|
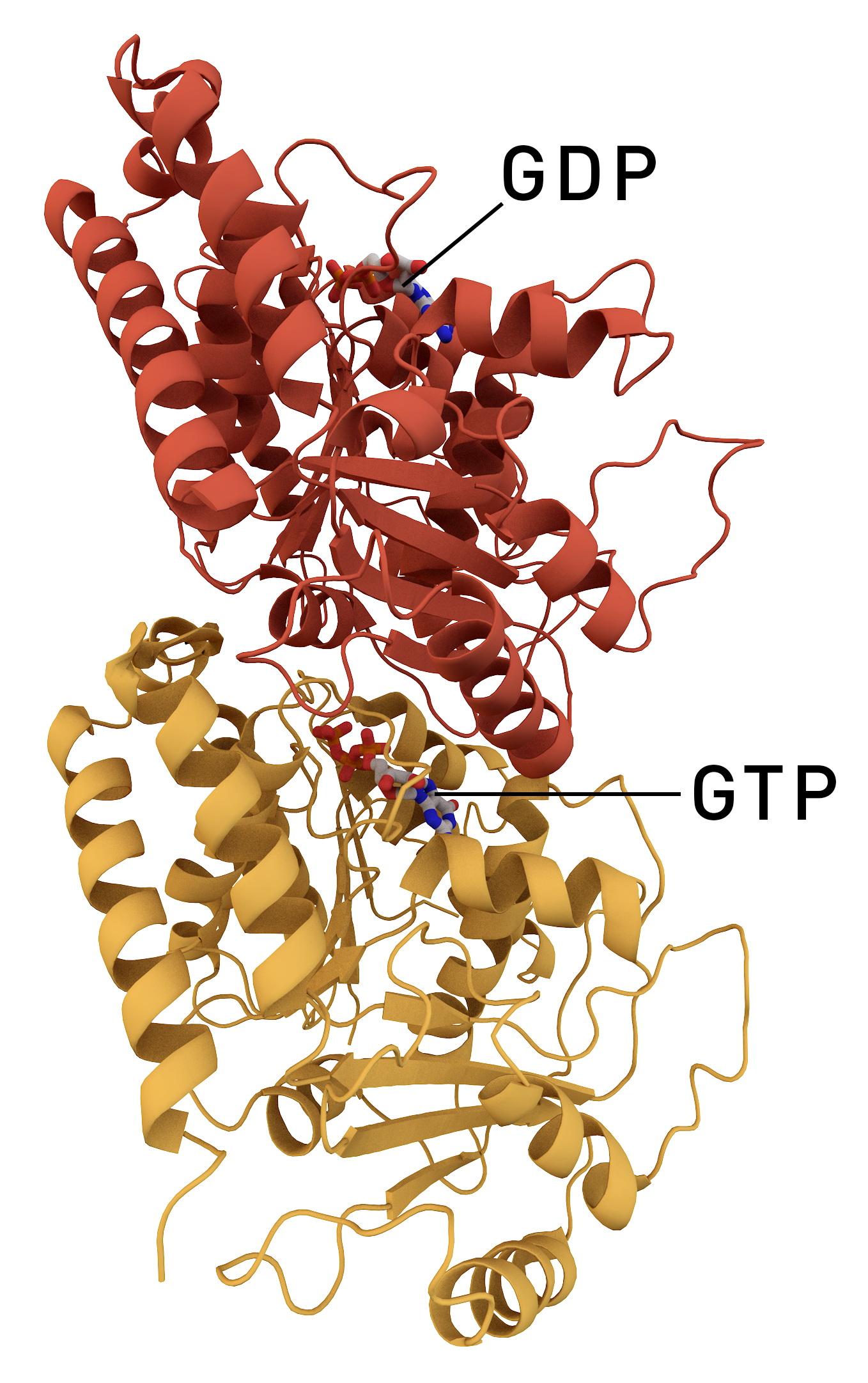
AURKA
Aurora kinase A also known as serine/threonine-protein kinase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AURKA'' gene. Aurora A is a member of a family of mitotic serine/threonine kinases. It is implicated with important processes during mitosis and meiosis whose proper function is integral for healthy cell proliferation. Aurora A is activated by one or more phosphorylations and its activity peaks during the G2 phase to M phase transition in the cell cycle. Discovery The aurora kinases were first identified in 1990 during a cDNA screen of ''Xenopus'' eggs. The kinase discovered, Eg2, is now referred to as Aurora A. It was not until 1998, however, that Aurora A's meiotic and mitotic importance was realized. Aurora kinase family The human genome contains three members of the aurora kinase family: Aurora kinase A, Aurora kinase B and Aurora C kinase. The ''Xenopus'', ''Drosophila'', and ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' genomes, on the other hand, contain orthologues on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine/threonine-specific Protein Kinase
A serine/threonine protein kinase () is a kinase enzyme, in particular a protein kinase, that phosphorylates the OH group of the amino-acid residues serine or threonine, which have similar side chains. At least 350 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases (STK). In enzymology, the term ''serine/threonine protein kinase'' describes a class of enzymes in the family of transferases, that transfer phosphates to the oxygen atom of a serine or threonine side chain in proteins. This process is called phosphorylation. Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes and is a very important posttranslational modification. The chemical reaction performed by these enzymes can be written as :ATP + a protein \rightleftharpoons ADP + a phosphoprotein Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and a protein, whereas its two products are ADP and phosphoprotein. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maximum condensation in late anaphase, to help chromosome segregation and the re-formation of the nucleus. Anaphase starts when the anaphase promoting complex marks an inhibitory chaperone called securin for destruction by ubiquinylating it. Securin is a protein which inhibits a protease known as separase. The destruction of securin unleashes separase which then breaks down cohesin, a protein responsible for holding sister chromatids together. At this point, three subclasses of microtubule unique to mitosis are involved in creating the forces necessary to separate the chromatids: kinetochore microtubules, interpolar microtubules, and astral microtubules. The centromeres are split, and the sister chromatids are pulled toward the poles by ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerize
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them. In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize. Alkanes can also be polymerized, but only with the help of strong acids. As alkenes can polymerize in somewhat straightforward radical reactions, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
γ-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesin
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (thus kinesins are ATPases, a type of enzyme). The active movement of kinesins supports several cellular functions including mitosis, meiosis and transport of cellular cargo, such as in axonal transport, and intraflagellar transport. Most kinesins walk towards the plus end of a microtubule, which, in most cells, entails transporting cargo such as protein and membrane components from the center of the cell towards the periphery. This form of transport is known as anterograde transport. In contrast, dyneins are motor proteins that move toward the minus end of a microtubule in retrograde transport. Discovery Kinesins were discovered in 1985, based on their motility in cytoplasm extruded from the giant axon of the squid. They turned out as MT-based anterograde intracellular trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, organell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitotic Spindle
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells, or the meiotic spindle during meiosis, a process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Besides chromosomes, the spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins. Microtubules comprise the most abundant components of the machinery. Spindle structure Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Depolymerization of microtubules generates tension at kinetochores; bipolar attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules emanating from opposite cell pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a nuclear envelope is re-assembled around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli reappear, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. The mitotic spindle is disassembled and remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized. Telophase accounts for approximately 2% of the cell cycle's duration. Cytokinesis typically begins before late telophase and, when complete, segregates the two daughter nuclei between a pair of separate daughter cells. Telophase is primarily driven by the dephosphorylation In biochemistry, dephosphorylation is the removal of a phosphate (PO43−) group from an organic compound by hydrolysis. It is a reversible post-translational modification. Dephosphoryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Phase
S phase (Synthesis Phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S-phase are tightly regulated and widely conserved. Regulation Entry into S-phase is controlled by the G1 restriction point (R), which commits cells to the remainder of the cell-cycle if there is adequate nutrients and growth signaling. This transition is essentially irreversible; after passing the restriction point, the cell will progress through S-phase even if environmental conditions become unfavorable. Accordingly, entry into S-phase is controlled by molecular pathways that facilitate a rapid, unidirectional shift in cell state. In yeast, for instance, cell growth induces accumulation of Cln3 cyclin, which complexes with the cyclin dependent kinase CDK2. The Cln3-CDK2 complex promotes transcription of S-phase genes by inactivating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G1 Phase
The G1 phase, gap 1 phase, or growth 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis. G1 phase ends when the cell moves into the S phase of interphase. Around 30 to 40 percent of cell cycle time is spent in the G1 phase. Overview G1 phase together with the S phase and G2 phase comprise the long growth period of the cell cycle cell division called interphase that takes place before cell division in mitosis (M phase). During G1 phase, the cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and protein that are required for DNA synthesis. Once the required proteins and growth are complete, the cell enters the next phase of the cell cycle, S phase. The duration of each phase, including the G1 phase, is different in many different types of cells. In human somatic cells, the cell cycle lasts about 10 hours, and the G1 H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |