|
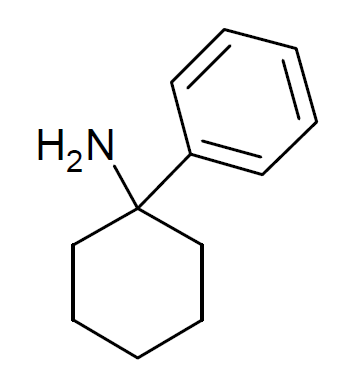
3-Methyl-PCPy
3-Methyl-PCPy (3-Me-PCPy) is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative with an unusual spectrum of pharmacological effects, acting as both a potent NMDA antagonist and also a triple reuptake inhibitor which inhibits reuptake of all three monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline. It also acts as a high affinity sigma receptor ligand, selective for the σ2 subtype. It produces both stimulant and dissociative effects in animal behavioural studies. Legal Status 3-Methyl-PCPy is covered by drug analogue laws in various jurisdictions (UK, Germany, Japan, Australia etc) as a generic arylcyclohexylamine derivative, and a structural isomer of phencyclidine. See also * 3-Methyl-PCP * BTCP * Deoxymethoxetamine Deoxymethoxetamine (3'-methyl-2-oxo-PCE, DMXE, 3D-MXE) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It is an analogue of methoxetamine where the 3-methoxy group has been replaced by methyl. It has ... * Eph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamines
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MDPCP
Methylenedioxyphencyclidine (3',4'-MD-PCP, MDPCP) is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, with similar effects to related drugs such as 3-MeO-PCP and 4-MeO-PCP. See also * 3-F-PCP * 3-Methyl-PCPy * MXiPr * MDMAR * Methylenedioxyphenmetrazine * Methylenedioxypyrovalerone Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI). It was first developed in the 1960s by a team at Boehringer Ingelheim. Its activity at the dopamine tr ... * 1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Benzodioxoles {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deoxymethoxetamine
Deoxymethoxetamine (3'-methyl-2-oxo-PCE, DMXE, 3D-MXE) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It is an analogue of methoxetamine where the 3-methoxy group has been replaced by methyl. It has been sold online since around October 2020, and was first definitively identified by a forensic laboratory in Denmark in February 2021. See also * 3-Methyl-PCP * 3-Methyl-PCPy * Hydroxetamine * Fluorexetamine * Methoxieticyclidine * MXiPr MXiPr (Methoxisopropamine, Isopropyloxetamine, Isopropyxetamine') is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as ketamine and methoxetamine. It was first identified in ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs Secondary amines Ketones {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Isomer
In chemistry, a structural isomer (or constitutional isomer in the IUPAC nomenclature) of a chemical compound, compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct chemical bond, bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept. For example, butanol , methyl propyl ether , and diethyl ether have the same molecular formula but are three distinct structural isomers. The concept applies also to polyatomic ions with the same total charge. A classical example is the cyanate ion and the fulminate ion . It is also extended to ionic compounds, so that (for example) ammonium cyanate and urea are considered structural isomers,William F. Bynum, E. Janet Browne, Roy Porter (2014): ''Dictionary of the History of Science''. 530 pages. and so are methylammonium formate and ammonium acetate . Structural isomerism is the most radical type of isomerism. It is opposed to stereoisomerism, in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephenidine
Ephenidine (also known as NEDPA and EPE) is a dissociative anesthetic that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is illegal in some countries as a structural isomer of the banned opioid drug lefetamine, but has been sold in countries where it is not yet banned. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Ephenidine and related diarylethylamines have been studied in vitro as treatments for neurotoxic injuries, and are antagonists of the NMDA receptor (Ki = 66.4 nM for ephenidine). Ephenidine also possesses weaker affinity for dopamine and norepinephrine transporters (379 nM and 841 nM, respectively) as well as σ1R (629 nM) and σ2R (722 nM) binding sites. Pharmacokinetics Metabolism Ephenidine's metabolic pathway consists of N-oxidation, N-dealkylation, mono- and bis-hydroxylation of the benzene ring, and hydroxylation of the phenyl ring only after N-dealkylation. The dihydroxy metabolites were conjugated by methylation of one hydroxy group, and hydroxy metab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTCP
Benocyclidine, also known as benzothiophenylcyclohexylpiperidine (BTCP), is a psychoactive recreational drug of the arylcyclohexylamine class which is related to phencyclidine (PCP). It was first described in a patent application naming Marc Caron and colleagues at Duke University in 1997. It acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) and a psychostimulant. Unlike related compounds like phencyclidine and ketamine, benocyclidine is a pure DRI with negligible affinity for the NMDA receptor, and it therefore lacks any anticonvulsant, anesthetic, hallucinogenic, or dissociative effects. It has been used to label the dopamine transporter. BCP was used to try to find a common pharmacophore for DRI type stimulants. More recently, benocyclidine has been found in several ecstasy tablets, sold as MDMA. Legal status in the United States Benocyclidine is not scheduled at the federal level in the United States, but may be considered an analog of PCP, in which ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Methyl-PCP
3-Methyl-PCP (3'-Methyl-PCP, ''meta''-Methyl-PCP, 3-Me-PCP) is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as 3'-MeO-PCP and 3'-Me-PCPy. It was first synthesised in the 1960s, but was only identified on the illicit market in Hungary in September 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021. See also * 3-Cl-PCP * 3-HO-PCP * 3-F-PCP * Deoxymethoxetamine * MXiPr MXiPr (Methoxisopropamine, Isopropyloxetamine, Isopropyxetamine') is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as ketamine and methoxetamine. It was first identified ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs O-methylated phenols Substances discovered in the 1960s {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco. Adverse effects may include seizures, coma, addiction, and an increased risk of suicide. Flashbacks may occur despite stopping usage. Chemically, PCP is a member of the arylcyclohexylamine class, and pharmacologically, it is a dissociative anesthetic. PCP works primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. PCP is most commonly used in the United States. While usage peaked in the US in the 1970s, between 2005 and 2011 an increase in visits to emergency departments as a result of the drug occurred. As of 2017 in the United States, about 1% of people in Twelfth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociative
Dissociatives, colloquially dissos, are a subclass of hallucinogens which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include dissociation, a general decrease in sensory experience, hallucinations, dream-like states or anesthesia. Some of these substances, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria or symptoms which are more akin to the effects of certain “hard drugs” or common drugs of abuse. This is likely why dissociatives are considered to be addictive with a fair to moderate potential for abuse, unlike psychedelics. Despite some dissociatives, such as phencyclidine (PCP) possessing stimulating properties, most dissociatives seem to have a general depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMDA Antagonist
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia. Several synthetic opioids function additionally as NMDAR-antagonists, such as pethidine, levorphanol, methadone, dextropropoxyphene, tramadol and ketobemidone. Some NMDA receptor antagonists, such as ketamine, dextromethorphan (DXM), phencyclidine (PCP), methoxetamine (MXE), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are sometimes used as recreational drugs, for their dissociative, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant properties. When used recreationally, they are classified as dissociative drugs. Uses and effects NMDA receptor antagonists induce a state called dissociative anesthesia, marked by catalepsy, amnesia, and analgesia. Ketamine is a favored anesthetic for emergency patients with unknown medical history and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have Sympathomimetic drug, sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or Prohibition (drugs), illicitly) as performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing or recreational drug use, recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or ''Comedown (drugs), comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
