|
360 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 360 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ambustus and Visolus (or, less frequently, year 394 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 360 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Egypt * With the help of King Agesilaus II of Sparta, Nectanebo II deposes Teos and becomes king of Egypt. Teos flees to Susa and makes peace with the Persians. Nectanebo II pays the Spartans 230 talents for their help. Judea * Jerusalem has been rebuilt and the power of Judaism's hereditary priesthood is firmly established. Greece * The King of Sparta, Agesilaus II, dies at Cyrene, Cyrenaica, on his way home to Greece from Egypt. He is succeeded by his son Archidamus III as Eurypontid king of Sparta. * As the Illyrians attack the Molossians, the Molossian king Arymbas brings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the Roman dictator, dictator Julius Caesar and Roman emperor, emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones (calendar), nones, and ides (calendar), ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's Egyptian calendar, former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the Byzantine Empire, later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between longitudes E16 and E25, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, also known as '' Pentapolis'' ("Five Cities") in antiquity, was part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into ''Libya Pentapolis'' and ''Libya Sicca''. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as ''Barqa'', after the city of Barca. Cyrenaica became an Italian colony in 1911. After the 1934 formation of Libya, the Cyrenaica province was designated as one of the three primary provinces of the country. During World War II, it fell under British military and civil administration from 1943 until 1951, and finally in the Kingdom of Libya from 1951 until 1963. The region that used to be Cyrenaica officially until 1963 has formed seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callisthenes
Callisthenes of Olynthus (; grc-gre, Καλλισθένης; 360327 BCE) was a well-connected Greek historian in Macedon, who accompanied Alexander the Great during his Asiatic expedition. The philosopher Aristotle was Callisthenes's great uncle. Early life His mother Hero was the niece of Aristotle, and daughter of Proxenus of Atarneus and Arimneste, which made Callisthenes the great-nephew of Aristotle by his sister Arimneste, Callisthenes's grandmother. They first met when Aristotle tutored Alexander the Great. Career Through his great-uncle's influence, Callisthenes was later appointed to attend Alexander the Great on his Asiatic expedition as the official historian. During the first years of Alexander's campaign in Asia, Callisthenes showered praises upon the Macedonian conqueror. As the king and army penetrated further into Asia, however, Callisthenes's tone began to change. He began to sharply criticize Alexander's adoption of Persian customs, with special scorn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
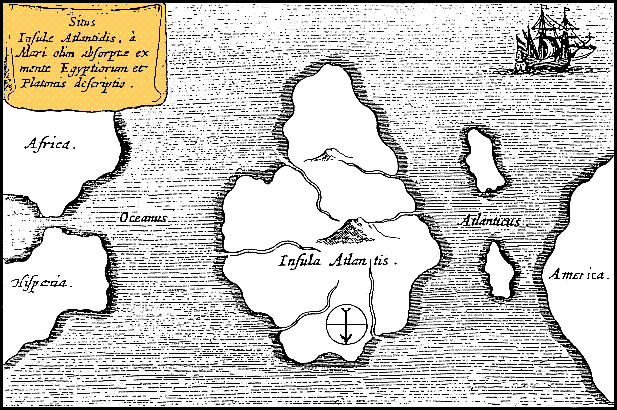
Atlantis
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of Atlas (mythology), Atlas) is a fictional island mentioned in an allegory on the hubris of nations in Plato's works ''Timaeus (dialogue), Timaeus'' and ''Critias (dialogue), Critias'', wherein it represents the antagonist naval power that besieges "Ancient Athens", the Counterfactual history, pseudo-historic embodiment of Plato's ideal state in ''The Republic (Plato), The Republic''. In the story, Athens repels the Atlantean attack unlike any other nation of the Ecumene, known world, supposedly bearing witness to the superiority of Plato's concept of a state. The story concludes with Atlantis falling out of favor with the deities and submerging into the Atlantic Ocean. Despite its minor importance in Plato's work, the Atlantis story has had a considerable impact on literature. The allegorical aspect of Atlantis was taken up in utopian works of several Renaissance writers, such as Francis Bacon's ''New Atlantis'' and Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critias
Critias (; grc-gre, Κριτίας, ''Kritias''; c. 460 – 403 BC) was an ancient Athenian political figure and author. Born in Athens, Critias was the son of Callaeschrus and a first cousin of Plato's mother Perictione. He became a leading and violent member of the Thirty Tyrants. He also was an associate of Socrates, a fact that did not endear Socrates to the Athenian public. Critias was noted in his day for his tragedies, elegies, and prose works. Sextus Empiricus attributed the ''Sisyphus fragment'' to Critias; others, however, attribute it to Euripides. His only known play is ''Peirithous.'' In addition, eight shorter quotations from unidentified plays have come down to us. Life Critias gave an account of his ancestry which was later recorded in Plato's '' Timaeus''. Critias's great-grandfather, Dropidas, was an intimate friend of Solon. Dropidas's son, also named Critias, was the grandfather and namesake of the author Critias. Critias was once a student of Socrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timaeus (dialogue)
''Timaeus'' (; grc-gre, Τίμαιος, Timaios, ) is one of Plato's dialogues, mostly in the form of long monologues given by Critias and Timaeus, written 360 BC. The work puts forward reasoning on the possible nature of the physical world and human beings and is followed by the dialogue ''Critias''. Participants in the dialogue include Socrates, Timaeus, Hermocrates, and Critias. Some scholars believe that it is not the Critias of the Thirty Tyrants who appears in this dialogue, but his grandfather, who is also named Critias. It has been suggested from some traditions (Diogenes Laertius (VIII 85) from Hermippus of Smyrna (3rd century BC) and Timon of Phlius ( 320 – 235 BC)) that ''Timaeus'' was influenced by a book about Pythagoras, written by Philolaus, although this assertion is generally considered false. Introduction The dialogue takes place the day after Socrates described his ideal state. In Plato's works, such a discussion occurs in the ''Republic''. Socrates fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy ( Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and into the Balkans, leading to war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settled in Anatolia, becoming known as Galatians. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arymbas
Arybbas ( grc, Ἀρύββας or Ἀρύβας; 373–343/2 BC) was a king of the Molossians. Family Arybbas was a son of Alcetas I, brother of Neoptolemus I and grandfather of Pyrrhus. He married his niece Troas (sister of Olympias). Arybbas's oldest son was Alcetas II, who reigned as a king of Epirus from 313 BC to 303 BC. It is very probable that the ''Aryptaeus, king of the Molossians'' mentioned by Diodorus 18.11.1, who joined the Hellenic cause during the Lamian War, is Arybbas. Arybbas' second son was Aeacides king of Epirus (ruled 331-316, 313 BC). Biography Upon the death of their father Alcetas I in 370 BCE, Arybbas and his brother Neoptolemus I divided the kingdom of Epirus in two and each ruled their own part, until Neoptolemus died around 360 BCE and Arybbas became king of all of Epirus. In ca. 360 BC, against an Illyrian attack, Arybbas evacuated his non-combatant population to Aetolia and let the Illyrians loot freely. The stratagem was successful, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molossians
The Molossians () were a group of ancient Greek tribes which inhabited the region of Epirus in classical antiquity. Together with the Chaonians and the Thesprotians, they formed the main tribal groupings of the northwestern Greek group. On their northern frontier, they neighbored the Chaonians and on their southern frontier neighbored the kingdom of the Thesprotians. They formed their own state around 370 BC and were part of the League of Epirus. The most famous Molossian ruler was Pyrrhus of Epirus, considered one of the greatest generals of antiquity. The Molossians sided against Rome in the Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) and were defeated. Following the war, 150,000 Molossians and other Epirotes were enslaved and transported to the Roman Republic, overwhelmingly in Italy itself. Ancient sources According to Strabo, the Molossians, along with the Chaonians and Thesprotians, were the most famous among the fourteen tribes of Epirus, who once ruled over the whole reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians. Illyrians spoke the Illyrian language, an Indo-European language, which in ancient times perhaps also had speakers in some parts of Southern Italy. The geographical term Illyris (distinct from ''Illyria'') was sometimes used to define approximately the area of northern and central Albania down to the Aoös valley (modern Vjosa), including in most periods much of the lakeland area. In Roman times the terms Illyria / Illyris / Illyricum were extended from the territory that was roughly located in the area of the south-eastern Adriatic coast (modern Albania and Montenegro) and its hinterland, to a broader region stretching between the Adriatic Sea and the Danube, and from the upper reaches of the Adriatic down to the Ardiaei. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |