|
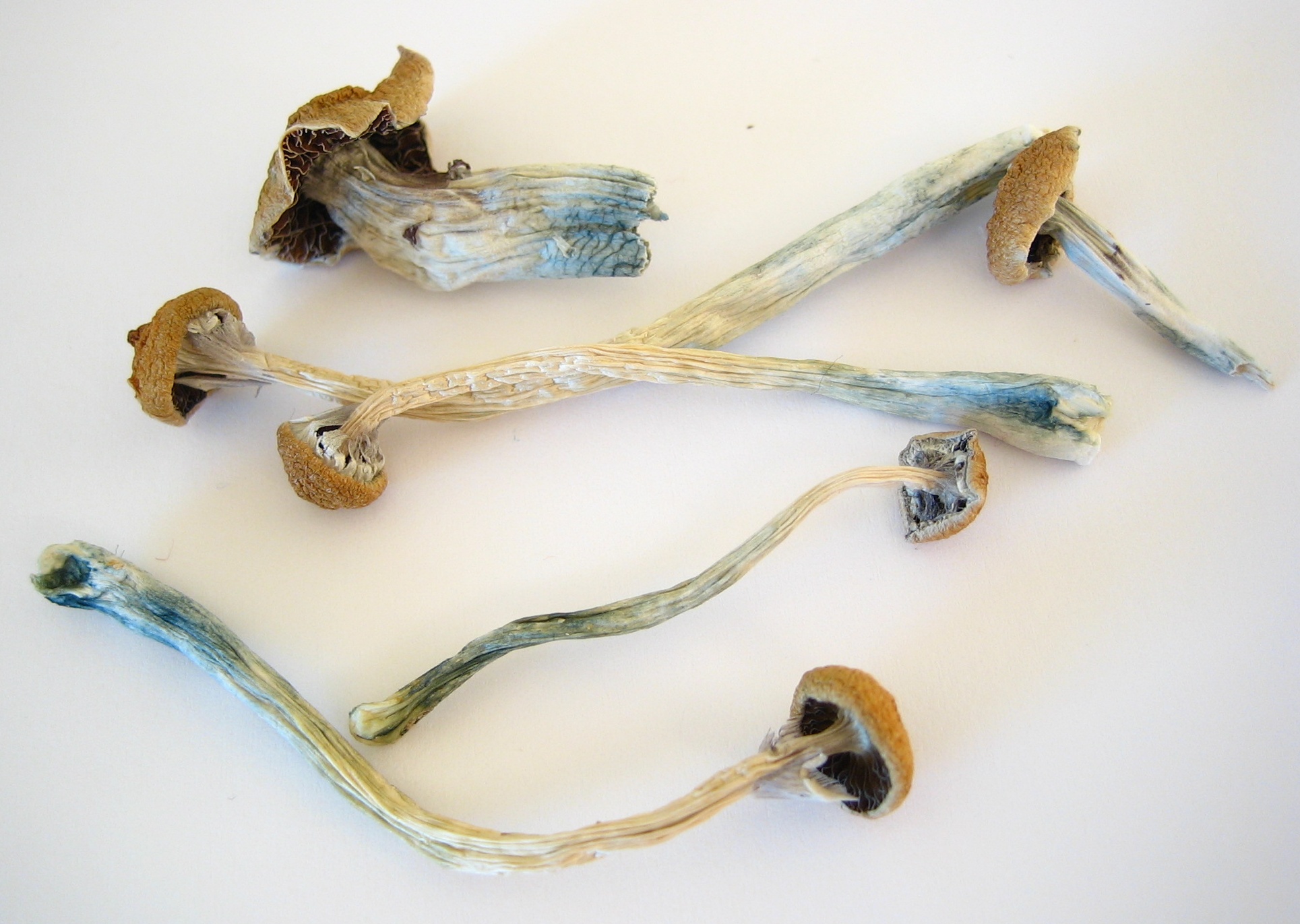
4-HO-EPT
4-HO-EPT (4-hydroxy-''N''-ethyl-''N''-propyltryptamine) is a rarely encountered chemical compound of the tryptamine class, which is structurally related to psilocin (4-HO-DMT). Legality * United Kingdom: 4-HO-EPT is illegal in the United Kingdom as a result of the Psychoactive Substances Act of 2016. * United States: 4-HO-EPT may be considered an analogue of psilocin, which is a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act. As such, the sale for human consumption would be illegal under the Federal Analogue Act. See also * 4-HO-DET * 4-HO-DPT * 4-HO-PiPT * 5-Fluoro-EPT 5-Fluoro-EPT (5F-EPT, 5-fluoro-''N''-ethyl-''N''-propyltryptamine) is a psychedelic tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as EPT and 5-MeO-EPT. It acts as a potent full agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor with an EC50 of 5.54 nM and an ef ... * 5-MeO-EPT * Ethylpropyltryptamine References External links 4-HO-EPT (Isomer Design) {{Tryptamines Tryptamines Designer drugs Psychedelic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamines
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained from numerous plant sources, like chacruna, and it is often used in ayahuasca brews. Many synthetic tryptamines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-HO-DPT
4-HO-DPT (4-hydroxy-''N'',''N''-dipropyltryptamine, Deprocin) is a substituted tryptamine with psychedelic effects. It is the 4-hydroxyl analog of dipropyltryptamine (DPT). In 2019, Chadeayne et al. solved the crystal structure of the fumarate salt of 4-HO-DPT. The authors describe the structure as follows: "The asymmetric unit contains one 4-HO-DPT cation, protonated at the dipropylamine N atom. There are also two independent water molecules, and half of a fumarate ion present." See also * 4-AcO-DPT * 4-HO-EPT * 4-HO-PiPT * UH-301 (S)-UH-301 is a drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It acts as a selective 5-HT1A receptor silent antagonist. It is structurally related to 8-OH-DPAT. UH-301 was found to produce a head-twitch response in mice which is ... References {{Tryptamines Tryptamines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
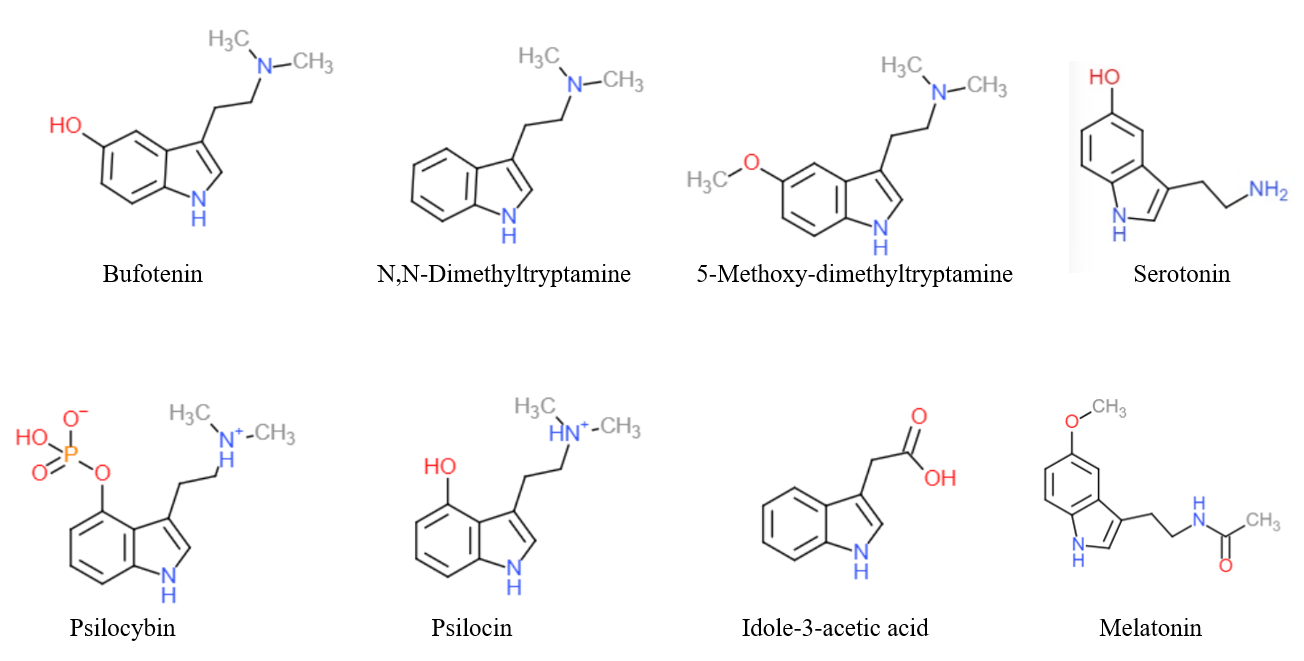
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocin
Psilocin (also known as 4-HO-DMT, 4-hydroxy DMT, psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic substance. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin. Psilocin is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Acting on the 5-HT2A receptors, psilocin modulates the production and reuptake of serotonin. The mind-altering effects of psilocin are highly variable and subjective and resemble those of LSD and DMT. Chemistry Psilocin and its phosphorylated cousin, psilocybin, were first isolated and named in 1958 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann. Hofmann obtained the chemicals from laboratory-grown specimens of the entheogenic mushroom ''Psilocybe mexicana''. Hofmann also succeeded in finding synthetic routes to these chemicals. Psilocin can be obtained by dephosphorylation of natural psilocybin under strongly acidic or under alkaline conditions (hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoactive Substances Act 2016
The Psychoactive Substances Act 2016 (c. 2) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom intended to restrict the production, sale and supply of a new class of psychoactive substances often referred to as "legal highs". The bill was given Royal Assent on 28 January 2016, and came into force on 26 May 2016 across the entire United Kingdom. Description The law defines as a "psychoactive substance" anything which "by stimulating or depressing the person’s central nervous system ... affects the person’s mental functioning or emotional state". The law bans all such substances but exempts alcohol, tobacco or nicotine-based products, caffeine, food and drink, medicinal products and any drug that is already regulated under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. The Act: * makes it an offence to produce, supply, offer to supply, possess with intent to supply, possess on custodial premises, import or export psychoactive substances; that is, any substance intended for human consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) is the statute establishing federal government of the United States, federal drug policy of the United States, U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use, and distribution of certain substances is regulated. It was passed by the 91st United States Congress as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970 and signed into law by President Richard Nixon. The Act also served as the national implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. The legislation created five schedules (classifications), with varying qualifications for a substance to be included in each. Two federal agencies, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), determine which substances are added to or removed from the various schedules, although the statute passed by Congress created the initial listing. Congress has sometimes scheduled other substances th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Analogue Act
The Federal Analogue Act, , is a section of the United States Controlled Substances Act passed in 1986 which allows any chemical "substantially similar" to a controlled substance listed in Schedule I or II to be treated as if it were listed in Schedule I, but only if intended for human consumption. These similar substances are often called designer drugs. The law's constitutionality has been questioned by now Supreme Court Justice Neil Gorsuch; its broad reach has been used to successfully prosecute possession of chemicals openly sold as dietary supplements and naturally contained in foods such as chocolate. Definition (32) *(A) Except as provided in subparagraph (C), the term ''controlled substance analogue'' means a substance - **(i) the chemical structure of which is substantially similar to the chemical structure of a controlled substance in schedule I or II; **(ii) which has a stimulant, depressant, or hallucinogenic effect on the central nervous system that is substantial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-HO-DET
4-HO-DET, also known as 4-hydroxy-diethyl-tryptamine, CZ-74, is a hallucinogenic drug and psychedelic compound of moderate duration. 4-HO-DET is a substituted tryptamine, structurally related to psilocin, ethocybin, and 4-HO-DIPT. Analogs The acetic acid ester of 4-HO-DET is known as 4-AcO-DET. The phosphoric acid ester of 4-HO-DET is known as 4-phosphoryloxy-DET, CEY-19, or ethocybin. History 4-HO-DET received the lab code CZ-74 in the late 1950s by the inventors of the substance, Albert Hofmann and Franz Troxler. The substance was used together with its phosphoryloxy-analog ethocybin in human clinical trials in the 1960s by the German researchers Hanscarl Leuner and G. Baer. Dosage 10–25 mg is the usual oral dosage for 4-HO-DET, while the acetate and phosphate esters are said to require a slightly higher dosage. Effects 4-HO-DET produces entheogenic effects similar to LSD and psilocybin. Drug prohibition laws Sweden ''Sveriges riksdags'' health ministry ''Staten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-HO-PiPT
4-Hydroxy-''N''-propyl-''N''-isopropyltryptamine (4-HO-PiPT, Piprocin) is a substituted tryptamine derivative which is claimed to have psychedelic effects. It has been sold as a designer drug, first being identified in 2021 in British Columbia, Canada. See also * 4-HO-DPT * 4-HO-DiPT * 4-HO-DSBT * 4-HO-McPT * 4-HO-McPeT * 5-MeO-PiPT * Ebalzotan * Propylisopropyltryptamine Propylisopropyltryptamine (PiPT) is a chemical in the tryptamine family, which reportedly produces psychedelic and hallucinogenic effects that resemble those of other related dialkyl tryptamine derivatives, although PiPT is reportedly relatively ... References Tryptamines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Fluoro-EPT
5-Fluoro-EPT (5F-EPT, 5-fluoro-''N''-ethyl-''N''-propyltryptamine) is a psychedelic tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as EPT and 5-MeO-EPT. It acts as a potent full agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor with an EC50 of 5.54 nM and an efficacy of 104% (compared to serotonin). It produces a head-twitch response in animal studies, and is claimed to have antidepressant activity. See also * 5-Fluoro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-AET * 5-Fluoro-DMT * 5-Fluoro-DET 5-Fluoro-DET (5F-DET, 5-fluoro-''N,N''-diethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as DET and 5-MeO-DET. It acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme myeloperoxidase, and is also thought to be an agonist An agonist is a che ... * 5-Fluoro-MET References Psychedelic tryptamines Tryptamines Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |