|
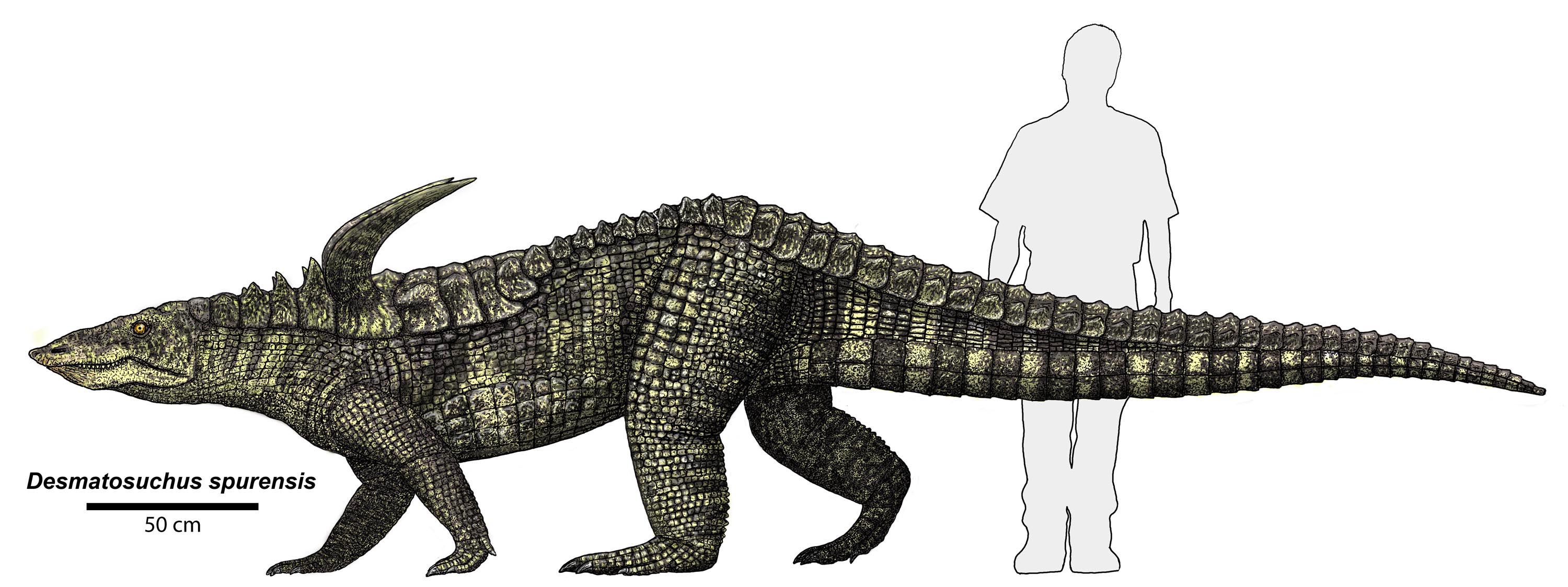
Aetosaur Osteoderms
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms (Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frugivores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur Skull Diagrams
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order (biology), order Aetosauria (; from Ancient Greek, Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized Omnivore, omnivorous or Herbivore, herbivorous Pseudosuchia, pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like Osteoderm, osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North America, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revueltosaurus
''Revueltosaurus'' ("Revuelto lizard") is an extinct genus of suchian pseudosuchian from Late Triassic (late Carnian to middle Norian stage) deposits of New Mexico, Arizona and North Carolina, United States. Many specimens, mostly teeth, have been assigned to ''Revueltosaurus'' over the years. Currently, three species are included in this genus, all of which were originally thought to represent monospecific genera of basal ornithischian dinosaurs. It was 1 meter (3.3 feet) long. Species ''Revueltosaurus callenderi'' ''R. callenderi'' was named by Adrian P. Hunt in 1989 and it is the type species of the genus. The generic name honors its type locality, Revuelto Creek, Quay County of New Mexico. Revuelto is derived from Spanish ''revuelta'', "revolution", in reference to the importance of the Late Triassic period for terrestrial vertebrate evolution. The specific name honours the director of the New Mexico Museum of Natural History Jonathan F. Callender. ''R. callenderi'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Fossil
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock Stratum, strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular Horizon (geology), horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the Sedimentary depositional environment, sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |