Angular resolution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an
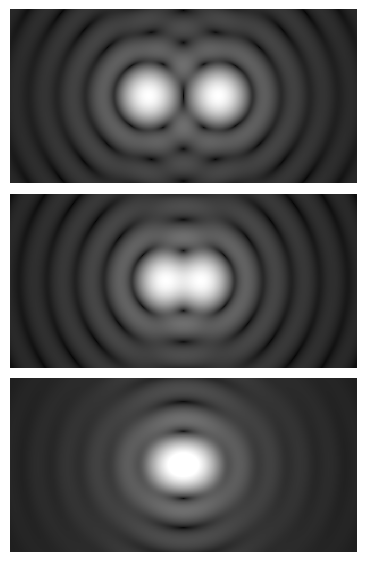 The imaging system's resolution can be limited either by aberration or by
The imaging system's resolution can be limited either by aberration or by
"Concepts and Formulas in Microscopy: Resolution"
by Michael W. Davidson, ''Nikon MicroscopyU'' (website). {{Portal bar, Science, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Angle Optics
 Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
or radio telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna (radio), antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the r ...
, a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
, a camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photograp ...
, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies ...
. It is used in optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
applied to light waves, in antenna theory applied to radio waves, and in acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
applied to sound waves. The colloquial use of the term "resolution" sometimes causes confusion; when an optical system is said to have a high resolution or high angular resolution, it means that the perceived distance, or actual angular distance, between resolved neighboring objects is small. The value that quantifies this property, ''θ,'' which is given by the Rayleigh criterion, is low for a system with a high resolution. The closely related term spatial resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resoluti ...
refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to space, which is directly connected to angular resolution in imaging instruments. The Rayleigh criterion shows that the minimum angular spread that can be resolved by an image-forming system is limited by diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
to the ratio of the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the waves to the aperture width. For this reason, high-resolution imaging systems such as astronomical telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
s, long distance telephoto camera lenses and radio telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna (radio), antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the r ...
s have large apertures.
Definition of terms
''Resolving power'' is the ability of an imaging device to separate (i.e., to see as distinct) points of an object that are located at a smallangular distance
Angular distance or angular separation is the measure of the angle between the orientation (geometry), orientation of two straight lines, ray (geometry), rays, or vector (geometry), vectors in three-dimensional space, or the central angle subtende ...
or it is the power of an optical instrument to separate far away objects, that are close together, into individual images. The term '' resolution'' or ''minimum resolvable distance'' is the minimum distance between distinguishable objects in an image, although the term is loosely used by many users of microscopes and telescopes to describe resolving power. As explained below, diffraction-limited resolution is defined by the Rayleigh criterion as the angular separation of two point sources when the maximum of each source lies in the first minimum of the diffraction pattern (Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best-focus (optics), focused Point source#Light, spot of light that a perfect lens (optics), lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of ...
) of the other. In scientific analysis, in general, the term "resolution" is used to describe the precision with which any instrument measures and records (in an image or spectrum) any variable in the specimen or sample under study.
The Rayleigh criterion
 The imaging system's resolution can be limited either by aberration or by
The imaging system's resolution can be limited either by aberration or by diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
causing blurring of the image. These two phenomena have different origins and are unrelated. Aberrations can be explained by geometrical optics
Geometrical optics, or ray optics, is a model of optics that describes light Wave propagation, propagation in terms of ''ray (optics), rays''. The ray in geometrical optics is an abstract object, abstraction useful for approximating the paths along ...
and can in principle be solved by increasing the optical quality of the system. On the other hand, diffraction comes from the wave nature of light and is determined by the finite aperture of the optical elements. The lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
' circular aperture is analogous to a two-dimensional version of the single-slit experiment. Light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
passing through the lens interferes with itself creating a ring-shape diffraction pattern, known as the Airy pattern, if the wavefront
In physics, the wavefront of a time-varying ''wave field (physics), field'' is the set (locus (mathematics), locus) of all point (geometry), points having the same ''phase (waves), phase''. The term is generally meaningful only for fields that, a ...
of the transmitted light is taken to be spherical or plane over the exit aperture.
The interplay between diffraction and aberration can be characterised by the point spread function
The point spread function (PSF) describes the response of a focused optical imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is the system's impulse response; the PSF is the impulse response or impulse response ...
(PSF). The narrower the aperture of a lens the more likely the PSF is dominated by diffraction. In that case, the angular resolution of an optical system can be estimated (from the diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions a ...
of the aperture and the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the light) by the Rayleigh criterion defined by Lord Rayleigh: two point sources are regarded as just resolved when the principal diffraction maximum (center) of the Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best-focus (optics), focused Point source#Light, spot of light that a perfect lens (optics), lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of ...
of one image coincides with the first minimum of the Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best-focus (optics), focused Point source#Light, spot of light that a perfect lens (optics), lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of ...
of the other,
as shown in the accompanying photos. (In the bottom photo on the right that shows the Rayleigh criterion limit, the central maximum of one point source might look as though it lies outside the first minimum of the other, but examination with a ruler verifies that the two do intersect.) If the distance is greater, the two points are well resolved and if it is smaller, they are regarded as not resolved. Rayleigh defended this criterion on sources of equal strength.
Considering diffraction through a circular aperture, this translates into:
:
where ''θ'' is the ''angular resolution'' ( radians), ''λ'' is the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of light, and ''D'' is the diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions a ...
of the lens' aperture. The factor 1.22 is derived from a calculation of the position of the first dark circular ring surrounding the central Airy disc of the diffraction
Diffraction is the deviation of waves from straight-line propagation without any change in their energy due to an obstacle or through an aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the Wave propagation ...
pattern. This number is more precisely 1.21966989... (), the first zero of the order-one Bessel function of the first kind divided by π.
The formal Rayleigh criterion is close to the empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how t ...
resolution limit found earlier by the English astronomer W. R. Dawes, who tested human observers on close binary stars of equal brightness. The result, ''θ'' = 4.56/''D'', with ''D'' in inches and ''θ'' in arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
s, is slightly narrower than calculated with the Rayleigh criterion. A calculation using Airy discs as point spread function shows that at Dawes' limit there is a 5% dip between the two maxima, whereas at Rayleigh's criterion there is a 26.3% dip.
Modern image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
techniques including deconvolution of the point spread function allow resolution of binaries with even less angular separation.
Using a small-angle approximation, the angular resolution may be converted into a ''spatial resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resoluti ...
'', Δ''ℓ'', by multiplication of the angle (in radians) with the distance to the object. For a microscope, that distance is close to the focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
''f'' of the objective. For this case, the Rayleigh criterion reads:
:.
This is the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
, in the imaging plane, of the smallest spot to which a collimated beam of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
can be focused, which also corresponds to the size of the smallest object that the lens can resolve. The size is proportional to wavelength, ''λ'', and thus, for example, blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB color model, RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB color model, RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between Violet (color), violet and cyan on the optical spe ...
light can be focused to a smaller spot than red light. If the lens is focusing a beam of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
with a finite extent (e.g., a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
beam), the value of ''D'' corresponds to the diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the centre of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest Chord (geometry), chord of the circle. Both definitions a ...
of the light beam, not the lens. Since the spatial resolution is inversely proportional to ''D'', this leads to the slightly surprising result that a wide beam of light may be focused on a smaller spot than a narrow one. This result is related to the Fourier properties of a lens.
A similar result holds for a small sensor imaging a subject at infinity: The angular resolution can be converted to a spatial resolution on the sensor by using ''f'' as the distance to the image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
; this relates the spatial resolution of the image to the f-number
An f-number is a measure of the light-gathering ability of an optical system such as a camera lens. It is calculated by dividing the system's focal length by the diameter of the entrance pupil ("clear aperture").Smith, Warren ''Modern Optical ...
, #:
:.
Since this is the radius of the Airy disk, the resolution is better estimated by the diameter,
Specific cases
Single telescope
Point-like sources separated by anangle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two R ...
smaller than the angular resolution cannot be resolved. A single optical telescope may have an angular resolution less than one arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
, but astronomical seeing
In astronomy, seeing is the degradation of the real image, image of an astronomical object due to turbulence in the atmosphere of Earth that may become visible as blurring, twinkling or variable Distortion (optics), distortion. The origin of this ...
and other atmospheric effects make attaining this very hard.
The angular resolution ''R'' of a telescope can usually be approximated by
:
where ''λ'' is the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the observed radiation, and ''D'' is the diameter of the telescope's objective. The resulting ''R'' is in radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. It is defined such that one radian is the angle subtended at ...
s. For example, in the case of yellow light with a wavelength of 580 nm, for a resolution of 0.1 arc second, we need D=1.2 m. Sources larger than the angular resolution are called extended sources or diffuse sources, and smaller sources are called point sources.
This formula, for light with a wavelength of about 562 nm, is also called the Dawes' limit.
Telescope array
The highest angular resolutions for telescopes can be achieved by arrays of telescopes calledastronomical interferometer
An astronomical interferometer or telescope array is a set of separate telescopes, mirror segments, or radio telescope antennas that work together as a single telescope to provide higher resolution images of astronomical objects such as stars, n ...
s: These instruments can achieve angular resolutions of 0.001 arcsecond at optical wavelengths, and much higher resolutions at x-ray wavelengths. In order to perform aperture synthesis imaging, a large number of telescopes are required laid out in a 2-dimensional arrangement with a dimensional precision better than a fraction (0.25x) of the required image resolution.
The angular resolution ''R'' of an interferometer array can usually be approximated by
:
where ''λ'' is the wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the observed radiation, and ''B'' is the length of the maximum physical separation of the telescopes in the array, called the baseline. The resulting ''R'' is in radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. It is defined such that one radian is the angle subtended at ...
s. Sources larger than the angular resolution are called extended sources or diffuse sources, and smaller sources are called point sources.
For example, in order to form an image in yellow light with a wavelength of 580 nm, for a resolution of 1 milli-arcsecond, we need telescopes laid out in an array that is 120 m × 120 m with a dimensional precision better than 145 nm.
Microscope
The resolution ''R'' (here measured as a distance, not to be confused with the angular resolution of a previous subsection) depends on the angular aperture : : where . Here NA is thenumerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, has the property ...
, is half the included angle of the lens, which depends on the diameter of the lens and its focal length, is the refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
of the medium between the lens and the specimen, and is the wavelength of light illuminating or emanating from (in the case of fluorescence microscopy) the sample.
It follows that the NAs of both the objective and the condenser should be as high as possible for maximum resolution. In the case that both NAs are the same, the equation may be reduced to:
:
The practical limit for is about 70°. In a dry objective or condenser, this gives a maximum NA of 0.95. In a high-resolution oil immersion lens, the maximum NA is typically 1.45, when using immersion oil with a refractive index of 1.52. Due to these limitations, the resolution limit of a light microscope using visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
is about 200 nm. Given that the shortest wavelength of visible light is violet (),
:
which is near 200 nm.
Oil immersion objectives can have practical difficulties due to their shallow depth of field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus (optics), focus in an image captured with a camera. See also the closely related depth of focus.
Factors affecting depth ...
and extremely short working distance, which calls for the use of very thin (0.17 mm) cover slips, or, in an inverted microscope, thin glass-bottomed Petri dish
A Petri dish (alternatively known as a Petri plate or cell-culture dish) is a shallow transparent lidded dish that biologists use to hold growth medium in which cells can be cultured,R. C. Dubey (2014): ''A Textbook Of Biotechnology For Class- ...
es.
However, resolution below this theoretical limit can be achieved using super-resolution microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a series of techniques in optical microscopy that allow such images to have Optical resolution, resolutions higher than those imposed by the Diffraction-limited system, diffraction limit, which is due to the diffra ...
. These include optical near-fields ( Near-field scanning optical microscope) or a diffraction technique called 4Pi STED microscopy. Objects as small as 30 nm have been resolved with both techniques.
In addition to this Photoactivated localization microscopy
Photo-activated localization microscopy (PALM or FPALM)
and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) are widefield (as opposed to point scanning techniques such as laser scanning confocal microscopy) fluorescence microscopy imaging meth ...
can resolve structures of that size, but is also able to give information in z-direction (3D).
List of telescopes and arrays by angular resolution
See also
*Angular diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular separation (in units of angle) describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the ''visual an ...
* Beam diameter
* Dawes' limit
* Diffraction-limited system
* Ground sample distance
* Image resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies ...
* Optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail, in the object that is being imaged.
An imaging system may have many individual components, including one or more lenses, and/or recording and display components. E ...
* Sparrow's resolution limit
* Visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
Notes
References
External links
"Concepts and Formulas in Microscopy: Resolution"
by Michael W. Davidson, ''Nikon MicroscopyU'' (website). {{Portal bar, Science, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Angle Optics