|
Acts 5
Acts 5 is the fifth chapter of the Acts of the Apostles in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It records the growth of the early church and the obstacles it encountered.Halley, Henry H., ''Halley's Bible Handbook'': an abbreviated Bible commentary. 23rd edition. Zondervan Publishing House. 1962. Text The original text was written in Koine Greek and is divided into 42 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: * Uncial 0189 (~AD 200) * Codex Vaticanus (325–350) * Codex Sinaiticus (330–360) * Papyrus 8 (4th century; extant verses 2–9) * Papyrus 57 (4th century; extant verses 1–2, 8–10) * Codex Bezae (~400) * Codex Alexandrinus (400–440) * Codex Ephraemi Rescriptus (~450; extant verses 35–42) * Codex Laudianus (~550) Ananias and Sapphira (5:1–11) The narrative underlines the authority of Peter, who could see through the deception by Ananias and Sapphira (verses 3–5, 8–9) and highlights the spiritual author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acts Of The Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles ( grc-koi, Πράξεις Ἀποστόλων, ''Práxeis Apostólōn''; la, Actūs Apostolōrum) is the fifth book of the New Testament; it tells of the founding of the Christian Church and the spread of its message to the Roman Empire. It gives an account of the ministry and activity of Christ's apostles in Jerusalem and other regions, after Christ's death, resurrection, and ascension. Acts and the Gospel of Luke make up a two-part work, Luke–Acts, by the same anonymous author. It is usually dated to around 80–90 AD, although some scholars suggest 90–110. The first part, the Gospel of Luke, tells how God fulfilled his plan for the world's salvation through the life, death, and resurrection of Jesus of Nazareth. Acts continues the story of Christianity in the 1st century, beginning with the ascension of Jesus to Heaven. The early chapters, set in Jerusalem, describe the Day of Pentecost (the coming of the Holy Spirit) and the growth of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Laudianus
Codex Laudianus, designated by Ea or 08 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), α 1001 ( von Soden), called ''Laudianus'' after the former owner, Archbishop William Laud. It is a diglot Latin — Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament, palaeographically assigned to the 6th century. The manuscript contains the Acts of the Apostles. Description The manuscript is a diglot, with Greek and Latin in parallel columns on the same page, with the Latin in the left-hand column. The codex contains 227 parchment leaves, sized , with almost the complete text of the Book of Acts (lacuna in 26:29-28:26). It is the earliest known manuscript to contain Acts 8:37. The text is written in two columns per page, 24 and more lines per page. It is arranged in very short lines of only one to three words each. The text is written colonmetrically. Text The Greek text of this codex exhibits a mixture of text-types, usually the Byzantine, but there are many Western and some Alexandrian readings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadducees
The Sadducees (; he, צְדוּקִים, Ṣədūqīm) were a socio-religious sect of Jewish people who were active in Judea during the Second Temple period, from the second century BCE through the destruction of the Temple in 70 CE. The Sadducees are often compared to other contemporaneous sects, including the Pharisees and the Essenes. Josephus, writing at the end of the 1st century CE, associates the sect with the upper social and economic echelon of Judean society. As a whole, they fulfilled various political, social, and religious roles, including maintaining the Temple in Jerusalem. The group became extinct some time after the destruction of Herod's Temple in Jerusalem in 70 CE. Etymology According to Abraham Geiger, the Sadducee sect of Judaism derived their name (Greek: Saddoukaioi; Hebrew: ṣāddūqim) from that of Zadok, the first High Priest of ancient Israel in the time of Solomon to serve in the First Temple; the leaders of the sect were proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquities Of The Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' ( la, Antiquitates Iudaicae; el, Ἰουδαϊκὴ ἀρχαιολογία, ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by historian Flavius Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of Roman emperor Flavius Domitian which was around AD 93 or 94.Freedman, David Noel, ed., ''The Anchor Bible Dictionary'', (New York: Doubleday, 1997, 1992). ''Antiquities of the Jews'' contains an account of the history of the Jewish people for Josephus' gentile patrons. In the first ten volumes, Josephus follows the events of the Hebrew Bible beginning with the creation of Adam and Eve. The second ten volumes continues the history of the Jewish people beyond the biblical text and up to the Jewish War, or the First Jewish–Roman War, 66 to 73 CE. This work, along with Josephus's other major work, ''The Jewish War'' (''De Bello Iudaico''), provides valuable background material for historians wishing to understand 1st-century AD Jud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius.Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judas Of Galilee
Judas of Galilee, or Judas of Gamala, was a Jewish leader who led resistance to the census imposed for Roman tax purposes by Quirinius in Judea Province around 6 CE. He encouraged Jews not to register and those that did had their houses burnt and their cattle stolen by his followers. He is credited with beginning the " fourth philosophy" of the Jews which Josephus blames for the disastrous war with the Romans in 66–70. These events are discussed by Josephus in ''The Jewish War'' and in ''Antiquities of the Jews'' and mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles. In ''Antiquities of the Jews'', Josephus states that Judas, along with Zadok the Pharisee, founded the Zealots, the "fourth sect" of 1st century Judaism (the first three being the Sadducees, the Pharisees, and the Essenes). Josephus blamed this fourth sect for the First Jewish–Roman War of 66–73. The Zealots were theocratic nationalists who preached that God alone was the ruler of Israel and urged that no taxes should be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theudas
Theudas (; ; died c. 46 AD) was a Jewish rebel of the 1st century AD. Scholars attribute to his name a Greek etymology possibly meant as "flowing with water", although with a Hellenist-styled ending. At some point between 44 and 46 AD, Theudas led his followers in a short-lived revolt. The revolt The principal source for the story of Theudas' revolt is Josephus, who wrote: It came to pass, while Cuspius Fadus was procurator of Judea, that a certain charlatan, whose name was Theudas, persuaded a great part of the people to take their effects with them, and follow him to the Jordan river; for he told them he was a prophet, and that he would, by his own command, divide the river, and afford them an easy passage over it. Many were deluded by his words. However, Fadus did not permit them to make any advantage of his wild attempt, but sent a troop of horsemen out against them. After falling upon them unexpectedly, they slew many of them, and took many of them alive. They also took The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
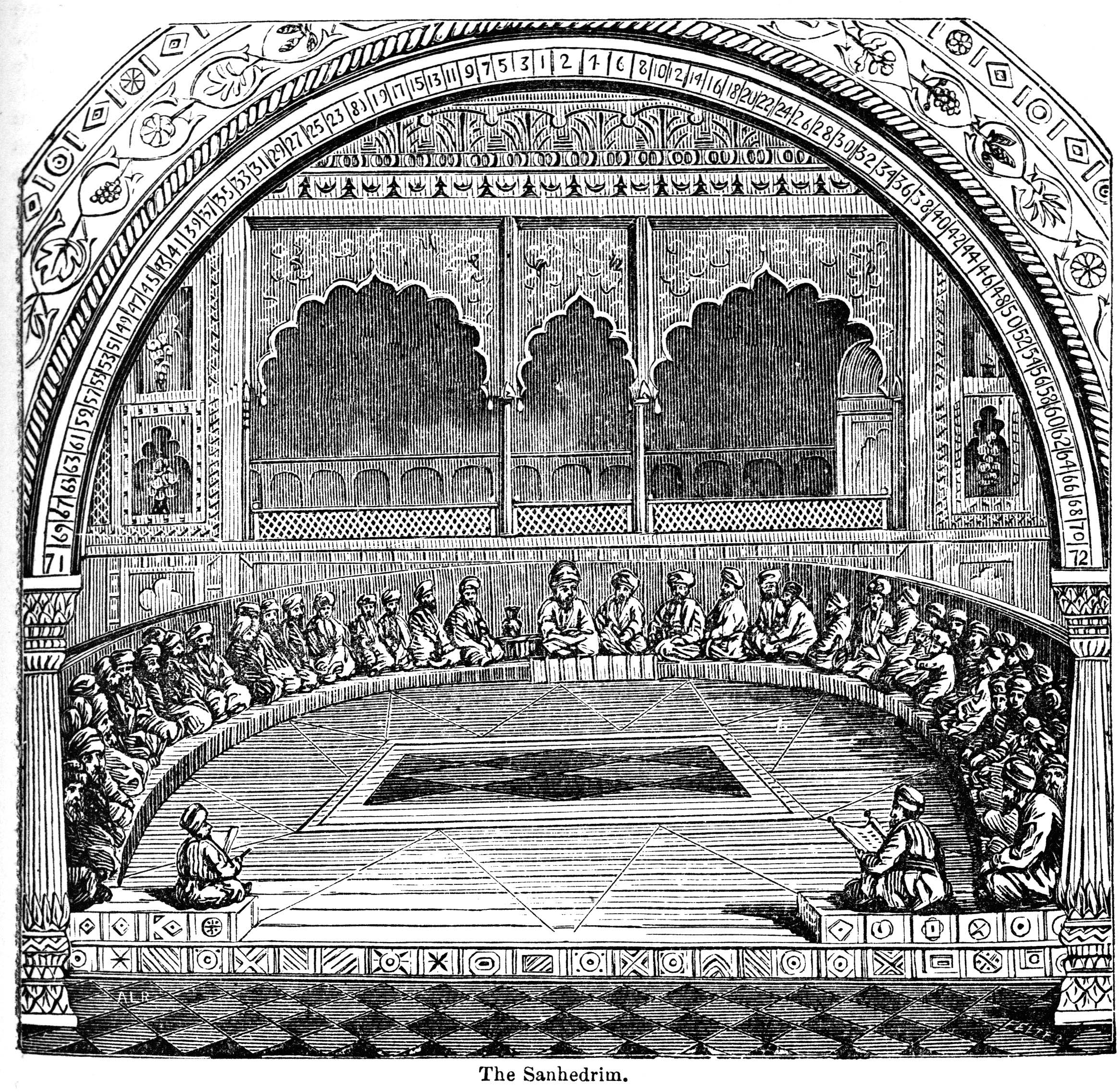
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , ''synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New King James Version
The New King James Version (NKJV) is an English translation of the Bible. The complete NKJV Bible was published in 1982 by Thomas Nelson, now HarperCollins. The NKJV is described by Thomas Nelson as being "scrupulously faithful to the original, yet truly updated to enhance its clarity and readability." History The NKJV translation project was conceived by Arthur Farstad. It was inaugurated in 1975 with two meetings (Nashville and Chicago) of 130 biblical scholars, pastors, and theologians. The men who were invited prepared the guidelines for the NKJV. The aim of its translators was to update the vocabulary and grammar of the King James Version, while preserving the classic style and literary beauty of the original 1769 edition of the King James Version. The 130 translators believed in faithfulness to the original Greek, Aramaic, and Hebrew texts including the Dead Sea Scrolls. Also agreed upon for most New King James Bibles were easier event descriptions, a history of each b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow Jews on ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acts 4
Acts 4 is the fourth chapter of the Acts of the Apostles in the New Testament of the Christianity, Christian Bible. The book containing this chapter is anonymous but early Christian tradition affirmed that Luke the Evangelist, Luke composed this book as well as the Gospel of Luke. This chapter records the aftermath of a healing by Simon Peter and his preaching in Solomon's Portico, that Sanhedrin arrested the apostles, but had to let them go.Halley, Henry H. ''Halley's Bible Handbook'': an abbreviated Bible commentary. 23rd edition. Zondervan Publishing House. 1962. Text The original text was written in Koine Greek and Chapters and verses of the Bible, is divided into 37 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: * Codex Vaticanus (AD 325–350) * Codex Sinaiticus (330–360) * Papyrus 8 (4th century; extant verses 31–37) * Codex Bezae (~400) * Codex Alexandrinus (400–440) * Codex Ephraemi Rescriptus (~450; extant verses 1–2) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippians 2
Philippians 2 is the second chapter of the Epistle to the Philippians in the New Testament of the Christianity, Christian Bible. It is Authorship of the Pauline epistles, authored by Paul the Apostle about mid-50s to early 60s AD and addressed to the Christians in Philippi. Jesuit theologian Robert Murray notes that a narrative in #Verses 5–11, verses 5-11 about Christ, "who humbled himself, by becoming obedient to death" is central to this chapter. German protestant theologian Ernst Lohmeyer argued in 1928 that were an existing hymn about Christ which Paul quotes in his letter, a theory which "has come to dominate both Biblical exegesis, exegesis of Philippians and study of early Christology and List of Christian creeds#Biblical creeds, credal formulas". Text The original text was written in Koine Greek. Chapters and verses of the Bible, This chapter is divided into 30 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are: *Codex Vaticanus (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)