|
4GLS
The 4GLS was a proposed 4th Generation Light Source, based at the Daresbury Laboratory in Cheshire, England, intended to combine energy recovery linac (ERL) and free electron laser technologies to provide synchronised sources of synchrotron radiation and free electron laser radiation covering the terahertz (THz) to soft X-ray regimes. In early 2008 the Science and Technology Facilities Council decided not to proceed with the 4GLS. See also * Diamond Light Source Diamond Light Source (or Diamond) is the UK's national synchrotron light source science facility located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire. Its purpose is to produce intense beams of light whose special characteristics ... References Free-electron lasers Science and Technology Facilities Council Synchrotron radiation facilities {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daresbury Laboratory
Daresbury Laboratory is a scientific research laboratory based at Sci-Tech Daresbury campus near Daresbury in Halton, Cheshire, England. The laboratory began operations in 1962 and was officially opened on 16 June 1967 as the Daresbury Nuclear Physics Laboratory by the then Prime Minister of United Kingdom, Harold Wilson. It was the second national laboratory established by the British National Institute for Research in Nuclear Science, following the Rutherford High Energy Laboratory (now Rutherford Appleton Laboratory). It is operated by the Science and Technology Facilities Council, part of UK Research and Innovation. As of 2018, it employs around 300 staff, with Paul Vernon appointed as director in November 2020, taking over from Professor Susan Smith who had been director from 2012. Description Daresbury Laboratory carries out research in fields such as accelerator science, bio-medicine, physics, chemistry, materials, engineering and computational science. Its facilities ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county town is the cathedral city of Chester, while its largest town by population is Warrington. Other towns in the county include Alsager, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Frodsham, Knutsford, Macclesfield, Middlewich, Nantwich, Neston, Northwich, Poynton, Runcorn, Sandbach, Widnes, Wilmslow, and Winsford. Cheshire is split into the administrative districts of Cheshire West and Chester, Cheshire East, Halton, and Warrington. The county covers and has a population of around 1.1 million as of 2021. It is mostly rural, with a number of towns and villages supporting the agricultural and chemical industries; it is primarily known for producing chemicals, Cheshire cheese, salt, and silk. It has also had an impact on popular culture, producin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Electron Laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a (fourth generation) light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions and behaves in many ways like a laser, but instead of using stimulated emission from atomic or molecular excitations, it employs relativistic electrons as a gain medium. Radiation is generated by a ''bunch'' of electrons passing through a magnetic structure (called undulator or wiggler). In an FEL, this radiation is further amplified as the radiation re-interacts with the electron bunch such that the electrons start to emit coherently, thus allowing an exponential increase in overall radiation intensity. As electron kinetic energy and undulator parameters can be adapted as desired, free-electron lasers are tunable and can be built for a wider frequency range than any other type of laser, currently ranging in wavelength from microwaves, through terahertz radiation and infrared, to the visible spectrum, ultraviolet, and X-ray. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
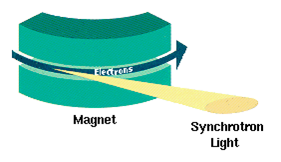
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terahertz Radiation
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency (THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the ITU-designated band of frequencies from 0.3 to 3 terahertz (THz), although the upper boundary is somewhat arbitrary and is considered by some sources as 30 THz. One terahertz is 1012 Hz or 1000 GHz. Wavelengths of radiation in the terahertz band correspondingly range from 1 mm to 0.1 mm = 100 µm. Because terahertz radiation begins at a wavelength of around 1 millimeter and proceeds into shorter wavelengths, it is sometimes known as the ''submillimeter band'', and its radiation as ''submillimeter waves'', especially in astronomy. This band of electromagnetic radiation lies within the transition region between microwave and far infrared, and can be regarded as either. Terahertz radiation is strongly absorbed by the gases o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Picometre, picometers to 10 Nanometre, nanometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 electronvolt, eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet, UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology Facilities Council
The Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC) is a United Kingdom government agency that carries out research in science and engineering, and funds UK research in areas including particle physics, nuclear physics, space science and astronomy (both ground-based and space-based). History STFC was formed in April 2007 when the Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council (PPARC), the Council for the Central Laboratory of the Research Councils (CCLRC), along with the nuclear physics activities of the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) were brought under the one Umbrella organization, umbrella organisation. The organisation's first Chief Executive was Professor Keith Mason, who held the position until 2011, when he was replaced by Professor John Womersley. Womersley servied as CEO until 2016 when he left to become Director General of the European Spallation Source. Dr Brian Bowsher, former CEO of the National Physical Laboratory and member of STFC's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Light Source
Diamond Light Source (or Diamond) is the UK's national synchrotron light source science facility located at the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire. Its purpose is to produce intense beams of light whose special characteristics are useful in many areas of scientific research. In particular it can be used to investigate the structure and properties of a wide range of materials from proteins (to provide information for designing new and better drugs), and engineering components (such as a fan blade from an aero-engine) to conservation of archeological artifacts (for example Henry VIII's flagship the Mary Rose). There are more than 50 light sources across the world. With an energy of 3 GeV, Diamond is a medium energy synchrotron currently operating with 32 beamlines. Design, construction and finance The Diamond synchrotron is the largest UK-funded scientific facility to be built in the UK since the Nimrod proton synchrotron which was sited at the Rutherfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |