|
2N2222
The 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It was originally made in the TO-18 metal can as shown in the picture. The 2N2222 is considered a very common transistor, and is used as an exemplar of an NPN transistor. It is frequently used as a small-signal transistor, and it remains a small general purpose transistor of enduring popularity. The 2N2222 was part of a family of devices described by Motorola at a 1962 IRE convention. Since then it has been made by many semiconductor companies, for example, Texas Instruments.''The Transistor and Diode Data Book for Design Engineers'', Texas Instruments Incorporated, no date, TI publication number CC413 71242-73-CSS, page 4-93 Specifications The JEDEC registration of a device number ensures particular rated values will be met by all p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2N2907
The 2N2907 is a commonly available PNP bipolar junction transistor used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. This transistor was made by several manufacturers; Texas Instruments released a data sheet for their version of this part dated March 1973. An "A" suffix indicates a slightly higher breakdown voltage. These transistors have an enduring popularity with electronics hobbyists. Specifications It is a 0.6-ampere, 60-volt, 400-milliwatt transistor. For the 2N2907, the gain–bandwidth product under specified test conditions, or , is 200 Megahertz, which is notionally the frequency at which the current gain drops to one. Practical use of a transistor requires that it be used for frequencies much less than . At low frequencies, the current gain (beta) is at least 100. The 2N2907 is used in a variety of analog amplification and switching appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TO-18
In electronics, TO-18 is a designation for a style of transistor metal case. The case is more expensive than the similarly sized plastic TO-92 package. The name is from JEDEC, signifying ''Transistor Outline Package, Case Style 18''. Construction and orientation The typical TO-18 metal can package has a base diameter of , a cap diameter of , a cap height of . The tab is located 45° from pin 1, which is typically the emitter. The lead diameter is nominally . The leads are arranged in a circle with a diameter of . The minimum length of the leads is . Different manufacturers have different tolerances, and the actual form factor may vary slightly, depending on function. Uses and variants The 3-lead TO-18 is used for transistors and other devices using no more than three leads. Variants for diodes, photodiodes and LEDs may have only two leads. Light-sensitive or light-emitting devices have a transparent window, lens, or parabolic reflectors in the top of the case rather than a sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BC548
The BC548 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly used in European and American electronic equipment. It is notably often the first type of bipolar transistor hobbyists encounter and is often featured in designs in hobby electronics magazines where a general-purpose transistor is required. The BC548 is low in cost and widely available. History and usage The BC548 is a part of a family of NPN and PNP epitaxial silicon transistors that originated with the metal-cased BC108 family of transistors. The BC548 is the modern plastic-packaged BC108; the BC548 article at the Radiomuseum website describes the BC548 as a successor to the BC238 and differing from the BC108 in only the shape of the package. Datasheets for the BC548 give specifications that are identical to, or exceed, those of the BC108, BC148 and BC238 predecessors. Thus the BC548 (or BC546 to 550) is a valid substitute in any circuit designed for the older BC108 (or BC148), which includes many Mullard an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JEDEC
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States. JEDEC has over 300 members, including some of the world's largest computer companies. Its scope and past activities includes standardization of part numbers, defining an electrostatic discharge (ESD) standard, and leadership in the lead-free manufacturing transition. The origin of JEDEC traces back to 1944, when RMA (subsequently renamed EIA) and NEMA established the Joint Electron Tube Engineering Council (JETEC) to coordinate vacuum tube type numberings. In 1958, with the advent of semiconductor technology, the joint JETEC-activity of EIA and NEMA was renamed into Joint Electron Device Engineering Council. NEMA discontinued its involvement in 1979. In the fall of 1999, JEDEC became a separate trade association under the current name, but maintained an EIA alliance, until EIA ceased o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PNP Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPN Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TO-92
The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost. History and origin The JEDEC TO-92 descriptor is derived from the original full name for the package: Transistor Outline Package, Case Style 92. The package is also known by the designation SOT54. By 1966 the package was being used by Motorola for their 2N3904 devices among others. Construction and orientation The case is molded around the transistor elements in two parts; the face is flat, usually bearing a machine-printed part number (some early examples had the part number printed on the top surface instead). The back is semi-circularly-shaped. A line of moulding flash from the injection-moulding process can be seen around the case. The leads protrude from the bottom of the case. When looking at the face of the transistor, the leads are commonly configured from left-to-right as the ''emitter'', ''ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2N3906
The 2N3906 is a commonly used PNP bipolar junction transistor intended for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low electric current and power and medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. Overview The 2N3906 is manufactured in a plastic TO-92 case. When looking at the flat side with the leads pointed downward, the three leads emerging from the transistor are, from left to right, the emitter, base, and collector leads. The 2N3906 is specified by a collector current of 200 mA, collector-base and collector-emitter voltages of 40 V, for power dissipation of 300 mW. Its transition frequency Ft is 250 MHz, with a beta of at least 100. The complementary NPN transistor to the 2N3906 is the 2N3904. Both types were registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-1960s. Part numbers The 2N3904 (NPN) and 2N3906 (PNP) are complementary transistor pairs. These transistors are available in package styles TO-92, SOT2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2N3055
The 2N3055 is a silicon NPN power transistor intended for general purpose applications. It was introduced in the early 1960s by RCA using a hometaxial power transistor process, transitioned to an epitaxial base in the mid-1970s. Its numbering follows the JEDEC standard. It is a transistor type of enduring popularity. Specifications The exact performance characteristics depend on the manufacturer and date; before the move to the epitaxial base version in the mid-1970s the fT could be as low as 0.8 MHz, for example. Packaged in a TO-3 case style, it is a 15 amp, 60 volt (or more, see below), 115 watt power transistor with a β (forward current gain) of 20 to 70 at a collector current of 4 A (this may be over 100 when testing at lower currents). It often has a transition frequency of around 3.0 MHz and 6 MHz is typical for the 2N3055A; at this frequency the calculated current gain (beta) drops to 1, indicating the transistor can no longer provide useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
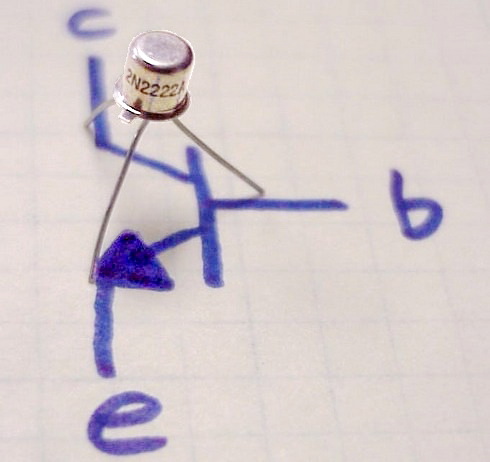


.jpg)
