|
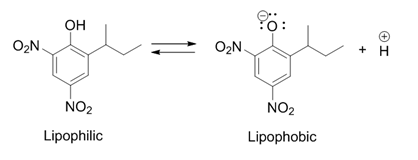
2,4-dinitrophenol
2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP or simply DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. It is a yellow, crystalline solid that has a sweet, musty odor. It sublimates, is volatile with steam, and is soluble in most organic solvents as well as aqueous alkaline solutions. When in a dry form, it is a high explosive and has an instantaneous explosion hazard. It is a precursor to other chemicals and is biochemically active, uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation from the electron transport chain in cells with mitochondria, by allowing protons to pass from the intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix. Oxidative phosphorylation is a highly regulated step in aerobic respiration that is inhibited, among other factors, by normal cellular levels of ATP. Uncoupling it results in chemical energy from diet and energy stores such as triglycerides being wasted as heat with minimal regulation, leading to dangerously high body temperatures that may develop into heatstroke. Its use as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncoupler
An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transport chain. The result is that the cell or mitochondrion expends energy to generate a proton-motive force, but the proton-motive force is dissipated before the ATP synthase can recapture this energy and use it to make ATP. Uncouplers are capable of transporting protons through mitochondrial and lipid membranes. Description Classical uncouplers have five properties: # the complete release of respiratory control # the substitution of all coupled processes (ATP synthesis, transhydrogenation, reverse electron flow, active transport of cations, etc.) by a cyclic proton transport mediated by the uncoupler # the elimination of all protonic and cationic gradients generated across the mitochondrial or prokaryotic membrane # no discrimination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonophore
A protonophore, also known as a proton translocator, is an ionophore that moves protons across lipid bilayers or other type of membranes. This would otherwise not occur as protons cations (H+) have positive charge and hydrophilic properties, making them unable to cross without a channel or transporter in the form of a protonophore. Protonophores are generally aromatic compounds with a negative charge, that are both hydrophobic and capable of distributing the negative charge over a number of atoms by π- orbitals which delocalize a proton's charge when it attaches to the molecule. Both the neutral and the charged protonophore can diffuse across the lipid bilayer by passive diffusion and simultaneously facilitate proton transport. Protonophores uncouple oxidative phosphorylation via a decrease in the membrane potential of the inner membrane of mitochondria. They stimulate mitochondria respiration and heat production. Protonophores (uncouplers) are often used in biochemistry research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncoupling Protein
An uncoupling protein (UCP) is a mitochondrial inner membrane protein that is a regulated proton channel or transporter. An uncoupling protein is thus capable of dissipating the proton gradient generated by NADH-powered pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. The energy lost in dissipating the proton gradient via UCPs is not used to do biochemical work. Instead, heat is generated. This is what links UCP to thermogenesis. However, not every type of UCPs are related to thermogenesis. Although UCP2 and UCP3 are closely related to UCP1, UCP2 and UCP3 do not affect thermoregulatory abilities of vertebrates. UCPs are positioned in the same membrane as the ATP synthase, which is also a proton channel. The two proteins thus work in parallel with one generating heat and the other generating ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate, the last step in oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondria respiration is coupled to ATP synthesis (ADP phosphorylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoseb
Dinoseb is a common industry name for 6-sec-butyl-2,4-dinitrophenol, a herbicide in the dinitrophenol family. It is a crystalline orange solid which does not readily dissolve in water. Dinoseb is banned as an herbicide in the European Union (EU) and the United States because of its toxicity. It also finds use as a polymerisation inhibitor, where it is often referred to as DNBP. It is used to prevent the thermally induced polymerisation of styrene and other unsaturated monomers when they are being purified by distillation. History In 1892, dinitro-''ortho''-cresol (2,4-dinitro-6-methylphenol), a chemical compound closely related to dinoseb, was discovered in Germany and first used as an insecticide. It was later also used as an herbicide and also fungicide after those characteristics were discovered. In 1945 the ''ortho''-methyl group was replaced by a ''sec''-butyl group, producing dinoseb. This compound had a superior contact and stomach activity on insects and mites. Dinoseb b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dye
Sulfur dyes are the most commonly used dyes manufactured for cotton in terms of volume. They are inexpensive, generally have good colour fastness, wash-fastness, and are easy to apply. Sulfur dyes are predominantly black, brown, and dark blue. Red sulfur dyes are unknown, although a pink or lighter scarlet (color), scarlet color is available. Chemistry Sulfur linkages are the integral part of chromophore in sulfur dyes. They are organosulfur compounds consisting of sulfide (organic), sulfide (–S–), disulfide (–S–S–) and polysulfide (–Sn–) links in heterocyclic rings. They feature thiazoles, thiazone, thianthrene, and phenothiazonethioanthrone subunits. Being nonionic, sulfur dyes are insoluble in water. Process Dyeing includes a few stages, viz. reduction, dyeing, washing, oxidation, soaping, and final washing. The anion is developed on reducing and solubilising at boil when it shows affinity for cellulose. Sodium sulfide (Na2S), the reducing and solubilising agent, pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane bound structure, down their electrochemical gradient. An important example is the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the movement of hydrogen ions (H+) across a membrane during cellular respiration or photosynthesis. Hydrogen ions, or protons, will diffuse from a region of high proton concentration to a region of lower proton concentration, and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make ATP. This process is related to osmosis, the movement of water across a selective membrane, which is why it is called "chemiosmosis". ATP synthase is the enzyme that makes ATP by chemiosmosis. It allows protons to pass through the membrane and uses the free energy difference to phosphorylate adenosine diphosphate (ADP), making ATP. The generation of ATP by chemiosmosis occurs in mitochondria and chloroplasts, as well as in most bacteria and archaea. For instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which in tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs, as well as organism structure and function.Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, which is the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.Ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioenergetics
Bioenergetics is a field in biochemistry and cell biology that concerns energy flow through living systems. This is an active area of biological research that includes the study of the transformation of energy in living organisms and the study of thousands of different cellular processes such as cellular respiration and the many other metabolic and enzymatic processes that lead to production and utilization of energy in forms such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules. Nelson, David L., Cox, Michael M. ''Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry.'' New York: W.H. Freeman and Company, 2013. Sixth ed., pg. 27. That is, the goal of bioenergetics is to describe how living organisms acquire and transform energy in order to perform biological work. Nelson, David L., Cox, Michael M. ''Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry.'' New York: W.H. Freeman and Company, 2013. Sixth ed., pg. 24. The study of metabolic pathways is thus essential to bioenergetics. Overview Bioenergetics is the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of UN Numbers 0001 To 0100
UN numbers from UN 0001 to UN 0100 as assigned by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods are as follows: __NOTOC__ UN 0001 to UN 0100 See also *Lists of UN numbers The UN numbers range from UN0001 to about UN3600 and are assigned by the United Nations Committee of Experts on the Transport of Dangerous Goods. UN 0001 to 0600 * List of UN numbers 0001 to 0100 * List of UN numbers 0101 to 0200 * List of UN nu ... References {{UN number list navbox Lists of UN numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Transport
In cellular biology, membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes, which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them. The regulation of passage through the membrane is due to selective membrane permeability - a characteristic of biological membranes which allows them to separate substances of distinct chemical nature. In other words, they can be permeable to certain substances but not to others. The movements of most solutes through the membrane are mediated by membrane transport proteins which are specialized to varying degrees in the transport of specific molecules. As the diversity and physiology of the distinct cells is highly related to their capacities to attract different external elements, it is postulated that there is a group of specific transport proteins for each cell type and for every specific physiological stage /sup>. This differential expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |