|
Arylcyclohexylamines
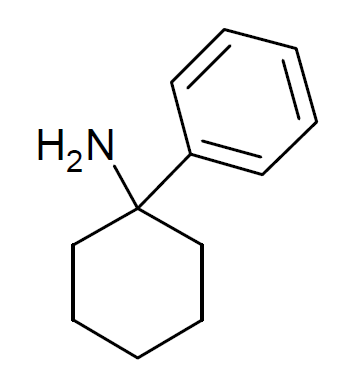
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phencyclidine Structure
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco. Adverse effects may include seizures, coma, addiction, and an increased risk of suicide. Flashbacks may occur despite stopping usage. Chemically, PCP is a member of the arylcyclohexylamine class, and pharmacologically, it is a dissociative anesthetic. PCP works primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. PCP is most commonly used in the United States. While usage peaked in the US in the 1970s, between 2005 and 2011 an increase in visits to emergency departments as a result of the drug occurred. As of 2017 in the United States, about 1% of people in Twelfth g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco. Adverse effects may include seizures, coma, addiction, and an increased risk of suicide. Flashbacks may occur despite stopping usage. Chemically, PCP is a member of the arylcyclohexylamine class, and pharmacologically, it is a dissociative anesthetic. PCP works primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. PCP is most commonly used in the United States. While usage peaked in the US in the 1970s, between 2005 and 2011 an increase in visits to emergency departments as a result of the drug occurred. As of 2017 in the United States, about 1% of people in Twelfth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent for pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eticyclidine
Eticyclidine (PCE, CI-400) is a dissociative anesthetic drug with hallucinogenic effects. It is similar in effects to phencyclidine but is slightly more potent. PCE was developed by Parke-Davis in the 1970s and evaluated for anesthetic potential under the code name CI-400, but research into PCE was not continued after the development of ketamine, a similar drug with more favourable properties. PCE is slightly more potent than PCP and has similar effects, but its unpleasant taste and tendency to cause nausea made it less accepted by users. Due to its similarity in effects to PCP, PCE was placed into the Schedule 1 list of illegal drugs in the 1970s, although it was only briefly abused in the 1970s and 1980s and is now little known. See also * Arylcyclohexylamine * 3-MeO-PCE * 3-MeO-PCP * 4-MeO-PCP * Phencyclidine * PCPr * Methoxetamine Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco. Adverse effects may include seizures, coma, addiction, and an increased risk of suicide. Flashbacks may occur despite stopping usage. Chemically, PCP is a member of the arylcyclohexylamine class, and pharmacologically, it is a dissociative anesthetic. PCP works primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. PCP is most commonly used in the United States. While usage peaked in the US in the 1970s, between 2005 and 2011 an increase in visits to emergency departments as a result of the drug occurred. As of 2017 in the United States, about 1% of people in Twelfth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl Ring
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with C6H5− and is represented by the symbol Ph or, archaically, Φ. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. For example, triphenylmethane (Ph3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, and typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name ''Piper (genus), Piper'', which is the Latin word for Black pepper, pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring Solenopsin, solenopsins. Production Piperidine was first reported in 1850 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson (chemist), Thomas Anderson and again, independently, in 1852 by the French chemist Auguste André Thomas Cahours, Auguste Cahours, who named it. Both of them obtained piperidine by reacting piperine with nitric acid. Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geminal
In chemistry, the descriptor geminal () refers to the relationship between two atoms or functional groups that are attached to the same atom. A geminal diol, for example, is a diol (a molecule that has two alcohol functional groups) attached to the same carbon atom, as in methanediol. Also the shortened prefix ''gem'' may be applied to a chemical name to denote this relationship, as in a ''gem''-dibromide for "geminal dibromide". The concept is important in many branches of chemistry, including synthesis and spectroscopy, because functional groups attached to the same atom often behave differently from when they are separated. Geminal diols, for example, are easily converted to ketones or aldehydes with loss of water.Peter Taylor (2002)''Mechanism and synthesis'' Book 10 of ''Molecular world''. Open University, Royal Society of Chemistry; . 368 pages The related term vicinal refers to the relationship between two functional groups that are attached to adjacent atoms. The rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moiety (chemistry)
In organic chemistry, a moiety ( ) is a part of a molecule that is given a name because it is identified as a part of other molecules as well. Typically, the term is used to describe the larger and characteristic parts of organic molecules, and it should not be used to describe or name smaller functional groups of atoms that chemically react in similar ways in most molecules that contain them. Occasionally, a moiety may contain smaller moieties and functional groups. A moiety that acts as a branch extending from the backbone of a hydrocarbon molecule is called a substituent or side chain, which typically can be removed from the molecule and substituted with others. Active moiety In pharmacology, an active moiety is the part of a molecule or ion – excluding appended inactive portions – that is responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of a drug substance. Inactive appended portions of the drug substance may include either the alcohol or acid moiety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

