|
Abv
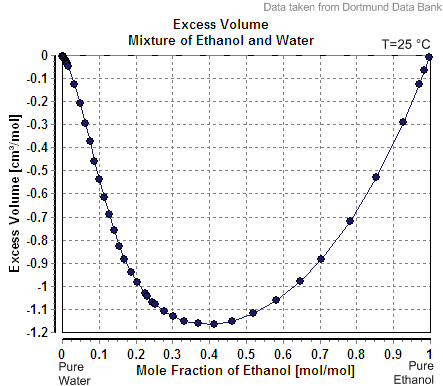
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as ABV, abv, or alc/vol) is a standard measure of how much alcohol (ethanol) is contained in a given volume of an alcoholic beverage (expressed as a volume percent). It is defined as the number of millilitres (mL) of pure ethanol present in of solution at . The number of millilitres of pure ethanol is the mass of the ethanol divided by its density at , which is . The ABV standard is used worldwide. The International Organization of Legal Metrology has tables of density of water–ethanol mixtures at different concentrations and temperatures. In some countries, e.g. France, alcohol by volume is often referred to as degrees Gay-Lussac (after the French chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac), although there is a slight difference since the Gay-Lussac convention uses the International Standard Atmosphere value for temperature, . Volume change Mixing two solutions of alcohol of different strengths usually causes a change in volume. Mixing pure water with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from cereal grains—most commonly from malted barley, though wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. During the brewing process, fermentation of the starch sugars in the wort produces ethanol and carbonation in the resulting beer.Barth, Roger. ''The Chemistry of Beer: The Science in the Suds'', Wiley 2013: . Most modern beer is brewed with hops, which add bitterness and other flavours and act as a natural preservative and stabilizing agent. Other flavouring agents such as gruit, herbs, or fruits may be included or used instead of hops. In commercial brewing, the natural carbonation effect is often removed during processing and replaced with forced carbonation. Some of humanity's earliest known writings refer to the production and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cider
Cider ( ) is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented juice of apples. Cider is widely available in the United Kingdom (particularly in the West Country) and the Republic of Ireland. The UK has the world's highest per capita consumption, as well as the largest cider-producing companies. Ciders from the South West of England are generally higher in alcoholic content. Cider is also popular in many Commonwealth countries, such as India, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. As well as the UK and its former colonies, cider is popular in Portugal (mainly in Minho and Madeira), France (particularly Normandy and Brittany), Friuli, and northern Spain (specifically Asturias). Central Europe also has its own types of cider with Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse producing a particularly tart version known as Apfelwein. In the U.S., varieties of fermented cider are often called ''hard cider'' to distinguish alcoholic cider from non-alcoholic apple cider or "sweet cider", also made from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absinthe ABV
Absinthe (, ) is an anise-flavoured spirit derived from several plants, including the flowers and leaves of ''Artemisia absinthium'' ("grand wormwood"), together with green anise, sweet fennel, and other medicinal and culinary herbs. Historically described as a highly alcoholic spirit, it is 45–74% Alcohol by volume, ABV or 90–148 proof US. Absinthe traditionally has a natural green color, but may also be colorless. It is commonly referred to in historical literature as ' ("the green fairy"). It is sometimes mistakenly referred to as a liqueur, but is not traditionally bottled with added sugar, so is classified as a spirit. Absinthe is traditionally bottled at a high level of alcohol by volume, but it is normally diluted with water before being consumed. Absinthe originated in the canton of Neuchâtel in Switzerland in the late 18th century. It rose to great popularity as an alcoholic drink in late 19th- and early 20th-century France, particularly among Parisian artists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-alcohol Beer
Low-alcohol beer is beer with little or no alcohol content and aims to reproduce the taste of beer while eliminating (or at least reducing) the inebriating effects of standard alcoholic brews. Most low-alcohol beers are lagers, but there are some low-alcohol ales. Low-alcohol beer is also known as light beer, non-alcoholic beer, small beer, small ale, or near-beer. History Low-alcoholic brews such as small beer date back at least to medieval Europe, where they served as a less risky alternative to water (which often was polluted by feces and parasites) and were less expensive than the full strength brews used at festivals. More recently, the temperance movements and the need to avoid alcohol while driving, operating machinery, taking certain medications, etc. led to the development of non-intoxicating beers. In the United States, according to John Naleszkiewicz, non-alcoholic brews were promoted during Prohibition. In 1917, President Wilson proposed limiting the alcohol content ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubâ
Tubâ () is a Filipino alcoholic beverage created from the sap of various species of palm trees. During the Spanish colonial period, tubâ was introduced to Guam, the Marianas, and Mexico via the Manila Galleons. They remain popular in Mexico, especially in the states of Colima, Jalisco, Michoacán, Nayarit, and Guerrero. Tubâ was also introduced to the Torres Strait Islands of Australia in the mid-19th century by Filipino immigrant workers in the pearling industry. History Tubâ has existed in the Philippines since pre-colonial times. They were widely consumed for recreation as well as play an important role in the animist religious rituals presided by ''babaylan'' shamans. Heavy consumption of tubâ and other alcoholic beverages in the Philippines were reported by early Spanish colonizers. Social drinking (''inuman'' or ''tagayan'' in Tagalog and Visayan languages) was and continues to be an important aspect of Filipino social interactions. A peculiar and universal drin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kombucha
Kombucha (also tea mushroom, tea fungus, or Manchurian mushroom when referring to the culture; Latin name ''Medusomyces gisevii'') is a fermented, lightly effervescent, sweetened black tea drink commonly consumed for its purported health benefits. Sometimes the beverage is called kombucha tea to distinguish it from the culture of bacteria and yeast. Juice, spices, fruit or other flavorings are often added. Kombucha is thought to have originated in China, where the drink is traditional. By the early 20th century it had spread to Russia, then other parts of Eastern Europe and Germany. Kombucha is now homebrewed globally, and also bottled and sold commercially. The global kombucha market was worth approximately billion . Kombucha is produced by symbiotic fermentation of sugared tea using a ''symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast'' (SCOBY) commonly called a "mother" or "mushroom". The microbial populations in a SCOBY vary. The yeast component generally includes ''Saccharomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palm Wine
Palm wine, known by several #Names, local names, is an alcoholic beverage created from the sap of various species of palm tree such as the Borassus, palmyra, date palms, and coconut palms. It is known by various names in different regions and is common in various parts of Africa, the Caribbean, South America, South Asia, Southeast Asia and Micronesia. Palm wine production by smallholders and individual farmers may promote conservation as palm trees become a source of regular household income that may economically be worth more than the value of timber sold. Tapping The sap is extracted and collected by a tapper. Typically the sap is collected from the cut flower of the palm tree. A container is fastened to the flower stump to collect the sap. The white liquid that initially collects tends to be very sweet and non-Alcoholic beverage, alcoholic before it is fermentation (food), fermented. An alternative method is the felling of the entire tree. Where this is practised, a fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol (data Page)
This page provides supplementary chemical data on ethanol. Material Safety Data Sheet External MSDS Structure and properties Thermodynamic properties Spectral data Vapor pressure of liquid Density of ethanol at various temperatures Data obtained from These data correlate as ρ /cm3= −8.461834 ''T'' �C+ 0.8063372 with an ''R''2 = 0.99999. Properties of aqueous ethanol solutions Data obtained from Boiling points of aqueous solutions Data obtained from ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry (Page 2117)'' ‡ Azeotropic mixture Charts References * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ethanol (data page) Chemical data pages Data page Chemical data pages cleanup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholic Beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol that acts as a drug and is produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The consumption of alcoholic drinks, often referred to as "drinking", plays an important social role in many cultures. Most countries have laws regulating the production, sale, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. Regulations may require the labeling of the percentage alcohol content (as ABV or proof) and the use of a warning label. Some countries ban such activities entirely, but alcoholic drinks are legal in most parts of the world. The global alcoholic drink industry exceeded $1 trillion in 2018. Alcohol is a depressant, which in low doses causes euphoria, reduces anxiety, and increases sociability. In higher doses, it causes drunkenness, stupor, unconsciousness, or death. Long-term use can lead to an alcohol use disorder, an incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume Percent
In chemistry and fluid mechanics, the volume fraction φ''i'' is defined as the volume of a constituent ''V''''i'' divided by the volume of all constituents of the mixture ''V'' prior to mixing: :\phi_i = \frac Being dimensionless quantity, dimensionless, its unit is 1; it is expressed as a number, e.g., 0.18. It is the same concept as volume percent (vol%) except that the latter is expressed with a denominator of 100, e.g., 18%. The volume fraction coincides with the volume concentration in ideal solutions where the volumes of the constituents are additive (the volume of the solution is equal to the sum of the volumes of its ingredients). The sum of all volume fractions of a mixture is equal to 1: :\sum_^ V_i = V ; \qquad \sum_^ \phi_i = 1 The volume fraction (percentage by volume, vol%) is one way of expressing the composition of a mixture with a dimensionless quantity; mass fraction (chemistry), mass fraction (percentage by weight, wt%) and mole fraction (percentage by mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chūhai
, an abbreviation of " shōchū highball" (焼酎ハイボール), is an alcoholic drink originating from Japan. Traditional chūhai is made with barley shōchū and carbonated water flavored with lemon, but some modern commercial variants use vodka in place of shōchū, and beverage companies have diversified into a variety of flavors, including lime, grapefruit, apple, orange, pineapple, grape, kyoho grape, kiwi, ''ume'', ''yuzu'', lychee, peach, strawberry cream, and cream soda. The alcohol content of chūhai sold in bars and restaurants can be quite low, allowing those with a low tolerance for alcohol to drink safely. Canned chūhai, however, can have higher levels of alcohol and is often sold in convenience stores and from vending machines. Although the amount varies (usually starting at 3%), canned chūhai contains less than 10% alcohol in Japan, as anything higher triggers a higher tax rate. Chūhai is served in tall glasses or mugs as drinks for individuals, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)