|
4th Century BCE
The 4th century BC started the first day of 400 BC and ended the last day of 301 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. This century marked the height of Classical Greek civilization in all of its aspects. By the year 400 BC Greek philosophy, art, literature and architecture had spread far and wide, with the numerous independent Greek colonies that had sprung up throughout the lands of the eastern Mediterranean. Arguably the most important series of political events in this period were the conquests of Alexander, bringing about the collapse of the once formidable Persian Empire and spreading Greek culture far into the east. Alexander dreamt of an east/west union, but when his short life ended in 323 BC, his vast empire was plunged into civil war as his generals each carved out their own separate kingdoms. Thus began the Hellenistic age, a period characterized by a more absolute approach to rule, with Greek kings taking on royal trapping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
400 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 400 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Esquilinus, Capitolinus, Vulso, Medullinus, Saccus and Vulscus (or, less frequently, year 354 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 400 BC for this year has been used in Europe since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became prevalent there. Events By place * Artaxerxes II, king of Persia, appoints Tissaphernes to take over all the districts in Asia Minor over which Artaxerxes II's brother Cyrus had been governor before his revolt. * Xenophon's " Ten Thousand" make their way back to Greece, with most of the men enlisting with the Spartans. Xenophon's successful march through the Persian Empire encourages Sparta to turn on the Persians and begin wars against the Persians in Asia Minor. * With the outbreak of the war between Sparta and the Persians, the Athenian admiral, Conon, obtains joint command, with Phar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (350-295 BCE) was a ruler in Ancient India who expanded a geographically-extensive kingdom based in Magadha and founded the Maurya dynasty. He reigned from 320 BCE to 298 BCE. The Maurya kingdom expanded to become an empire that reached its peak under the reign of his grandson, Asoka, from 268 BCE to 231 BCE. The nature of the political formation that existed in Chandragupta's time is not certain. The Mauryan empire was a loose-knit empire. Quote: "The geography of the Mauryan Empire resembled a spider with a small dense body and long spindly legs. The highest echelons of imperial society lived in the inner circle composed of the ruler, his immediate family, other relatives, and close allies, who formed a dynastic core. Outside the core, empire travelled stringy routes dotted with armed cities. Outside the palace, in the capital cities, the highest ranks in the imperial elite were held by military commanders whose active loyalty and success in war determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
399 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 399 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Augurinus, Longus, Priscus, Cicurinus, Rufus and Philo (or, less frequently, year 355 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 399 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * February 15 – The Greek philosopher Socrates is sentenced to death by Athenian authorities, condemned for impiety and the corruption of youth. He refuses to flee into exile and dies by drinking hemlock. * Sparta forces Elis to surrender in the spring. * The Spartan admiral, Lysander, tries to effect a political revolution in Sparta by suggesting that the king should not automatically be given the leadership of the army. He also suggests that the position of king should be elective. However, he is unsuccessful in achieving these reforms, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
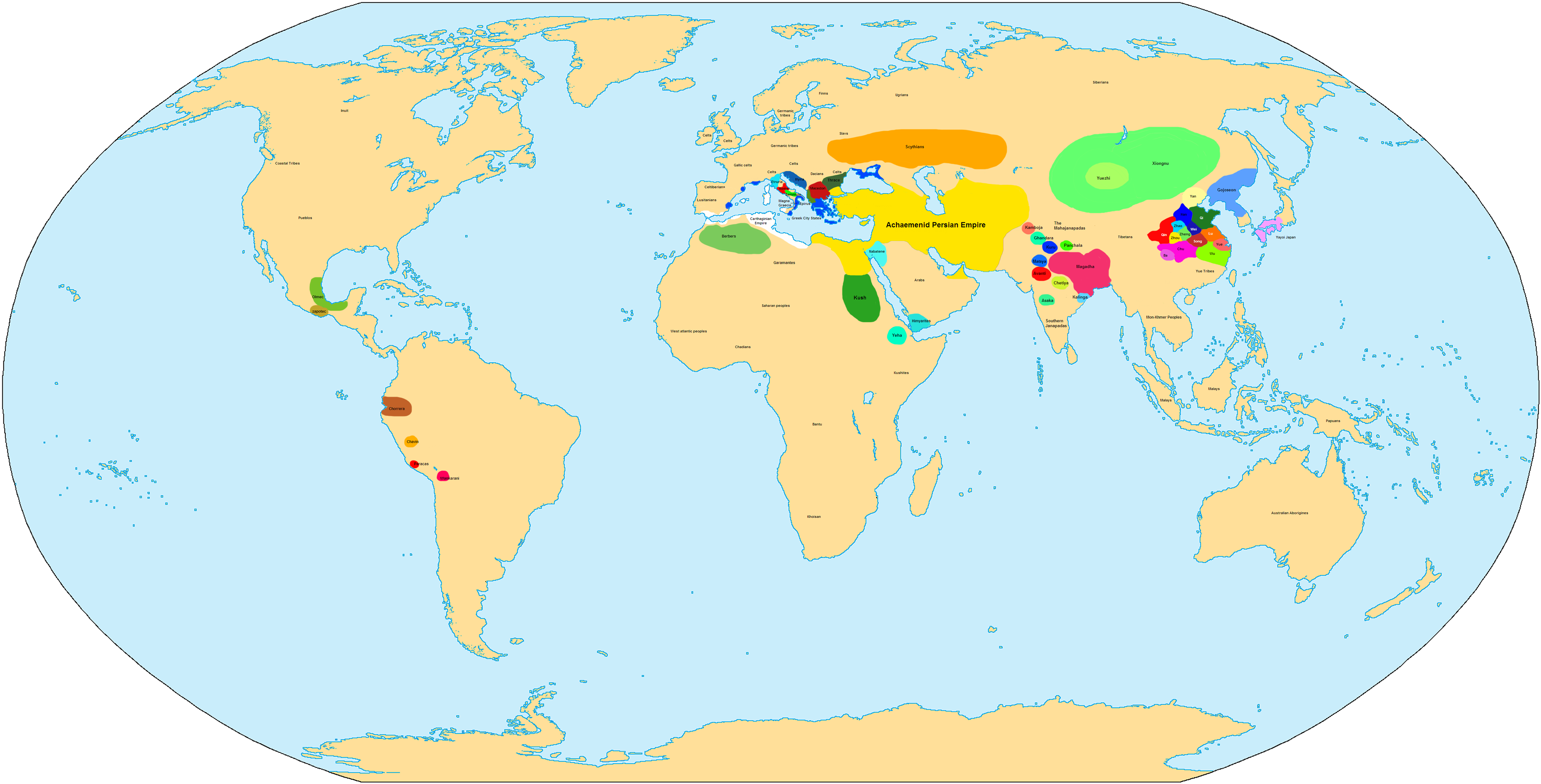
World In 300 BCE
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In '' scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World In 400 BCE
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In '' scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legalism (Chinese Philosophy)
Legalism or ''Fajia'' is one of the six classical schools of thought in Chinese philosophy. Literally meaning "house of (administrative) methods / standards (法, Fa)", the Fa "school" represents several branches of "men of methods", in the west often termed " realist" statesmen,who played foundational roles in the construction of the bureaucratic Chinese empire.Peng He 2011. p. 646. The Difference of Chinese Legalism and Western Legalism The earliest persona of the Fajia may be considered Guan Zhong (720–645 BC), but following the precedent of the '' Han Feizi'' (c. 240 BC), Warring States period figures Shen Buhai (400–337 BC) and Shang Yang (390–338 BC) have commonly been taken as its "founders." Commonly thought of as the greatest of all "Legalist" texts, the ''Han Feizi'' is believed to contain the first commentaries on the '' Dao De Jing'' in history.Ewan Ferlie, Laurence E. Lynn, Christopher Pollitt 2005 p. 30, ''The Oxford Handbook of Public Management''Pines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The ''Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize '' wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the Three Treasures: , compassio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a way of life, Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius (551–479 BCE). Confucius considered himself a transmitter of cultural values inherited from the Xia (c. 2070–1600 BCE), Shang (c. 1600–1046 BCE) and Western Zhou dynasties (c. 1046–771 BCE). Confucianism was suppressed during the Legalist and autocratic Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE), but survived. During the Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), Confucian approaches edged out the "proto-Taoist" Huang–Lao as the official ideology, while the emperors mixed both with the realist techniques of Legalism. A Confucian revival began during the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE). In the late Tang, Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 479 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, the Zhou royal authority over the various feudal states eroded as more and more dukes and marquesses obtained ''de facto'' regional autonomy, defying the king's court in Luoyi and waging wars amongst themselves. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, marked the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng and Shen — the latter polity being the fief of the grandfather of the disinherited crown prince Yijiu — destroyed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu (state)
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou heartland and lasted during the Spring and Autumn period. At the end of the Warring States period it was destroyed by the Qin in 223 BCE during the Qin's wars of unification. Also known as Jing () and Jingchu (), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan and Xi Rivers near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying. The house of Chu originally bore the clan name Nai ( OC: /*rneːlʔ/) which was later written as Mi ( OC: /*meʔ/). They also bore the lineage name Yan ( OC: /*qlamʔ/, /*qʰɯːm/) which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |