|
4-Keto-PCP
4-Keto-PCP is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has potency in between that of ketamine and phencyclidine but with somewhat more sedating effects in animal studies. See also * 3-HO-PCP * 3-Fluoro-PCP * Bromadol * Dimetamine * Methoxetamine Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs 1-Piperidinyl compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamines
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
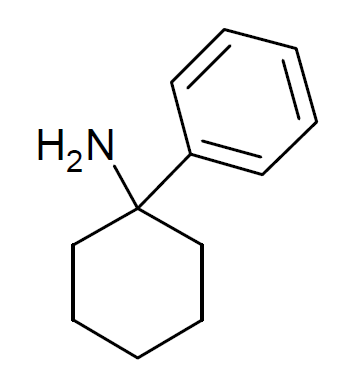
Arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-HO-PCP
3-Hydroxyphencyclidine (3-HO-PCP) is a dissociative of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) that has been sold online as a designer drug. Pharmacology 3-HO-PCP acts as a high-affinity uncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor via the dizocilpine (MK-801) site (Ki = 30 nM). It has much higher affinity than PCP for this site (Ki = 250 nM, for comparison; 8-fold difference). The drug also has high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) (Ki = 39–60 nM) in animal test subjects, the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) (Ki = 140 nM), and the sigma σ1 receptor (Ki = 42 nM; IC50 = 19 nM), whereas it has only low affinity for the δ-opioid receptor (Ki = 2,300 nM). The high affinity of 3-HO-PCP for opioid receptors is unique among arylcyclohexylamines and is in contrast to PCP, which has only very low affinity for the MOR (Ki = 11,000–26,000 nM; 282- to 433-fold difference) and the other opioid receptors (Ki = 4,100 n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Fluoro-PCP
3-Fluoro-PCP (3'-F-PCP, 3F-PCP) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It was first identified in Slovenia in October 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021. See also * 3-Fluorodeschloroketamine * 3-Chloro-PCP * 3-Methyl-PCP * 3-MeO-PCP * 4-Keto-PCP * Fluorexetamine Fluorexetamine (3'-Fluoro-2-oxo-PCE, FXE) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. Effects are slightly more stimulating than regular ketamine. Still produces analgesic effects with stimulat ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs 4-Piperidinyl compounds Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromadol
BDPC (systematic name 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-phenylethyl)cyclohexanol; also known as bromadol) is a potent narcotic analgesic with a distinctive arylcyclohexylamine chemical structure. It was developed by Daniel Lednicer at Upjohn in the 1970s. Initial studies estimated that it was around 10,000 times the strength of morphine in animal models. However, later studies using more modern techniques assigned a value of 504 times the potency of morphine for the more active ''trans''-isomer. This drug was first seized along with three kilograms of acetylfentanyl in an April 25, 2013 police action in Montreal, Canada, and has reportedly continued to be available on the designer drug black market internationally. Analogues where the ''para''-bromine is replaced by chlorine or a methyl group retain similar activity, as does the ''meta''-hydroxyl derivative. ] ] See also * 3-OH-PCP * 4-Keto-PCP * C-8813 * Cebranopadol * Ciramadol * Dimetamine * Faxeladol * Profadol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Dimethylamino-4-(p-tolyl)cyclohexanone
4-Dimethylamino-4-(''p''-tolyl)cyclohexanone (sometimes known as dimetamine) is a narcotic analgesic with an arylcyclohexylamine chemical structure. It was developed by Daniel Lednicer at Upjohn in the 1970s. It has around the same analgesic potency as morphine, with analogues where the ''p''-methyl group is replaced by chlorine or bromine being slightly weaker. However derivatives where the ketone group has been reacted with a Grignard reagent to add a phenethyl substitution are several hundred times stronger, and in this series it is the bromo compound BDPC that is the most potent. Legal Status 4-Dimethylamino-4-(p-tolyl)cyclohexanone is specifically listed as an illegal drug in Latvia. It is also covered by drug analogue laws in various jurisdictions as a generic arylcyclohexylamine derivative. See also * 3-HO-PCP * 4-Keto-PCP * Tramadol Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drug
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociative
Dissociatives, colloquially dissos, are a subclass of hallucinogens which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include dissociation, a general decrease in sensory experience, hallucinations, dream-like states or anesthesia. Some of these substances, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria or symptoms which are more akin to the effects of certain “hard drugs” or common drugs of abuse. This is likely why dissociatives are considered to be addictive with a fair to moderate potential for abuse, unlike psychedelics. Despite some dissociatives, such as phencyclidine (PCP) possessing stimulating properties, most dissociatives seem to have a general depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent for pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco. Adverse effects may include seizures, coma, addiction, and an increased risk of suicide. Flashbacks may occur despite stopping usage. Chemically, PCP is a member of the arylcyclohexylamine class, and pharmacologically, it is a dissociative anesthetic. PCP works primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. PCP is most commonly used in the United States. While usage peaked in the US in the 1970s, between 2005 and 2011 an increase in visits to emergency departments as a result of the drug occurred. As of 2017 in the United States, about 1% of people in Twelfth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxetamine
Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general anesthetics in that it was designed specifically for recreational use. It is a rare example of a drug being so widely controlled without having an existing medical use. MXE is an arylcyclohexylamine. It acts mainly as an NMDA receptor antagonist, similarly to other arylcyclohexylamines like ketamine and PCP. Recreational use Effects MXE is reported to have a similar effect to ketamine. It was often believed to possess opioid properties due to its structural similarity to 3-HO-PCP, but this assumption is not supported by data, which shows insignificant affinity for the μ-opioid receptor by the compound. Recreational use of MXE has been associated with hospitalizations from high and/or combined consumption in the US and UK. Acute rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)