|
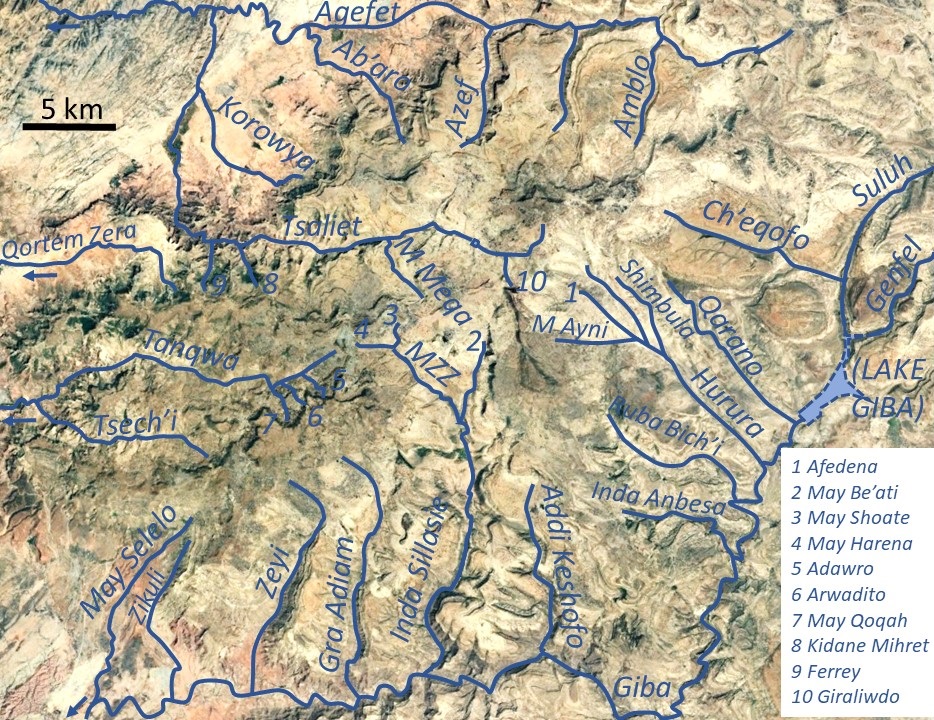
Agefet
Agefet is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Gheralta in northern Ethiopia, it flows westward to empty finally in Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 13 metres per kilometre. At the end of its course, it occupies a sandy pediment. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. Physical conservation structures such as stone bunds and check dams intercept runoff. On many steep slopes, exclosures have been establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agefet Downstream
Agefet is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Hawzen_(woreda)#Gere-alta, Gheralta in northern Ethiopia, it flows westward to empty finally in Wari River, Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 13 metres per kilometre. At the end of its course, it occupies a sandy pediment. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. Physical conservation structures such as Terrace (earthworks) , stone bunds and check dams intercept ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azef River
The Azef River is a river in the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral bedrock river, with an average slope gradient of 63 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanced infiltration, less flooding and better baseflow. Physical con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degua Tembien
Dogu'a Tembien (, "Upper Tembien", sometimes transliterated as Degua Tembien) is a woreda in Tigray Region, Ethiopia. It is named in part after the former province of Tembien. Nowadays, the mountainous district is part of the Southeastern Tigray Zone. The administrative centre of this woreda is Hagere Selam. History Dogu’a Tembien holds numerous prehistoric sites, which have been dated to the Middle Stone Age in Ayninbirkekin, or Pastoral Neolithic in Aregen and Menachek. Geography Topography and landscapes Major mountains :* Tsatsen, 2815 metres, a wide mesa between Hagere Selam and Inda Maryam Qorar () :* Ekli Imba, 2799 metres, summit of the Arebay massif in Arebay ''tabia'' or district () :* Imba Zuw’ala, 2710 metres, near Hagere Selam () :* Aregen, 2660 metres, in Aregen ''tabia'' () :* Dabba Selama, 2630 metres, in Haddinnet ''tabia'' () (not to be confused with the homonymous monastery) :* Imba Dogu’a, 2610 metres, in Mizane Birhan ''tabia'' () :* Imba Ra’ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsigereda
Tsigereda () is the capital of Gere-alta woreda (up to 1993, and again starting 2020). Tsigereda means "rose" in the local Tigrinya language. History In Imperial times (before 1975), Tsigereda used to be the center of the Gere-alta woreda, part of the former Enderta province. This Gere-alta woreda consisted of the western part of the current Hawzen and Kilte Awulaelo districts. Geography The ''tabia'' stretches down from the Arebay peaks in Dogu'a Tembien towards the headwaters of Agefet river. Geology From the higher to the lower locations, the following geological formations are present: * Antalo Limestone * Quaternary alluvium and freshwater tufa Climate The rainfall pattern shows a very high seasonality with 70 to 80% of the annual rain falling in July and August. Mean temperature in Tsigereda is 22 °C, oscillating between average daily minimum of 12.5 °C and maximum of 31 °C. The contrasts between day and night air temperatures are much larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wari River
Wari River is a river of northern Ethiopia and a tributary of the Tekezé River. It rises in the Gar'alta and flows to the southwest into the Tekezé at . Tributaries of the Wari include the Assam, Chemit, Meseuma, Tsedia, Agefet and Tsaliet rivers. The general drainage is westward, to the Tekezze River. Main tributaries in Dogu’a Tembien district are, from upstream to downstream * Agefet River ** Amblo River, in ''tabia'' Addi Walka ** Azef River, at the border of ''tabias'' Addi Walka and Haddinnet ** Ab'aro River, in ''tabia'' Haddinnet and ''woreda'' Kola Tembien * May Leiba, in ''tabia'' Ayninbirkekin, which becomes Tinsehe R. in Selam and Mahbere Sillasie, and Tsaliet River, downstream from the Dabba Selama monastery ** Khunale River, in ''tabia'' Selam ** Harehuwa River, in ''tabia'' Mahbere Sillasie ** Kidan Mihret River, in ''tabia'' Mahbere Sillasie ** Ferrey River, at the border of ''tabias'' Mahbere Sillasie and Degol Woyane See also * List of ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginda'i
Ginda'i (also spelled Gindae) is a reservoir located in the Kilte Awula’ilo ''woreda'' of the Tigray Region in Ethiopia. The earthen dam that holds the reservoir was built in 1998 by SAERT. Dam characteristics * Dam height: 19.5 metres * Dam crest length: 483 metres * Spillway width: 23.2 metres Capacity * Original capacity: 793170 m³ * Dead storage: 142405 m³ * Reservoir area: 13.5 ha In 2002, the life expectancy of the reservoir (the duration before it is filled with sediment) was estimated at 20 years. Irrigation * Designed irrigated area: 54 ha * Actual irrigated area in 2002: 6 ha Environment The catchment of the reservoir is 11.16 km² large. A net erosion map for the Ginda’i catchment shows that sediment deposition occurs at the footslopes, while the maximum erosion rate (more than 150 tonnes per hectare per year) occurred on the steepest slopes. Erosion rates in the cultivated lands are often low, as in the Gind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsaliet
Tsaliet is a river in northern Ethiopia, belonging to the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien, where it is first called May Leiba River and then Tinsehe River, it flows westward through a deep gorge, to become Tsaliet in its lower course, where it empties in Weri’i River, just upstream of the main Weri’i bridge along the road to Adwa. Characteristics It is mostly a confined river, locally meandering in its narrow alluvial plain, with an average slope gradient of 25 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut deep gorges. Along the middle of its course, it occupies sandy pediments in Addeha. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amblo
Amblo is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northward to empty finally in Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics It is a confined ephemeral bedrock river, with an average slope gradient of 63 metres per kilometre. With its tributaries, the river has cut a deep gorge. Flash floods and flood buffering Runoff mostly happens in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. The magnitude of floods in this river has however been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. On steep slopes, exclosures have been established; the dense vegetation largely contributes to enhanced infiltration, less flooding and better baseflow. Physical conservation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab'aro
Ab’aro is a river of the Nile basin. Rising in the mountains of Dogu’a Tembien in northern Ethiopia, it flows northwestward to empty finally in Weri’i and Tekezé River. Characteristics Ab’aro is a confined ephemeral river in its upper part, whereas it widely meanders in the lower plains, with an average slope gradient of 60 metres per kilometre. Towards the footslope the river has cut a deep gorge (a cluse). Flash floods Runoff mostly occurs in the form of high runoff discharge events that occur in a very short period (called flash floods). These are related to the steep topography, often little vegetation cover and intense convective rainfall. The peaks of such flash floods have often a 50 to 100 times larger discharge than the preceding baseflow. In contrast to neighbouring rivers such as May Meqa, May Shoate or Giraliwdo, the magnitude of floods in Ab’aro has not been decreased due to interventions in the catchment. Physical conservation structures such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhumance In Ethiopia
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Generally only the herds travel, with a certain number of people necessary to tend them, while the main population stays at the base. In contrast, ''horizontal transhumance'' is more susceptible to being disrupted by climatic, economic, or political change. Traditional or fixed transhumance has occurred throughout the inhabited world, particularly Europe and western Asia. It is often important to pastoralist societies, as the dairy products of transhumance flocks and herds (milk, butter, yogurt and cheese) may form much of the diet of such populations. In many languages there are words for the higher summer pastures, and frequently these words have been used as place na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclosure
An exclosure, in an area being used extensively for grazing, is a limited area from which unwanted browsing animals, such as domestic cattle or wildlife such as deer, are excluded by fencing or other means. Environmental protection Most commonly, exclosures are areas that are set aside for regreening. Wood harvesting and livestock range are not allowed there. Effects on environment The establishment of an exclosure has positive effects on: * biodiversity * water infiltration * protection from flooding * sediment deposition * carbon sequestration Economic benefits In developing countries, people commonly have economic benefits from these exclosures through grass harvesting, beekeeping and other non-timber forest products. The local inhabitants also consider it as “land set aside for future generations”. Carbon credits Exclosures have as an additional benefit that the surrounding communities may receive carbon credits for the sequestered CO2, as part of a carbon offs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infiltration (hydrology)
Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. It is commonly used in both hydrology and soil sciences. The infiltration capacity is defined as the maximum rate of infiltration. It is most often measured in meters per day but can also be measured in other units of distance over time if necessary. The infiltration capacity decreases as the soil moisture content of soils surface layers increases. If the precipitation rate exceeds the infiltration rate, runoff will usually occur unless there is some physical barrier. Infiltrometers, permeameters and rainfall simulators are all devices that can be used to measure infiltration rates. Infiltration is caused by multiple factors including; gravity, capillary forces, adsorption and osmosis. Many soil characteristics can also play a role in determining the rate at which infiltration occurs. Factors that affect infiltration Precipitation and Precipitation can impact infiltration in many ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |