|
904
__NOTOC__ Year 904 ( CMIV) was a leap year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * July 29 – Sack of Thessalonica: A Muslim fleet, led by the Greek renegade Leo of Tripoli, appears outside Thessalonica and begins its attack after a short and silent inspection of the fortification of the city. After attacks from the sea for two days, the Saracens are able to storm the city walls, overcome the Thessalonians' resistance and capture the city. The sacking continues for a full week, before the raiders depart for their base in the Levant. Having freed 4,000 Muslim prisoners and captured 60 ships, gaining a large loot, they carry off 22,000 men and women as slaves.Faith and Sword: A short history of Christian-Muslim conflict by Alan G. Jamieson, p. 32. * Arab–Byzantine War: The Byzantines under Andronikos Doukas, along with Eustathios Argyros, campaign against the Abbasids and defeat the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sack Of Thessalonica (904)
The Sack of Thessalonica refers to the capture, and subsequent sack, of the Byzantine city of Thessalonica by the Abbasid Caliphate in the year 904, led by Leo of Tripoli, a privateer and Muslim convert. Background The city, which is now in modern-day Greece, was in 904 A.D. a part of the Byzantine Empire, and was considered the greatest city in the empire, second only to Constantinople. Following the weakening of centralized power in the Abbasid Caliphate due to the Fourth Fitna and the Anarchy at Samarra, many areas of the vast Abbasid Caliphate began to breakaway from the Caliph's control and while still paying religious lip service, acted independently on military and state matters. The attention of these largely autonomous Muslim dynasties was subsequently turned to the Mediterranean sea. In 860 the Muslim dynasties attempted to reassert their dominance over the Mediterranean seaway and built naval bases at Tripoli and Tarsus. In 898, the eunuch admiral Raghib, a forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Of Tripoli
Leo of Tripoli ( el, Λέων ὸ Τριπολίτης), known in Arabic as Rashīq al-Wardāmī (), and Ghulām Zurāfa (), was a Greek renegade and fleet commander for the Abbasid Caliphate in the early tenth century. He is most notable for his sack of Thessalonica, the Byzantine Empire's second city, in 904. Life Nothing is known of Leo's early life except that he was born in or near Attaleia, the capital of the maritime Cibyrrhaeot Theme, and was captured in an Arab raid and brought to Tripoli. In captivity, he converted to Islam, and entered the service of his captors as a seaman and commander. In Arabic sources he is called Lāwī Abū'l-Ḥārith and given the sobriquet ghulām Zurāfa, "servant/page of Zurafa", probably reflecting the name of his first Muslim master. He is also referred to as Rashīq al-Wardāmī. Alexander Vasiliev interpreted the element ''Wardāmī'' in his second Arabic name to mean that Leo was a Mardaite. The details of Leo's early career in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurszán
Kurszán (died 904), was a kende of the Magyars in the dual leadership with Árpád serving as a gyula - according to a mainstream theory. While ''kende'' probably corresponded roughly to the Khazar title ''khagan'', Kurszán's role equated to the Khazar military title '' bek''. In Latin sources he was referred to as '' rex'' and some scholars say he had a political status as a sacred king until he was massacred in a political plot of Western rulers and was temporarily succeeded by Árpád. Hungarian conquest He had a crucial role in the Hungarian Conquest (Honfoglalás). In 892/893 together with Arnulf of Carinthia he attacked Great Moravia to secure the eastern borders of the Frankish Empire. Arnulf gave him all the captured lands in Moravia. Kurszán also occupied the southern part of Hungary that had belonged to the Bulgarian Kingdom. He entered into an alliance with the Byzantine emperor Leo VI after realizing the country's vulnerability from the south. Together they surpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) ... and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares land borders with Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south. Tirana is its capital and largest city, followed by Durrës, Vlorë, and Shkodër. Albania displays varied climatic, geological, hydrological, and morphological conditions, defined in an area of . It possesses significant diversity with the landscape ranging from the snow-capped mountains in the Accursed Mountains, Albanian Alps as well as the Korab, Central Mountain R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
July 29
Events Pre-1600 *587 BC – The Neo-Babylonian Empire sacks Jerusalem and destroys the First Temple. * 615 – Pakal ascends the throne of Palenque at the age of 12. * 904 – Sack of Thessalonica: Saracen raiders under Leo of Tripoli sack Thessaloniki, the Byzantine Empire's second-largest city, after a short siege, and plunder it for a week. * 923 – Battle of Firenzuola: Lombard forces under King Rudolph II and Adalbert I, margrave of Ivrea, defeat the dethroned Emperor Berengar I of Italy at Firenzuola (Tuscany). * 1014 – Byzantine–Bulgarian wars: Battle of Kleidion: Byzantine emperor Basil II inflicts a decisive defeat on the Bulgarian army, and his subsequent treatment of 15,000 prisoners reportedly causes Tsar Samuil of Bulgaria to die of a heart attack less than three months later, on October 6. *1018 – Count Dirk III defeats an army sent by Emperor Henry II in the Battle of Vlaardingen. * 1030 – Ladejarl- Fairhair success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustathios Argyros (general Under Leo VI)
Eustathios Argyros ( el, Εὐστάθιος Ἀργυρός; died ca. 910) was a Byzantine aristocrat and one of the most prominent generals under Emperor Leo VI the Wise (r. 886–912). The first member of the Argyros family to rise to high posts, he fought with distinction against the Arabs in the east, before being disgraced ca. 907, possibly in connection with the flight of Andronikos Doukas to the Arabs. Rehabilitated soon after, he was appointed as ''strategos'' of Charsianon, from which post he oversaw the settlement of Armenian lords as march-wardens along the Empire's eastern frontier. Promoted to commander of the imperial bodyguard in late 908, he again fell into disgrace shortly after and died of poison (apparently a suicide) on his way to his estates. Life Eustathios Argyros was the son of the ''tourmarches'' Leo Argyros, the founder of the noble Argyros family. Nothing is known of his life or prior to the turn of the 10th century, although he may have been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capital city, capital of the geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, the administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek language, Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Vardar, Axios. The Thessaloniki (municipality), municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo VI The Wise
Leo VI, called the Wise ( gr, Λέων ὁ Σοφός, Léōn ho Sophós, 19 September 866 – 11 May 912), was Byzantine Emperor from 886 to 912. The second ruler of the Macedonian dynasty (although his parentage is unclear), he was very well read, leading to his epithet. During his reign, the renaissance of letters, begun by his predecessor Basil I, continued; but the Empire also saw several military defeats in the Balkans against Bulgaria and against the Arabs in Sicily and the Aegean. His reign also witnessed the formal discontinuation of several ancient Roman institutions, such as the separate office of Roman consul. Early life Born on 19 September 866 to the empress Eudokia Ingerina, Leo was either the illegitimate son of Emperor Michael III or the second son of Michael's successor, Basil I the Macedonian. Eudokia was both Michael III's mistress and Basil's wife. In 867, Michael was assassinated by Basil, who succeeded him as emperor. As the second-eldest son of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
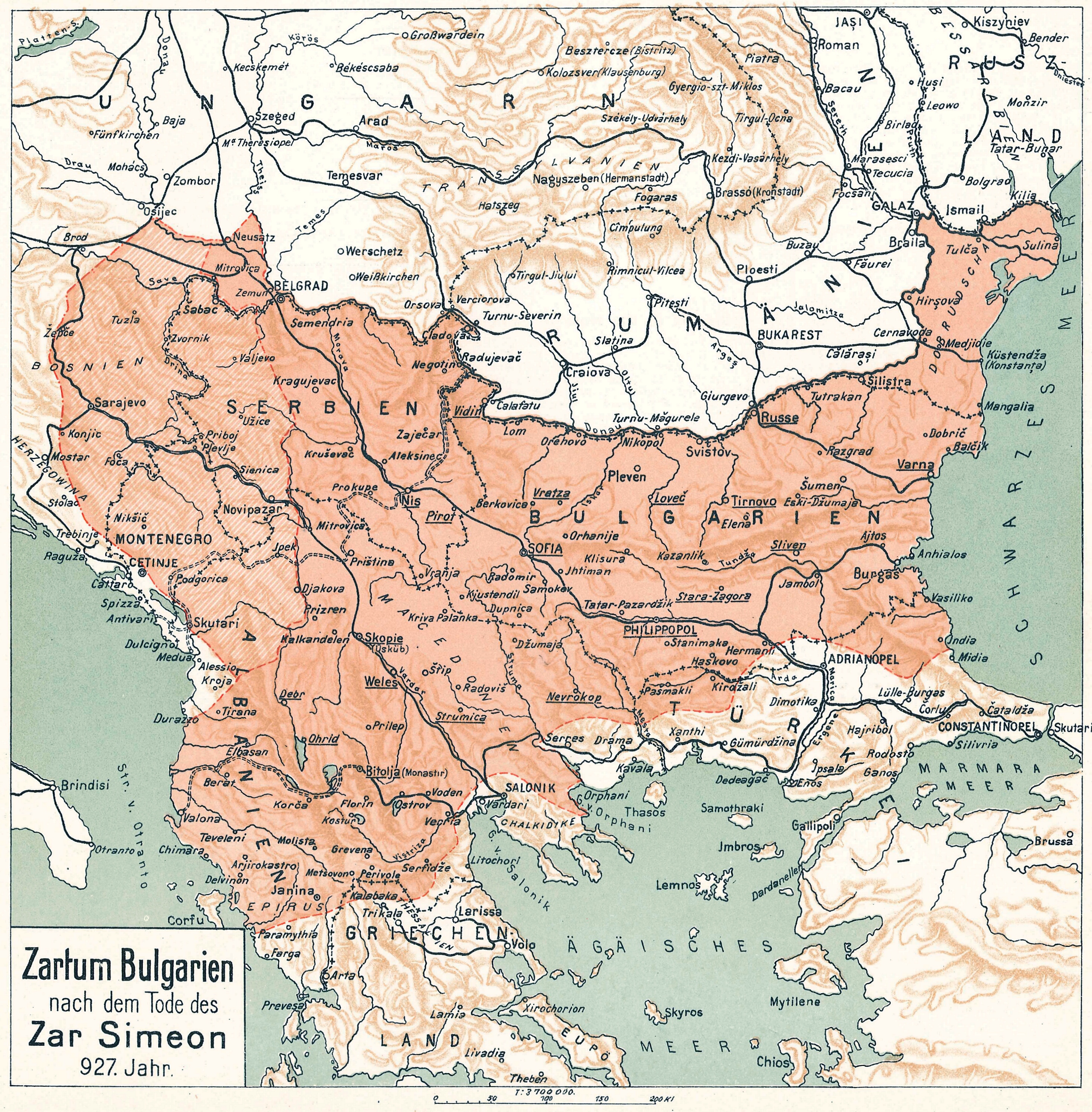
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos Doukas (general Under Leo VI)
Andronikos Doukas or Doux ( gr, Ἀνδρόνικος Δούκας/Δούξ, died circa 910) was a Byzantine general and rebel in the reign of Emperor Leo VI the Wise (r. 886–912). The first member of the illustrious Doukas line to achieve prominence as a successful general, his rivalry with the powerful eunuch Samonas led to his revolt and eventual defection to the Arabs in 906–907. He died in exile in Baghdad. Biography Andronikos Doukas is the first prominent member of the Doukas family whose life is known in some detail. He was possibly the son of the first recorded Doukas, an official active circa 855, but nothing is known of his origin and early life. Andronikos first appears in the sources in 904, already a holder of the exalted title of ''patrikios'' and a general. In November or December of that year, along with Eustathios Argyros, he campaigned against the Arabs and won a major victory over the combined forces of Mopsuestia and Tarsos near Germanikeia. Alexander Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |