|
AAAS (gene)
AladinTM, also known as adracalin, is a nuclear envelope protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AAAS'' gene. It is named after the achalasia–addisonianism–alacrima syndrome (triple A syndrome) which occurs when the gene is mutated. Function Aladin is a component of the nuclear pore complex, to which it is attached by nucleoporin NDC1. Mutant aladin causes selective failure of nuclear protein import and hypersensitivity to oxidative stress. Mutant aladin also causes decreased nuclear import of aprataxin, a repair protein for single-strand breaks, and DNA ligase I, employed in DNA base excision repair. These decreases in DNA repair proteins may increase the susceptibility of cells to oxidative stress by allowing accumulation of oxidative DNA damages that trigger cell death. Clinical significance Mutations in the AAAS gene are responsible for Triple A syndrome (also known as Allgrove Syndrome). Triple-A syndrome is an autosomal recessive neuroendocrinological dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIG1
DNA ligase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''LIG1'' gene. DNA ligase I is the only known eukaryotic DNA ligase involved in both DNA replication and repair, making it the most studied of the ligases. Discovery It was known that DNA replication occurred through the breakage of the double DNA strand, but the enzyme responsible for ligating the strands back together, and mechanism of action, was unknown until Lehman, Gellert, Richardson, and Hurwitz laboratories, made significant contributions to the discovery of DNA ligase in 1967. Recruitment and regulation The LIG1 gene encodes a, 120kDa enzyme, 919 residues long, known as DNA ligase I. The DNA ligase I polypeptide contains an N-terminal replication factory-targeting sequence (RFTS), followed by a nuclear localization sequence A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
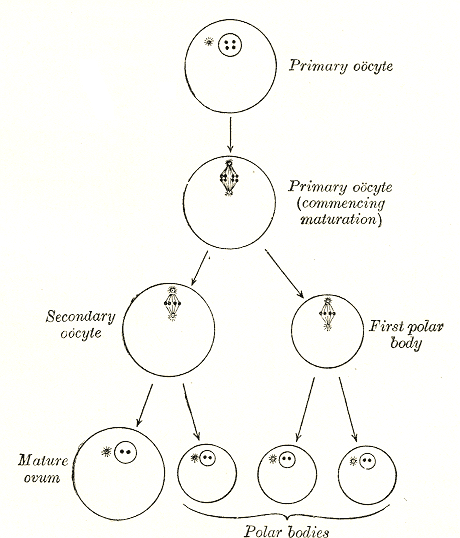
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrinology
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology (specifically of physiology) which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine systems often act together in a process called neuroendocrine integration, to regulate the physiological processes of the human body. Neuroendocrinology arose from the recognition that the brain, especially the hypothalamus, controls secretion of pituitary gland hormones, and has subsequently expanded to investigate numerous interconnections of the endocrine and nervous systems. The endocrine system consists of numerous glands throughout the body that produce and secrete hormones of diverse chemical structure, including peptides, steroids, and neuroamines. Collectively, hormones regulate many physiological processes. The neuroendocrine system is the mechanism by which the hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, regulating reproduction, metab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid human genome, genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY syndrome, XYY, Klinefelter syndrome, XXY, Triple X syndrome, XXX, XXXX syndrome, XXXX, XXXXX syndrome, XXXXX or XXYY syndrome, XXYY, among Aneuploidy, other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple-A Syndrome
Triple-A syndrome or AAA syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder. In most cases, there is no family history of AAA syndrome. The syndrome was first identified by Jeremy Allgrove and colleagues in 1978, since then just over 100 cases have been reported. The syndrome, is called triple aaa due to the manifestation of the illness which include achalasia (a dysfunction of the esophagus), addisonianism (adrenal insufficiency of primary type), and alacrima (insufficiency of tears). Alacrima is usually the earliest manifestation. Neurodegeneration or atrophy of the nerve cells and autonomic dysfunction may be seen in the disorder, therefore some have suggested the disorder be called 4A syndrome. It is a progressive disorder that can take years to develop the full-blown clinical picture. The disorder also has variability and heterogeneity in presentation. Presentation Individuals affected by AAA have adrenal insufficiency/Addison's disease due to ACTH resistance, alac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple A Syndrome
Triple-A syndrome or AAA syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder. In most cases, there is no family history of AAA syndrome. The syndrome was first identified by Jeremy Allgrove and colleagues in 1978, since then just over 100 cases have been reported. The syndrome, is called triple aaa due to the manifestation of the illness which include achalasia (a dysfunction of the esophagus), addisonianism ( adrenal insufficiency of primary type), and alacrima (insufficiency of tears). Alacrima is usually the earliest manifestation. Neurodegeneration or atrophy of the nerve cells and autonomic dysfunction may be seen in the disorder, therefore some have suggested the disorder be called 4A syndrome. It is a progressive disorder that can take years to develop the full-blown clinical picture. The disorder also has variability and heterogeneity in presentation. Presentation Individuals affected by AAA have adrenal insufficiency/Addison's disease due to ACTH resistance, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Oxidation
DNA oxidation is the process of oxidative damage of deoxyribonucleic acid. As described in detail by Burrows et al., 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) is the most common oxidative lesion observed in duplex DNA because guanine has a lower one-electron reduction potential than the other nucleosides in DNA. The one electron reduction potentials of the nucleosides (in volts versus NHE) are guanine 1.29, adenine 1.42, cytosine 1.6 and thymine 1.7. About 1 in 40,000 guanines in the genome are present as 8-oxo-dG under normal conditions. This means that >30,000 8-oxo-dGs may exist at any given time in the genome of a human cell. Another product of DNA oxidation is 8-oxo-dA. 8-oxo-dA occurs at about 1/10 the frequency of 8-oxo-dG. The reduction potential of guanine may be reduced by as much as 50%, depending on the particular neighboring nucleosides stacked next to it within DNA. Excess DNA oxidation is linked to certain diseases and cancers, while normal levels of oxidized nucleot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Excision Repair
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky helix-distorting lesions. BER is important for removing damaged bases that could otherwise cause mutations by mispairing or lead to breaks in DNA during replication. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. These are then cleaved by an AP endonuclease. The resulting single-strand break can then be processed by either short-patch (where a single nucleotide is replaced) or long-patch BER (where 2–10 new nucleotides are synthesized). Lesions processed by BER Single bases in DNA can be chemically damaged by a variety of mechanisms, the most common ones being deamination, oxidation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


