahlak Archipelago and several of the Hanish Islands. Human remains found in Eritrea have been dated to 1 million years old and anthropological research indicates that the area may contain significant records related to the evolution of humans. Contemporary Eritrea is a multi-ethnic country with nine recognised ethnic groups. Nine different languages are spoken by the nine recognised ethnic groups, the most widely spoken language being Tigrinya, the others being Tigre, Saho, Kunama, Nara, Afar, Beja, Bilen and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.70 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's List of African countries by area, third-largest country by area, and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum, secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by Algeria. Its Capital city, capital is Khartoum and its most populated city is Omdurman (part of the metropolitan area of Khar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gash Group
The Gash Group is a neolithic, prehistoric culture that flourished around 3000 to 1800 BC in Eritrea Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ... and the Eastern Sudan. It was followed by the Jebel Mokram Group. The name Gash relates to the river in Eritrea with the Mareb River, same name. Description This culture is mainly defined by its pottery. In the early phase around 2500 BC these are often bowls decorated with a comb pattern. Typical for the middle phase of the culture are black cups. Around 2000 BC bowls and cups are typical with impressed or incised rim bands. Certain pottery vessels also show connections with other cultures, such as with Kerma culture, the C-Group, the Pan-Grave and the Yemeni Bronze age. Finds of Egyptian pottery and faience beads (perhaps made i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barka (Eritrea)
The Provinces of Eritrea existed between Eritrea's incorporation as a colony of Italy until the conversion of the provinces into administrative regions. Overview In Italian Eritrea, the Italian colonial administration had divided the colony into eight provinces (administrative regions) called Akele Guzay, Barka, Denkalia, Hamasien, Sahel, Semhar, Senhit and Serae. These administrative regions relied heavily upon the historical political boundaries in the region, including, but not exclusively, that of local nobility. These Provinces of Eritrea were also used by the Federated Eritrean Government from 1952-1962 and as districts ( awrajja) in Eritrea when it was annexed by Ethiopia from 1962-1991. After independence, the Provisional Government of Eritrea converted the original eight Provinces of Eritrea (from the Italian colonial period) to nine provinces by splitting the Barka province in two (the north known as Barka Province and the south as Gash-Setit Province), while at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Eritrea
The regions of Eritrea are the primary geographical divisions through which Eritrea is administered. Six in total, they include the Central, Anseba, Gash-Barka, Southern, Northern Red Sea and Southern Red Sea regions. At the time of independence in 1993 Eritrea was arranged into ten provinces. These provinces were similar to the nine provinces operating during the colonial period. In 1996, these were consolidated into six regions (''zobas''). Gash-Barka Region was the largest and the most densely populated region and is called the "bread-basket". The People's Front for Democracy and Justice or PFDJ (originally Eritrean People's Liberation Front) rules the country and its regions as a single-party totalitarian government. The regional and local elections are conducted on a periodic basis on a restricted framework. All men and women of any ethnic or religious background are eligible to vote. No parties or groups other than PFDJ are allowed to contest and the elections are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Eritrea
"Eritrea" is an ancient name, associated in the past with its Greek form ''Erythraia'', Ἐρυθραία, and its derived Latin form ''Erythræa''. This name relates to that of the Red Sea, then called the ''Erythræan Sea'', from the Greek for "red", ἐρυθρός, ''erythros''. The Italians created the colony of Eritrea in the 19th century around Asmara, and named it with its current name. After World War II, Eritrea was annexed to Ethiopia. In 1991, the communist Ethiopian government was toppled by TPLFand Eritrean people liberation front are earned their independence. Eritrea officially celebrated its 1st anniversary of independence on May 24, 1994. Prehistory At Buya in Eritrea, one of the oldest hominids representing a possible link between ''Homo erectus'' and an archaic '' Homo sapiens'' was discovered by Eritrean and Italian scientists. Dated to over 1 million years old, it is the oldest skeletal find of its kind and provides a link between hominids and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)