|
Abhir
Ahir or Aheer are a community of traditionally non-elite pastoralists in India, most members of which identify as being of the Indian Yadav community because they consider the two terms to be synonymous. The Ahirs are variously described as a caste, a clan, a community, a race and a tribe. The traditional occupations of Ahirs are cattle-herding and agriculture. Since late 19th century to early 20th century, Ahirs have adopted ''Yadav'' word for their community and have claimed descent from the mythological king Yadu as a part of a movement of social and political resurgence Quote: "The movement, which had a wide interregional spread, attempted to submerge regional names such as Goala, Ahir, Ahar, Gopa, etc., in favour of the generic term Yadava (Rao 1979). Hence a number of pastoralist castes were subsumed under Yadava, in accordance with decisions taken by the regional and national level caste sabhas. The Yadavas became the first among the shudras to gain the right to wear th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abhira Tribe
The Abhira tribe is mentioned in the ancient Indian epic Mahabharata. A historical people of the same name are mentioned in the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea''. They are thought to be people who moved in from eastern Iran in the aftermath of the invasion of Alexander the Great. Their main base was in the Indus delta (modern Sindh and Kathiawar), where their country is mentioned as "Abiria" and "Aberia" in classical sources. There were also other communities of Abhiras in modern Haryana. Etymology Etymologically, he who can cast terror on all sides is called an Abhira., History Sunil Kumar Bhattacharya says that the Abhiras are mentioned in the first-century work of classical antiquity, the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea''. He considers them to be a race rather than a tribe. Scholars such as Ramaprasad Chanda believe that they were Indo-Aryan peoples. but others, such as Romila Thapar, believe them to have been indigenous. The Puranic Abhiras occupied the territories of Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yadav
Yadav refers to a grouping of traditionally non-elite, Quote: "The Yadavs were traditionally a low-to-middle-ranking cluster of pastoral-peasant castes that have become a significant political force in Uttar Pradesh (and other northern states like Bihar) in the last thirty years." peasant- pastoral communities or castes in India that since the 19th and 20th centuries Quote: "In a not dissimilar way the various cow-keeping castes of northern India were combining in 1931 to use the common term of Yadava for their various castes, Ahir, Goala, Gopa, etc., and to claim a Rajput origin of extremely doubtful authenticity." have claimed descent from the mythological king Yadu as a part of a movement of social and political resurgence. Quote: "The movement, which had a wide interregional spread, attempted to submerge regional names such as Goala, Ahir, Ahar, Gopa, etc., in favour of the generic term Yadava (Rao 1979). Hence a number of pastoralist castes were subsumed under Yadava, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the ''Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the Kurukshetra War and the fates of the Kaurava and the Pāṇḍava princes and their successors. It also contains philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the '' Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyāsa. There have been many attempts to unravel its historical growth and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yadu
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions. From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent – Indus Valley (roughly today's Punjab), Western India, Northern India, Central India, and also in areas of the southern part like Sri Lanka and the Maldives through and after a complex process of migration, assimilation of other peoples and language shift.Mallory, J.P.; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. . Ancestors *Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers) **Proto-Indo-Iranians (common ancestors of the Iranian, Nuristani and Indo-Aryan peoples) ( Proto-Indo-Iranian speakers) ***Proto-Indo-Aryans (Proto-Indo-Aryan language, Proto-Indo-Aryan speakers) Vedic tribes * Alina people (RV 7.18.7) * Āndhra (tribe), Andhras * Anu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Indo-Aryan languages, excluding earlier inscriptions and the later Pali. ''Prākṛta'' literally means "natural", as opposed to ''saṃskṛta'', which literally means "constructed" or "refined". Prakrits were considered the regional spoken (informal) languages of people, and Sanskrit was considered the standardized (formal) language used for literary, official and religious purposes across Indian kingdoms of the subcontinent. Literary registers of Prakrits were also used contemporaneously (predominantly by śramaṇa traditions) alongside Classical Sanskrit of higher social classes. Etymology The dictionary of Monier Monier-Williams (1819–1899), and other modern authors however, interpret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry, comprising 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. Covering the southern part of the peninsular Deccan Plateau, South India is bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse with two mountain ranges – the Western and Eastern Ghats – bordering the plateau heartland. The Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Tungabhadra, Periyar, Bharathappuzha, Pamba, Thamirabarani, Palar, and Vaigai rivers are important perennial rivers. The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major Dravidian languages: Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam and Kannada (all 4 of which are among the 6 Classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966, which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The bank also maintains 31 field offices around the world to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries. From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members. The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public. The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
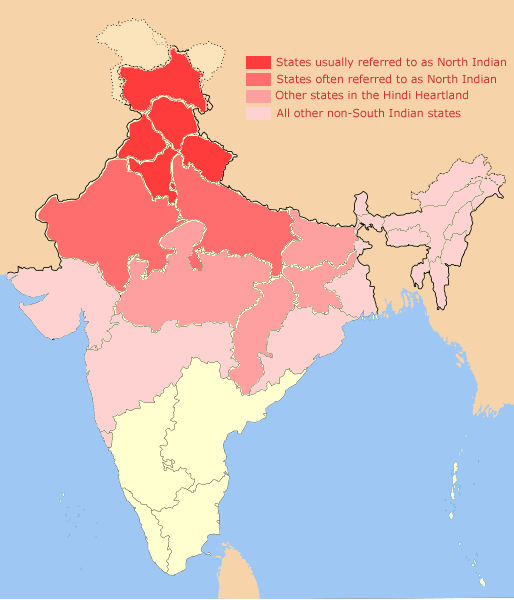
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaduvanshi
Yadu () is the founder of the Yadu dynasty in Hinduism. He is described to be the eldest son of King Yayati, and his queen, Devayani. Legend According to a narrative found in the Mahabharata, and the Vishnu Purana, Yadu refused to exchange his years of youth with his father, Yayati, when the latter was cursed with senility by his father-in-law, Shukra. Thus, he was cursed by Yayati to have his progeny disinherited of the dominion. Due to this proclamation, Yadu was replaced by his step-brother, Puru, as the heir to the throne of the Chandravamsha dynasty. Yadu founded his own cadet branch of the dynasty, called the Yaduvamsha. Descendants The Agni Purana states that Yadu's lineage was continued by his eldest son, Sahasrajit. Sahasrajit had three sons: Haihaya, Reṇuhaya, and Haya. A historical dynasty called the Haihayas claimed descent from Haihaya. Several castes and communities in modern India, such as Ahir or Yadav, Chudasama, claim descent from Yadu. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundelkhand
Bundelkhand (, ) is a geographical and cultural region and a proposed state and also a mountain range in central & North India. The hilly region is now divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion lying in the latter state. Jhansi is the largest city in Bundelkhand. Another major city of Bundelkhand is Sagar being second largest city of Bundelkhand and headquarter of Sagar Division. Etymology Bundelkhand means "Bundela domain". The region was earlier known as Jejabhukti or Jejakabhukti ("Jeja's province"). According to the inscriptions of the Chandela dynasty, this name derived from Jeja, the nickname of their ruler Jayashakti. However, it is possible that the name derives from an even earlier name of the region: "Jajhauti" or "Jijhoti". After the Bundelas replaced the Chandelas around 14th century, the region came to be known as Bundelkhand after them. History Under the British Raj, Bundelkhand included the princely states of Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |