Genera on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Genus (; : genera ) is a
 *
*
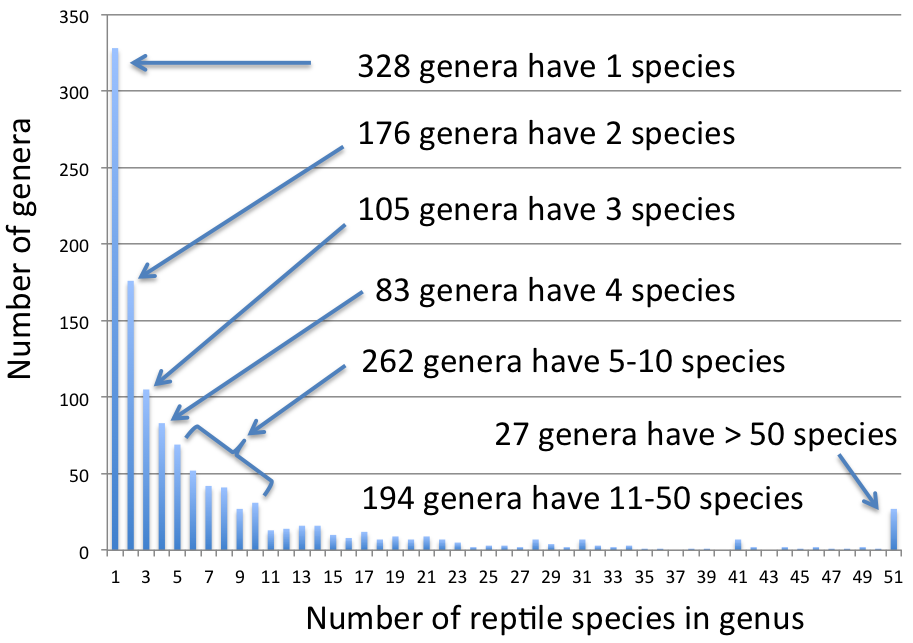 The number of species in genera varies considerably among taxonomic groups. For instance, among (non-avian)
The number of species in genera varies considerably among taxonomic groups. For instance, among (non-avian)
Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG)
includes an estimated 95% of published genus names (accepted and unaccepted) in all groups (semi-continuously updated)
''Nomenclator Zoologicus''
: index of genus and subgenus names (accepted and unaccepted) in zoological nomenclature from 1758 to 2004
Index to Organism Names
includes zoological taxon names at all ranks (including genera) as continuously indexed for the '' Zoological Record''
''Index Nominum Genericorum'' (ING)
a compilation of generic names (accepted and unaccepted) published for organisms covered by the ICN: International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (semi-continuously updated)
LPSN – List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature
includes all currently accepted Bacteria and Archaea genus names (continuously updated)
ICTV taxonomy releases
latest and historical lists of accepted virus names compiled by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), including all currently accepted virus genus names (updated via regular releases) {{DEFAULTSORT:Genus *01
taxonomic rank
In biology, taxonomic rank (which some authors prefer to call nomenclatural rank because ranking is part of nomenclature rather than taxonomy proper, according to some definitions of these terms) is the relative or absolute level of a group of or ...
above species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
and below family as used in the biological classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon), and these groups are give ...
of living and fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.
:E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae.
The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful:
# monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
analysis should clearly demonstrate both monophyly and validity as a separate lineage).
# reasonable compactness – a genus should not be expanded needlessly.
# distinctness – with respect to evolutionarily relevant criteria, i.e. ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
, morphology, or biogeography; DNA sequences
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession is denoted by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of the ...
are a ''consequence'' rather than a ''condition'' of diverging evolutionary lineages except in cases where they directly inhibit gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
(e.g. postzygotic barriers).
Moreover, genera should be composed of phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
units of the same kind as other (analogous) genera.
Etymology
The term "genus" comes fromLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, a noun form cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language.
Because language change can have radical effects on both the s ...
with ' ('to bear; to give birth to'). The Swedish taxonomist Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
popularized its use in his 1753 ''Species Plantarum
' (Latin for "The Species of Plants") is a book by Carl Linnaeus, originally published in 1753, which lists every species of plant known at the time, classified into genus, genera. It is the first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature ...
'', but the French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort (1656–1708) is considered "the founder of the modern concept of genera".
Use
The scientific name (or the scientific epithet) of a genus is also called the generic name; in modern style guides and science, it is always capitalised. It plays a fundamental role inbinomial nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
, the system of naming organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s, where it is combined with the scientific name of a species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
: see Botanical name and Specific name (zoology).
Use in nomenclature
The rules for thescientific name
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin gramm ...
s of organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s are laid down in the nomenclature codes
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern the naming of living organisms. Standardizing the scientific names of biological organisms allows researchers to discuss findings (including the discovery of new s ...
, which allow each species a single unique name that, for animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s (including protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s), plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s (also including algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
) and prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s (bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
), is Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and binomial in form; this contrasts with common or vernacular names, which are non-standardized, can be non-unique, and typically also vary by country and language of usage.
Except for viruses, the standard format for a species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
name comprises the generic name, indicating the genus to which the species belongs, followed by the specific epithet, which (within that genus) is unique to the species. For example, the gray wolf's scientific name is with '' Canis'' (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for 'dog') being the generic name shared by the wolf's close relatives and (Latin for 'wolf') being the specific name particular to the wolf. A botanical example would be '' Hibiscus arnottianus'', a particular species of the genus '' Hibiscus'' native to Hawaii. The specific name is written in lower-case and may be followed by subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
names in zoology
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the anatomy, structure, embryology, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and ...
or a variety of infraspecific names in botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
.
When the generic name is already known from context, it may be shortened to its initial letter, for example, ''C. lupus'' in place of ''Canis lupus''. Where species are further subdivided, the generic name (or its abbreviated form) still forms the leading portion of the scientific name, for example, for the Eurasian wolf subspecies, or as a botanical example, . Also, as visible in the above examples, the Latinised portions of the scientific names of genera and their included species (and infraspecies, where applicable) are, by convention, written in italics
In typography, italic type is a cursive font based on a stylised form of calligraphic handwriting. Along with blackletter and roman type, it served as one of the major typefaces in the history of Western typography.
Owing to the influence f ...
.
The scientific names of virus species are descriptive, not binomial in form, and may or may not incorporate an indication of their containing genus; for example, the virus species " Salmonid herpesvirus 1", " Salmonid herpesvirus 2" and " Salmonid herpesvirus 3" are all within the genus '' Salmonivirus''; however, the genus to which the species with the formal names " Everglades virus" and " Ross River virus" are assigned is '' Alphavirus''.
As with scientific names at other ranks, in all groups other than viruses, names of genera may be cited with their authorities, typically in the form "author, year" in zoology, and "standard abbreviated author name" in botany. Thus in the examples above, the genus ''Canis'' would be cited in full as "''Canis'' Linnaeus, 1758" (zoological usage), while ''Hibiscus'', also first established by Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
but in 1753, is simply "''Hibiscus'' L." (botanical usage).
The type concept
Each genus should have a designated type, although in practice there is a backlog of older names without one. In zoology, this is thetype species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
, and the generic name is permanently associated with the type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wikt:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to ancho ...
of its type species. Should the specimen turn out to be assignable to another genus, the generic name linked to it becomes a junior synonym and the remaining taxa in the former genus need to be reassessed.
Categories of generic name
In zoological usage, taxonomic names, including those of genera, are classified as "available" or "unavailable". Available names are those published in accordance with theInternational Code of Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted Convention (norm), convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific name, scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the I ...
; the earliest such name for any taxon (for example, a genus) should then be selected as the " valid" (i.e., current or accepted) name for the taxon in question.
Consequently, there will be more available names than valid names at any point in time; which names are currently in use depending on the judgement of taxonomists in either combining taxa described under multiple names, or splitting taxa which may bring available names previously treated as synonyms back into use. "Unavailable" names in zoology comprise names that either were not published according to the provisions of the ICZN Code, e.g., incorrect original or subsequent spellings, names published only in a thesis, and generic names published after 1930 with no type species indicated. According to "Glossary" section of the zoological Code, suppressed ''names'' (per published "Opinions" of the International Commission of Zoological Nomenclature) remain available but cannot be used as the valid name for a taxon; however, the names published in suppressed ''works'' are made unavailable via the relevant Opinion dealing with the work in question.
In botany, similar concepts exist but with different labels. The botanical equivalent of zoology's "available name" is a validly published name. An invalidly published name is a or ; a rejected name is a or ; a later homonym of a validly published name is a or ; for a full list refer to the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants
The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN or ICNafp) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all tho ...
'' and the work cited above by Hawksworth, 2010. In place of the "valid taxon" in zoology, the nearest equivalent in botany is " correct name" or "current name" which can, again, differ or change with alternative taxonomic treatments or new information that results in previously accepted genera being combined or split.
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
and virus codes of nomenclature also exist which serve as a reference for designating currently accepted genus names as opposed to others which may be either reduced to synonymy, or, in the case of prokaryotes, relegated to a status of "names without standing in prokaryotic nomenclature".
An available (zoological) or validly published (botanical) name that has been historically applied to a genus but is not regarded as the accepted (current/valid) name for the taxon is termed a synonym; some authors also include unavailable names in lists of synonyms as well as available names, such as misspellings, names previously published without fulfilling all of the requirements of the relevant nomenclatural code, and rejected or suppressed names.
A particular genus name may have zero to many synonyms, the latter case generally if the genus has been known for a long time and redescribed as new by a range of subsequent workers, or if a range of genera previously considered separate taxa have subsequently been consolidated into one. For example, the World Register of Marine Species
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive catalogue and list of names of marine organisms.
Content
The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scien ...
presently lists 8 genus-level synonyms for the sperm whale genus '' Physeter'' Linnaeus, 1758, and 13 for the bivalve genus '' Pecten'' O.F. Müller, 1776.
Identical names (homonyms)
Within the same kingdom, one generic name can apply to one genus only. However, many names have been assigned (usually unintentionally) to two or more different genera. For example, the platypus belongs to the genus ''Ornithorhynchus'' although George Shaw named it ''Platypus'' in 1799 (these two names are thus ''synonyms''). However, the name ''Platypus'' had already been given to a group of ambrosia beetles by Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Herbst in 1793. A name that means two different things is a ''homonym''. Since beetles and platypuses are both members of the kingdom Animalia, the name could not be used for both. Johann Friedrich Blumenbach published the replacement name ''Ornithorhynchus'' in 1800. However, a genus in one kingdom is allowed to bear a scientific name that is in use as a generic name (or the name of a taxon in another rank) in a kingdom that is governed by a different nomenclature code. Names with the same form but applying to different taxa are called "homonyms". Although this is discouraged by both theInternational Code of Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted Convention (norm), convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific name, scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the I ...
and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants
The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN or ICNafp) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all tho ...
, there are some five thousand such names in use in more than one kingdom. For instance,
* '' Anura'' is the name of the order of frogs but also is the name of a non-current genus of plants;
* ''Aotus'' is the generic name of both golden peas and night monkeys;
* ''Oenanthe'' is the generic name of both wheatears and water dropworts;
* ''Prunella'' is the generic name of both accentors and self-heal; and
* ''Proboscidea'' is the order of elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
s and the genus of devil's claws.
* The name of the genus '' Paramecia'' (an extinct red alga) is also the plural of the name of the genus '' Paramecium'' (which is in the SAR supergroup), which can also lead to confusion.
A list of generic homonyms (with their authorities), including both available (validly published) and selected unavailable names, has been compiled by the Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG).
Use in higher classifications
The type genus forms the base for higher taxonomic ranks, such as the family name ("Canids") based on ''Canis''. However, this does not typically ascend more than one or two levels: the order to which dogs and wolves belong is ("Carnivores").Numbers of accepted genera
The numbers of either accepted, or all published genus names is not known precisely; Rees et al., 2020 estimate that approximately 310,000 accepted names (valid taxa) may exist, out of a total of c. 520,000 published names (including synonyms) as at end 2019, increasing at some 2,500 published generic names per year. "Official" registers of taxon names at all ranks, including genera, exist for a few groups only such as viruses and prokaryotes, while for others there are compendia with no "official" standing such as ''Index Fungorum
''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. As of 2015, the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and th ...
'' for fungi, ''Index Nominum Algarum'' and AlgaeBase for algae, ''Index Nominum Genericorum'' and the International Plant Names Index
The International Plant Names Index (IPNI) describes itself as "a database of the names and associated basic bibliographical details of seed plants, ferns and lycophytes." Coverage of plant names is best at the rank of species and genus. It inclu ...
for plants in general, and ferns through angiosperms, respectively, and '' Nomenclator Zoologicus'' and the Index to Organism Names for zoological names.
Totals for both "all names" and estimates for "accepted names" as held in the '' Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera'' (IRMNG) are broken down further in the publication by Rees et al., 2020 cited above. The accepted names estimates are as follows, broken down by kingdom:
 *
* Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
ia: 239,093 accepted genus names (± 55,350)
* Plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
ae: 28,724 (± 7,721)
* Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
: 10,468 (± 182)
* Chromista: 11,114 (± 1,268)
* Protozoa: 3,109 (± 1,206)
* Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
: 3,433 (± 115)
* Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
: 140 (± 0)
* Viruses: 851 (± 0)
The cited ranges of uncertainty arise because IRMNG lists "uncertain" names (not researched therein) in addition to known "accepted" names; the values quoted are the mean of "accepted" names alone (all "uncertain" names treated as unaccepted) and "accepted + uncertain" names (all "uncertain" names treated as accepted), with the associated range of uncertainty indicating these two extremes.
Within Animalia, the largest phylum is Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
a, with 151,697 ± 33,160 accepted genus names, of which 114,387 ± 27,654 are insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s (class Insecta). Within Plantae, Tracheophyta (vascular plants) make up the largest component, with 23,236 ± 5,379 accepted genus names, of which 20,845 ± 4,494 are angiosperms (superclass Angiospermae).
By comparison, the 2018 annual edition of the Catalogue of Life (estimated >90% complete, for extant species in the main) contains currently 175,363 "accepted" genus names for 1,744,204 living and 59,284 extinct species, also including genus names only (no species) for some groups.
Genus size
 The number of species in genera varies considerably among taxonomic groups. For instance, among (non-avian)
The number of species in genera varies considerably among taxonomic groups. For instance, among (non-avian) reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, which have about 1180 genera, the most (>300) have only 1 species, ~360 have between 2 and 4 species, 260 have 5–10 species, ~200 have 11–50 species, and only 27 genera have more than 50 species. However, some insect genera such as the bee genera '' Lasioglossum'' and '' Andrena'' have over 1000 species each. The largest flowering plant genus, '' Astragalus'', contains over 3,000 species.
Which species are assigned to a genus is somewhat arbitrary. Although all species within a genus are supposed to be "similar", there are no objective criteria for grouping species into genera. There is much debate among zoologists whether enormous, species-rich genera should be maintained, as it is extremely difficult to come up with identification keys or even character sets that distinguish all species. Hence, many taxonomists argue in favor of breaking down large genera. For instance, the lizard genus '' Anolis'' has been suggested to be broken down into 8 or so different genera which would bring its ~400 species to smaller, more manageable subsets.
See also
* List of the largest genera of flowering plantsReferences
External links
Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera (IRMNG)
includes an estimated 95% of published genus names (accepted and unaccepted) in all groups (semi-continuously updated)
''Nomenclator Zoologicus''
: index of genus and subgenus names (accepted and unaccepted) in zoological nomenclature from 1758 to 2004
Index to Organism Names
includes zoological taxon names at all ranks (including genera) as continuously indexed for the '' Zoological Record''
''Index Nominum Genericorum'' (ING)
a compilation of generic names (accepted and unaccepted) published for organisms covered by the ICN: International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (semi-continuously updated)
LPSN – List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature
includes all currently accepted Bacteria and Archaea genus names (continuously updated)
ICTV taxonomy releases
latest and historical lists of accepted virus names compiled by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), including all currently accepted virus genus names (updated via regular releases) {{DEFAULTSORT:Genus *01
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
Plant taxonomy
Zoological nomenclature
Bacterial nomenclature
Taxa named by Joseph Pitton de Tournefort