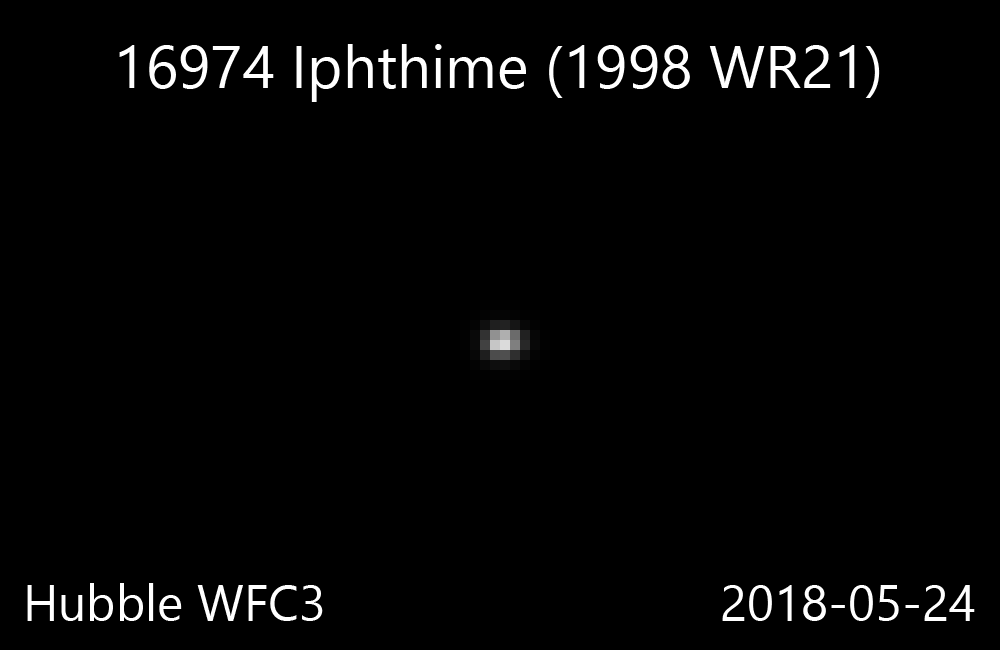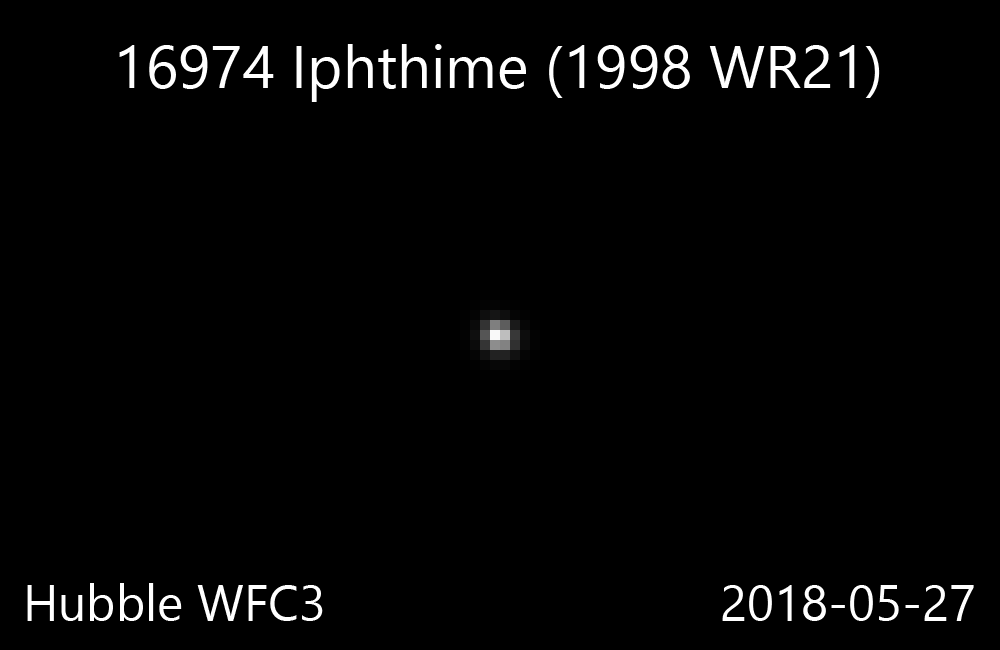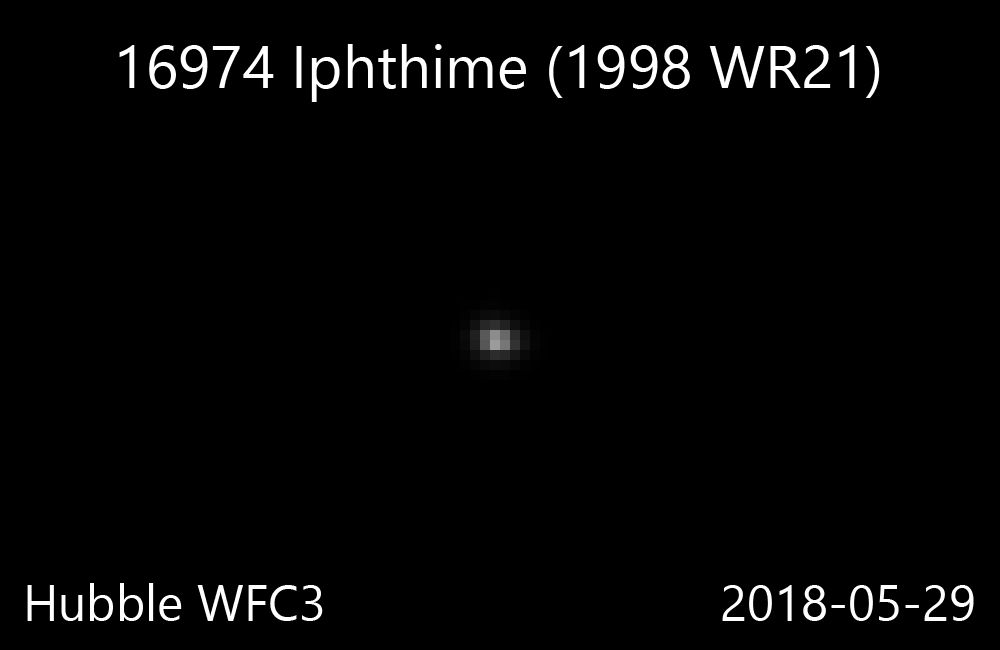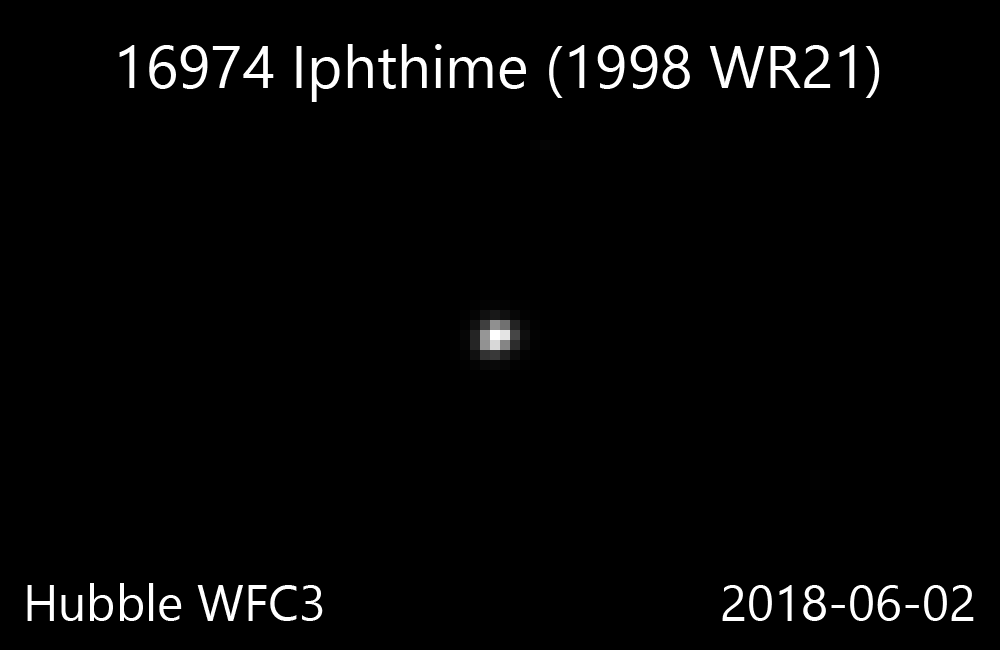|
624 Hektor
624 Hektor is the largest Jupiter trojan and the namesake of the Hektor family, with a highly elongated shape equivalent in volume to a sphere of approximately 225 to 250 kilometers diameter. It was discovered on 10 February 1907, by astronomer August Kopff at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany, and named after the Trojan prince Hector, from Greek mythology. It has one small 12-kilometer sized satellite, Skamandrios, discovered in 2006. Description ''Hektor'' is a D-type asteroid, dark and reddish in colour. It lies in Jupiter's leading Lagrangian point, , called the Greek camp after one of the two sides in the legendary Trojan War. Hektor is named after the Trojan hero Hektor and is thus one of two trojan asteroids that is "misplaced" in the wrong camp (the other one being 617 Patroclus in the Trojan camp). Contact-binary hypothesis Hektor is one of the most elongated bodies of its size in the Solar System, being approximately 403 km in its longest dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Kopff
August Kopff (February 5, 1882 – April 25, 1960) was a German astronomer and discoverer of several comets and asteroids. Kopff studied and worked in Heidelberg, getting his PhD there in 1906 and he then joined the Humboldt University of Berlin where he became the Director of the Institute for Astronomical Calculation. He discovered some comets, including periodic comet 22P/Kopff and the non-periodic C/1906 E1. He discovered a number of asteroids, including notably the Trojan asteroids 617 Patroclus and 624 Hektor 624 Hektor is the largest Jupiter trojan and the namesake of the Hektor family, with a highly elongated shape equivalent in volume to a sphere of approximately 225 to 250 kilometers diameter. It was discovered on 10 February 1907, by astronomer .... The lunar crater '' Kopff'' is named after him, as is the asteroid 1631 Kopff. Minor planet 805 Hormuthia is named after his wife, Hormuth. List of discovered minor planets References {{DEFAULTSOR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
617 Patroclus
617 Patroclus ( ) is a large binary Jupiter trojan asteroid. It is a dark D-type asteroid and a slow rotator, due to the 103-hour orbital period of its two components. It is one of five Jovian asteroids targeted by the ''Lucy'' space probe, and is scheduled for a flyby in 2033. Patroclus was discovered on 17 October, 1906, by astronomer August Kopff at the Heidelberg Observatory in Germany, and was named after Patroclus in Greek mythology. It was the second trojan to be discovered and the only member of the Trojan camp named after a Greek figure, as the convention of naming one 'camp' after Greek figures of the Trojan War and the other after Trojan figures had not yet been established. Patroclus was long thought to be one of the largest Jupiter trojans, with a diameter on the order of 150 km. However, in 2001 it was discovered to be a binary asteroid of two similarly sized objects. The name ''Patroclus'' is now assigned to the larger component, some 110–115 km in dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3548 Eurybates
3548 Eurybates ( ) is a carbonaceous Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp and the parent body of the Eurybates family, approximately in diameter. It is a target to be visited by the ''Lucy'' mission in August 2027. Discovered during the second Palomar–Leiden Trojan survey in 1973, it was later named after Eurybates from Greek mythology. The C/P-type asteroid belongs to the 60 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 8.7 hours. ''Eurybates'' has one known satellite, named ''Queta'', that was discovered in images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in September 2018. Discovery ''Eurybates'' was discovered on 19 September 1973, by Dutch astronomers Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden, on photographic plates taken by Tom Gehrels at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. In 1951, it was first observed as ' at the Goethe Link Observatory, extending the asteroid's observation arc by 22 years prior to its official discovery observation at Palo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16974 Iphthime
16974 Iphthime (; ''prov. designation'': ) is a Jupiter trojan and a binary system from the Greek camp, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 18 November 1998, by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the ETS Test Site in Socorro, New Mexico. The dark Jovian asteroid belongs to the 80 largest Jupiter trojans and has a notably slow rotation of 78.9 hours. It was named after Iphthime from Greek mythology. The discovery of its companion by Hubble Space Telescope was announced in March 2016. Orbit and classification ''Iphthime'' is a dark Jovian asteroid orbiting in the leading Greek camp at Jupiter's Lagrangian point, 60 ° ahead of its orbit in a 1:1 resonance . It is also a non-family asteroid in the Jovian background population. It orbits the Sun at a distance of 4.8–5.6 AU once every 11 years and 10 months (4,319 days; semi-major axis of 5.19 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.07 and an inclination of 15 ° with respe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of atmospheric distortion, in microscopy, optical fabrication and in retinal imaging systems to reduce optical aberrations. Adaptive optics works by measuring the distortions in a wavefront and compensating for them with a device that corrects those errors such as a deformable mirror or a liquid crystal array. Adaptive optics should not be confused with active optics, which works on a longer timescale to correct the primary mirror geometry. Other methods can achieve resolving power exceeding the limit imposed by atmospheric distortion, such as speckle imaging, aperture synthesis, and lucky imaging, or by moving outside the atmosphere with space telescopes, such as the Hubble Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Guide Star
A laser guide star is an artificial star image created for use in astronomical adaptive optics systems, which are employed in large telescopes in order to correct atmospheric distortion of light (called ''astronomical seeing''). Adaptive optics (AO) systems require a wavefront reference source of light called a guide star. Natural stars can serve as point sources for this purpose, but sufficiently bright stars are not available in all parts of the sky, which greatly limits the usefulness of natural guide star adaptive optics. Instead, one can create an artificial guide star by shining a laser into the atmosphere. Light from the beam is reflected by components in the upper atmosphere back into the telescope. This star can be positioned anywhere the telescope desires to point, opening up much greater amounts of the sky to adaptive optics. Because the laser beam is deflected by astronomical seeing on the way up, the returning laser light does not move around in the sky as ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keck Telescopes
The W. M. Keck Observatory is an astronomical observatory with two telescopes at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes have aperture primary mirrors, and when completed in 1993 (Keck 1) and 1996 (Keck 2) were the largest astronomical telescopes in the world. They are currently the 3rd and 4th largest. Overview With a concept first proposed in 1977, telescope designers at the University of California, Berkeley (Terry Mast) and Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory (Jerry Nelson) had been developing the technology necessary to build a large, ground-based telescope. With a design in hand, a search for the funding began. In 1985, Howard B. Keck of the W. M. Keck Foundation gave $70 million to fund the construction of the Keck I telescope, which began in September 1985, with first light occurring on 24 November 1990 using nine of the eventual 36 segments. With construction of the first telescope well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution. It is used in optics applied to light waves, in antenna theory applied to radio waves, and in acoustics applied to sound waves. The colloquial use of the term "resolution" sometimes causes confusion; when an optical system is said to have a high resolution or high angular resolution, it means that the perceived distance, or actual angular distance, between resolved neighboring objects is small. The value that quantifies this property, ''θ,'' which is given by the Rayleigh criterion, is low for a system with a high resolution. The closely related term spatial resolution refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to space, which is directly connected to angular resolution in imaging instruments. The Rayleigh criterion shows th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
216 Kleopatra
216 Kleopatra is a large M-type asteroid with a mean diameter of and is noted for its elongate bone or dumbbell shape. It was discovered on 10 April 1880 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at the Austrian Naval Pola Observatory, in what is now Pula, Croatia, and was named after Cleopatra, the famous Egyptian queen. It has two small minor-planet moons which were discovered in 2008 and later named Alexhelios and Cleoselene. Orbit and classification ''Kleopatra'' is a non-family asteroid from the main belt's background population. It orbits the Sun in the central asteroid belt at a distance of 2.1–3.5 AU once every 4 years and 8 months (1,706 days; semi-major axis of 2.79 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.25 and an inclination of 13 ° with respect to the ecliptic. The body's observation arc begins at Leipzig Observatory on 20 April 1880, ten days after to its official discovery observation at Pola Observatory. : Physical characteristics Size and Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Binary (asteroid)
A contact binary is a small Solar System body such as a minor planet or a comet that is composed of two bodies that have gravitated toward each other until they touch, resulting in a bilobated, peanut-like overall shape. Contact binaries are often rubble piles but distinct from real binary systems such as binary asteroids. The term is also used for stellar contact binaries. An example of what is thought to be a contact binary is the Kuiper belt object 486958 Arrokoth, which was imaged by the '' New Horizons'' spacecraft during its flyby in January 2019. Description Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko and Comet Tuttle are most likely contact binaries, while asteroids suspected of being contact binaries include the unusually elongated 624 Hektor and the bilobated 216 Kleopatra and 4769 Castalia. 25143 Itokawa, which was photographed by the ''Hayabusa'' probe, also appears to be a contact binary which has resulted in an elongated, bent body. Asteroid 417 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |