|
Acropolis Museum Of Athens
The Old Acropolis Museum ( el, (Παλαιό) Μουσείο Ακρόπολης ''(Palaio) Mouseio Akropolis'') was an archaeological museum located in Athens, Greece on the archeological site of Acropolis. It is built in a niche at the eastern edge of the rock and most of it lies beneath the level of the hilltop, making it largely invisible. It was considered one of the major archaeological museums in Athens. Due to its limited size, the Greek government decided in the late 1980s to build a new museum. The New Acropolis Museum is now built at the foot of the Acropolis. In June 2007 the old museum closed its doors so that its antiquities could be moved to their new home, which opened on 20 June 2009. History The museum was home to many of the Greek world's ancient relics found in and around the Acropolis of Athens since excavations started. It was designed by architect Panagis Kalkos and was constructed between 1865 and 1874. It was expanded in the 1950s to a modern design e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erechtheum
The Erechtheion (latinized as Erechtheum /ɪˈrɛkθiəm, ˌɛrɪkˈθiːəm/; Ancient Greek: Ἐρέχθειον, Greek: Ερέχθειο) or Temple of Athena Polias is an ancient Greek Ionic temple-telesterion on the north side of the Acropolis, Athens, which was primarily dedicated to the goddess Athena. The building, made to house the statue of Athena Polias, has in modern scholarship been called the Erechtheion (the sanctuary of Erechtheus or Poseidon) in the belief that Pausanias' description of the Erechtheion applies to this building. However, whether the Erechtheion referred to by Pausanias is indeed the Ionic temple or an entirely different building has become a point of contention in recent decades. In the official decrees the building is referred to as “... το͂ νεὸ το͂ ἐμ πόλει ἐν ο͂ι τὸ ἀρχαῖον ἄγαλμα” (the temple on the Acropolis within which is the ancient statue). In other instances it is referred to as the Temple o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
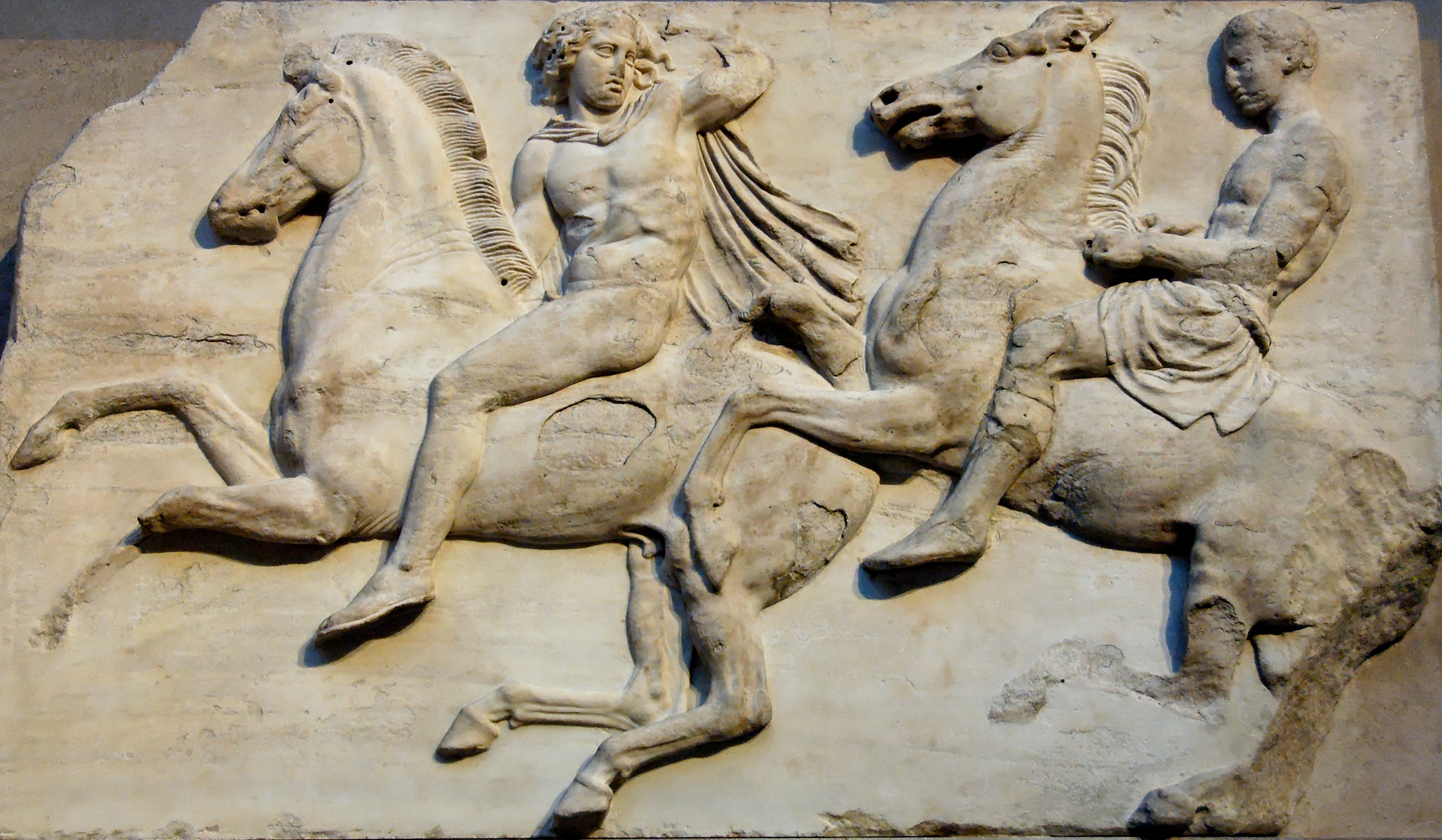
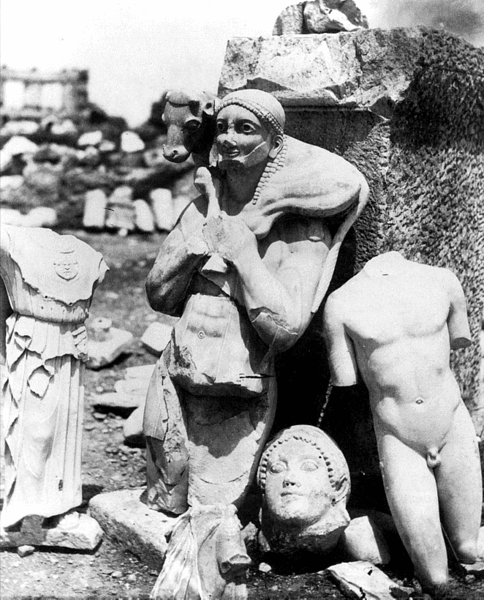
Parthenon Frieze
The Parthenon frieze is the high-relief Pentelic marble sculpture created to adorn the upper part of the Parthenon’s naos. It was sculpted between c. 443 and 437 BC, most likely under the direction of Pheidias. Of the 160 meters (524 ft) of the original frieze, 128 meters (420 ft) survives—some 80 percent. The rest is known only from the drawings attributed to French artist Jacques Carrey in 1674, thirteen years before the Venetian bombardment that ruined the temple. At present, the majority of the frieze is at the British Museum in London (forming the major part of the Elgin Marbles); the largest proportion of the rest is at the Acropolis Museum in Athens, and the remainder of fragments shared between six other institutions. Casts of the frieze may be found in the Beazley archive at the Ashmolean Museum at Oxford, at the Spurlock Museum in Urbana, in the Skulpturhalle at Basel and elsewhere. Construction Plutarch’s ''Life of Pericles'', 13.4–9, informs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odeon Of Pericles
The Odeon of Athens or Odeon of Pericles in Athens was a odeon, built at the southeastern foot of the Acropolis in Athens, next to the entrance to the Theatre of Dionysus. History It was first built in 435 BC by Pericles for the musical contests that formed part of the Panathenaea, for audiences from the theatre to shelter in case of bad weather and for chorus rehearsals. Few remains of it now survive, but it seems to have been "adorned with stone pillars" (according to Vitruvius and Plutarch) and square instead of the usual circular shape for an odeon. It was covered with timber made from captured Persian ships, culminating in a square pyramid-like roof resembling a tent. Pausanias wrote that the 1st century BC rebuild of it was "said to be a copy of Xerxes' tent", and that might well have applied to the original building. Plutarch writes that the original building had many seats and many pillars. Modern excavation work has revealed its foundations as , and it is now known that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Of Dionysus
The Theatre of Dionysus (or Theatre of Dionysos, el, Θέατρο του Διονύσου) is an ancient Greek theatre in Athens. It is built on the south slope of the Acropolis hill, originally part of the sanctuary of Dionysus Eleuthereus (Dionysus the Liberator). The first ''orchestra'' terrace was constructed on the site around the mid- to late-sixth century BC, where it hosted the City Dionysia. The theatre reached its fullest extent in the fourth century BC under the ''epistates'' of Lycurgus when it would have had a capacity of up to 17,000, and was in continuous use down to the Roman period. The theatre then fell into decay in the Byzantine era and was not identified, excavated and restored to its current condition until the nineteenth century. Sanctuary and first theatre The cult of Dionysus was introduced to Attica in the Archaic period with the earliest representation of the God dating to c. 580 BC. The City Dionysia (or Great Dionysia) began sometime in the Peisist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asclepieion
Asclepieia ( grc, Ἀσκληπιεῖον ''Asklepieion''; Ἀσκλαπιεῖον in Doric dialect; Latin ''aesculapīum'') were healing temples located in ancient Greece (and in the wider Hellenistic and Roman world), dedicated to Asclepius, the first doctor-demigod in Greek mythology. Asclepius was said to have been such a skilled doctor that he could even raise people from the dead. So stemming from the myth of his great healing powers, pilgrims would flock to temples built in his honor in order to seek spiritual and physical healing. Asclepieia included carefully controlled spaces conducive to healing and fulfilled several of the requirements of institutions created for healing. Treatment at these temples largely centered around promoting healthy lifestyles, with a particular emphasis on a person's spiritual needs. Characteristic of the Asclepieion was the practice of '' incubatio'', also known as 'temple sleep.' This was a process by which patients would go to sleep in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of Apollo), Coronis, or Arsinoe (Greek myth), Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represents the healing aspect of the medical arts; his daughters, the "Asclepiades", are: Hygieia ("Health, Healthiness"), Iaso (from ἴασις "healing, recovering, recuperation", the goddess of recuperation from illness), Aceso (from ἄκεσις "healing", the goddess of the healing process), Aegle (mythology), Aegle (the goddess of good health) and Panacea (the goddess of universal remedy). He has several sons as well. He was associated with the Roman/Etruscan god Vediovis and the Egyptian Imhotep. He shared with Apollo the epithet ''Paean'' ("the Healer"). The rod of Asclepius, a snake-entwined staff, (similar to the caduceus) remains a symbol of medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odeon Of Herodes Atticus
The Odeon of Herodes Atticus (Greek: Ωδείο Ηρώδου του Αττικού; also called Herodeion or Herodion; Greek: Ηρώδειο) is a stone Roman theatre structure located on the southwest slope of the Acropolis of Athens, Greece. The building was completed in AD 161 and then renovated in 1950. Ancient times It was built in AD 161 by Herodes Atticus in memory of his Roman wife, Aspasia Annia Regilla. It was originally a steep-sloped theatre with a three-story stone front wall and a wooden roof made of expensive cedar of Lebanon timber. It was used as a venue for music concerts with a capacity of 5,000. It lasted intact until it was destroyed and left in ruins by the Heruli in AD 267. Modern events The audience stands and the orchestra (stage) were restored using Pentelic marble in the 1950s. Since then it has been the main venue of the Athens Festival, which runs from May through October each year, featuring a variety of acclaimed Greek as well as International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Temple Of Athena
The Old Temple of Athena or the Archaios Neos (Greek: Ἀρχαῖος Νεώς) was an archaic Greek limestone Doric temple on the Acropolis of Athens probably built in the second half of the sixth-century BCE, and which housed the xoanon of Athena Polias. The existence of an archaic temple to Athena had long been conjectured from literary references until the discovery of substantial building foundations under the raised terrace between the Erechtheion and Parthenon in 1886 confirmed it. While it is uncontroversial that a temple stood on the central acropolis terrace in the late archaic period and was burnt down in the Persian invasion of 480, nevertheless questions of its nature, name, reconstruction and duration remain unresolved. Evidence Prior to the archaeological discoveries of the late 19th century, the existence of the archaic temple on the acropolis was known only from literary testimonia, and the few remains from the archaic buildings which have been visible continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandroseion
The Pandroseion (pronounced: panδrosion, Greek: Πανδρόσειον) was a sanctuary dedicated to Pandrosus, one of the daughters of Cecrops I, the first king of Attica Greece, located on the Acropolis of Athens. It occupied the space adjacent to the Erechtheum and the old Temple of Athena Polias. The sanctuary was a walled trapezoidal courtyard containing the altar of Zeus Herkeios (protector of the hearth, of the courtyard) under the sacred Olive Tree planted by Athena. At the west was an entrance stoa from the Propylea. In the northeast corner was an elaborate entrance into the north porch and the entire Etrechtheion complex. At the east, there was also a small opening through which the Thalassa of Poseidon could be viewed. The south-east corner gave access to what some thought was the tomb of Cecrops. The sanctuary also contained the sacred olive tree which was presented by Athena to the city of Athens, after her victory over Poseidon in the contest for the land of Attic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalkotheke
The Chalkotheke (Greek for "bronze store") was a structure on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece. Its name and function are only known from 4th century BC inscriptions. One decree orders the listing of all objects stored in the Chalkotheke and the erection of a '' stele'' inscribed with that list in front of the building.Inscriptiones Graecae II² 120. Remains of a structure discovered to the east of the sanctuary of Artemis Brauronia and immediately to the southwest of the Parthenon have been suggested to be those of the Chalkotheke. Only scant limestone foundations and rock-cut foundation trenches survive. The building stood in front of the southern Acropolis wall and was ''circa'' 43 m long and 14 m wide, fronted on its northern long side by a portico of 4.5 m width. To make room for that portico, the southernmost portion of the rock-cut steps leading up to the west facade of the Parthenon had to be cut away. Thus, the portico is assumed to have been an early fourth century BC addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |