|
Accipiter Melanoleucus
The black sparrowhawk (''Accipiter melanoleucus''), sometimes known as the black goshawk or great sparrowhawk, is the largest African member of the genus ''Accipiter''.Arkive. Black goshawk (''Accipiter melanoleucus''). In: Arkive: Images of Life on Earth.. Retrieved 6 October 2011. It occurs mainly in forest and non-desert areas south of the Sahara, particularly where there are large trees suitable for nesting; favored habitat includes suburban and human-altered landscapes. It preys predominantly on birds of moderate size, such as pigeons and doves, in suburban areas.Curtis O.E., Hockey P.A.R., Koeslag A. 2007Competition with Egyptian geese ''Alopochen aegyptiaca'' overrides environmental factors in determining productivity of Black Sparrowhawks ''Accipiter melanoleucus'' ''Ibis'' 149: 502‐508. Taxonomy There are 2 subspecies of black sparrowhawk: ''Accipiter melanoleucus melanoleucus'', which was named by A. Smith in 1830, and ''Accipiter melanoleucus temminckii'', which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Smith (zoologist)
Sir Andrew Smith (3 December 1797 – 11 August 1872) was a British surgeon, explorer, ethnologist and zoologist. He is considered the father of zoology in South Africa having described many species across a wide range of groups in his major work, ''Illustrations of the Zoology of South Africa''. Smith was born in Hawick, Roxburghshire. He qualified in medicine at the University of Edinburgh obtaining an M.D. degree in 1819, having joined the Army Medical Services in 1816. South Africa 1820–1837 In 1820 he was ordered to the Cape Colony and was sent to Grahamstown to supervise the medical care of European soldiers and soldiers of the Cape Corps. He was appointed the Albany district surgeon in 1822 and started the first free dispensary for indigent patients in South Africa. He led a scientific expedition into the interior and was able to indulge in his interests of natural history and anthropology. On several occasions, he was sent by governors on confidential missions to vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Goshawk
The northern goshawk (; ''Accipiter gentilis'') is a species of medium-large bird of prey, raptor in the Family (biology), family Accipitridae, a family which also includes other extant diurnal raptors, such as eagles, buzzards and harrier (bird), harriers. As a species in the genus ''Accipiter'', the goshawk is often considered a "true hawk". The scientific name is Latin; ''Accipiter'' is "hawk", from ''accipere'', "to grasp", and ''gentilis'' is "noble" or "gentle" because in the Middle Ages only the nobility were permitted to fly goshawks for falconry. This species was first described by Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus in his ''Systema naturae'' in 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 1758 as ''Falco gentilis''. It is a widespread species that inhabits many of the temperate parts of the Northern Hemisphere. The northern goshawk is the only species in the genus ''Accipiter'' found in both Eurasia and North America. It may have the second widest distribution of any true member of the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an animal or a plant to avoid observation or detection by other animals. It may be a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation. Methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle and mimicry. Crypsis can involve visual, olfactory (with pheromones) or auditory concealment. When it is visual, the term cryptic coloration, effectively a synonym for animal camouflage, is sometimes used, but many different methods of camouflage are employed by animals or plants. Overview There is a strong evolutionary pressure for animals to blend into their environment or conceal their shape, for prey animals to avoid predators and for predators to be able to avoid detection by prey. Exceptions include large herbivores without natural enemies, brilliantly colored birds that rely on flight to escape predators, and venomous or otherwise powerfully armed animals with warning coloration. Cryptic animals include the tawny frogmouth (feather pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by change in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations that interlock with those of the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
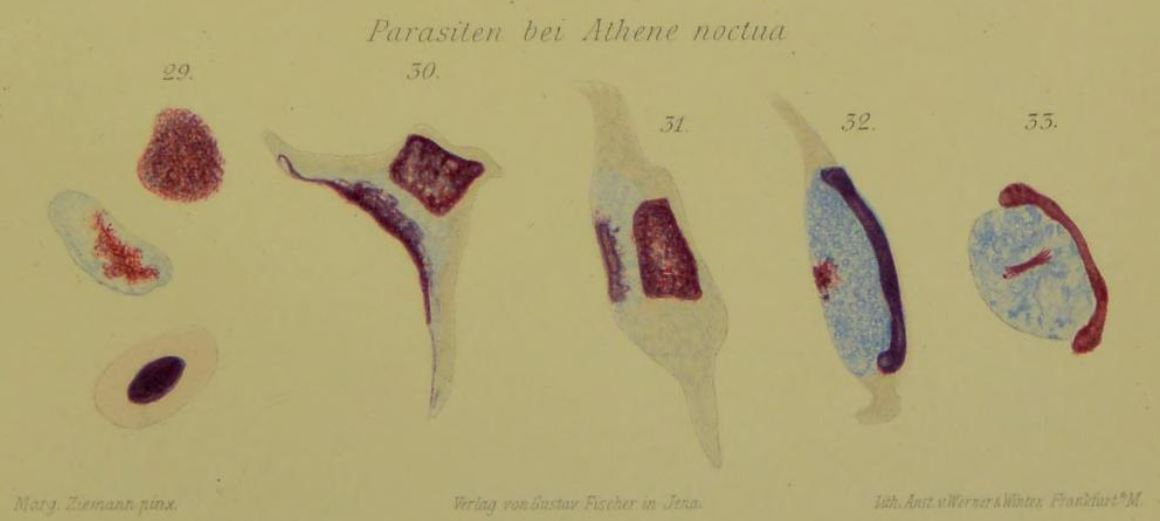
Haemoproteus
''Haemoproteus'' is a genus of alveolates that are parasitic in birds, reptiles and amphibians. Its name is derived from Greek: ''Haima'', "blood", and ''Proteus'', a sea god who had the power of assuming different shapes. The name ''Haemoproteus'' was first used in the description of '' H. columbae'' in the blood of the pigeon ''Columba livia'' by Kruse in 1890. This was also the first description of this genus. Two other genera — '' Halteridium'' and '' Simondia'' — are now considered to be synonyms of ''Haemoproteus''. The protozoa are intracellular parasites that infect the erythrocytes. They are transmitted by blood sucking insects including mosquitoes, biting midges (''Culicoides''), louse flies (''Hippoboscidae'') and horse-flies (" tabanids", "tabanid flies"). Infection with this genus is sometimes known as pseudomalaria because of the parasites' similarities with ''Plasmodium'' species. Within the genus there are at least 173 species, 5 varieties and 1 subspecies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucocytozoon
''Leucocytozoon '' (or ''Leukocytozoon'') is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa (which also includes the malaria parasites). The species of this genus use either blackflies ('' Simulium'' species) or a biting midge as their definitive host and birds as their intermediate host. There are over 100 species in this genus. Over 100 species of birds have been recorded as hosts to these parasites. Life cycle Parasites in the genus ''Leucocytozoon'' have a life cycle that involves both a bird host, and a black fly (with the exception of ''Leucocytozoon caulleryi'' which cycles between a bird host and a biting midge). Parasites enter the bird host in a form called a sporozoite through the bite of the blood-sucking black fly. The sporozoites invade host cells in the liver where they undergo asexual replication, forming numerous daughter cells called merozoites within 4–5 days. The duration of this stage depends in part upon the species. In some spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematozoa
Hematozoa is a subclass of blood parasites of the Apicomplexa clade. Well known examples include the ''Plasmodium'' spp. which cause malaria in humans and Theilera which causes theileriosis in cattle. A large number of species are known to infect birds and are transmitted by insect vectors. The pattern in which Haematozoa infect a host cell depends on the genera of the blood parasite. ''Plasmodium'' and ''Leucozytozoon'' displace the nucleus of the host cell so that the parasite can take control of the cell where as ''Hemoproteus'' completely envelops the nucleus in a host cell. Infections of haematozoa can have adverse fitness effects on certain species. Species that have been isolated or have not been exposed to the infection have been found to be especially vulnerable to pathogenic effects. The infection effects can persist in avian host species through long-distance migrations. Blood parasites that have been studied were found to be transmitted by hematophagous (bloodsucking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratopogonidae
Ceratopogonidae is a family of flies commonly known as no-see-ums, or biting midges, generally in length. The family includes more than 5,000 species, distributed worldwide, apart from the Antarctic and the Arctic. Ceratopogonidae are holometabolous, meaning their development includes four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and imago or adult. Most common species in warmer climates will take about two to six weeks to complete a life cycle. Both adult males and females feed on nectar. Most females also feed on the blood of vertebrates, including humans, to get protein for egg-laying. Their bites are painful, and can cause intensely itchy lesions. Their mouthparts are well-developed for cutting the skin of their hosts. Some species prey on other insects. Larvae need moisture to develop, but also air and food. They are not strictly aquatic or terrestrial. Some species within the biting midges are thought to be predatory on other small insects. Particularly mosquito larvae have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Fly
A black fly or blackfly (sometimes called a buffalo gnat, turkey gnat, or white socks) is any member of the family Simuliidae of the Culicomorpha infraorder. It is related to the Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae, and Thaumaleidae. Over 2,200 species of black flies have been formally named, of which 15 are extinct. They are divided into two subfamilies: Parasimuliinae contains only one genus and four species; Simuliinae contains all the rest. Over 1,800 of the species belong to the genus ''Simulium''. Most black flies gain nourishment by feeding on the blood of mammals, including humans, although the males feed mainly on nectar. They are usually small, black or gray, with short legs, and antennae. They are a common nuisance for humans, and many U.S. states have programs to suppress the black fly population. They spread several diseases, including river blindness in Africa (''Simulium damnosum'' and ''S. neavei'') and the Americas (''S. callidum'' and ''S. metallicum'' in Central Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy (from Greek , 'more', and , 'way') occurs when one gene influences two or more seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits. Such a gene that exhibits multiple phenotypic expression is called a pleiotropic gene. Mutation in a pleiotropic gene may have an effect on several traits simultaneously, due to the gene coding for a product used by a myriad of cells or different targets that have the same signaling function. Pleiotropy can arise from several distinct but potentially overlapping mechanisms, such as gene pleiotropy, developmental pleiotropy, and selectional pleiotropy. Gene pleiotropy occurs when a gene product interacts with multiple other proteins or catalyzes multiple reactions. Developmental pleiotropy occurs when mutations have multiple effects on the resulting phenotype. Selectional pleiotropy occurs when the resulting phenotype has many effects on fitness (depending on factors such as age and gender). An example of pleiotropy is phenylketonuria, an inherited d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution. ::"The chromosomal or genomic location of a gene or any other genetic element is called a locus (plural: loci) and alternative DNA sequences at a locus are called alleles." The simplest alleles are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). but they can also be insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Popular definitions of 'allele' typically refer only to different alleles within genes. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles (variants). In population genetics, nearly every living human's phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |