|
1817 In Archaeology
The year 1817 in archaeology involved some significant events. Events *The Elgin Marbles go on display in the British Museum in London. * Stamford Raffles publishes ''The History of Java''. Explorations * Giovanni Battista Belzoni travels extensively through Egypt, visiting Abu Simbel, Karnak and the Valley of the Kings, creating several excavation sites. * Major Stephen H. Long commands an expedition exploring the southern part of Arkansas, as well as the Louisiana border of the Red River; he also explores the Wisconsin River to its headwaters and the Mississippi River to the Falls of Saint Anthony. Excavations * October - The KV16 burial site of Ramesses I in the East Valley of the Kings is discovered and excavated by Giovanni Battista Belzoni. * Near Cairo, the Great Sphinx of Giza is excavated to chest level by Giovanni Battista Caviglia. * Giovanni Battista Belzoni clears the Great Temple of Abu Simbel of sand. * The tophet in Carthage is first excavated; since then, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elgin Marbles
The Elgin Marbles (), also known as the Parthenon Marbles ( el, Γλυπτά του Παρθενώνα, lit. "sculptures of the Parthenon"), are a collection of Classical Greek marble sculptures made under the supervision of the architect and sculptor Phidias and his assistants. They are original parts of the Parthenon and other sacred and ceremonial structures built on the Acropolis of Athens in the 5th century BCE. The collection is on display in the British Museum, in the purpose-built Duveen Gallery. The presence of the Elgin Marbles in the British Museum is the subject of international controversy. From 1801 to 1812, agents of Thomas Bruce, 7th Earl of Elgin removed about half of the surviving sculptures of the Parthenon, as well as sculptures from the Propylaea and Erechtheion,''Encyclopædia Britannica'', "Elgin Marbles", 2008, O.Ed. and had them transported by sea to Britain. Elgin argued as his authority for this that he had obtained an official decree (a firman) fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV16
Tomb KV16 is located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was used for the burial of Pharaoh Ramesses I of the Nineteenth Dynasty. The burial place was discovered by Giovanni Belzoni in October 1817. As Ramesses I ruled for less than two years, his sepulchre is rather truncated, being only twenty-nine metres long. It consists of two descending staircases, linking a sloping corridor and leading to the burial chamber. Like the tomb of Horemheb (KV57), the grave is decorated with the ''Book of Gates.'' The sarcophagus, still in place in the final chamber, is constructed of red quartzite Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tect .... References *Reeves, N & Wilkinson, R.H. The Complete Valley of the Kings, 1996, Thames and Hudson, London. *Siliotti, A. Guide to the Valley of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frédéric Cailliaud
Frédéric Cailliaud (9 June 1787 – 1 May 1869) was a French naturalist, mineralogist and conchologist. He was born, and died, in Nantes, where he was the curator of the Natural History Museum of Nantes from 1836 to 1869. He travelled in Egypt, Nubia, and Ethiopia, collecting minerals and making observations. He was a part of the military expedition that his patron Viceroy Muhammad Ali sent south to conquer the Kingdom of Sennar, but also marched further into Fazogli where Caillaud searched for outcroppings of gold while the commander Ismail, son of Muhammad Ali, enslaved locals and slaughtered all who resisted him. Although he failed to find any sizeable deposits of gold in the mountains along the modern Sudan-Ethiopia border, he did make a sufficiently detailed survey of the area to be published after he returned to France in 1827. Andrew Bednarski and W. Benson Harer, Jr. write: Shortly after his return, he published ''Travels in the Oasis of Thebes'', with never-befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV21
Tomb KV21 is an ancient Egyptian tomb located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was discovered in 1817 by Giovanni Battista Belzoni, Giovanni Belzoni and later re-excavated by Donald P. Ryan in 1989. It contains the mummy#Egyptian mummies, mummies of two women, thought to be Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty queens. In 2010, a team headed by Zahi Hawass used DNA evidence to tentatively identify one mummy, KV21A, as the biological mother of the 317a and 317b mummies, two fetuses preserved in the tomb of King Tutankhamun. Layout The tomb consists of a sloping descending passageway, a staircase, and another descending passage. The passage ends in a room with a single central column and a small chamber adjoining it. The walls are well cut and ready to receive plaster if plastering was intended. The tomb is most similar in layout scale to KV32, the tomb of Tiaa, mother of Thutmose IV. Marc Gabolde considers that the more precise cutting and regular layout of this tomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seti I
Menmaatre Seti I (or Sethos I in Greek) was the second pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the New Kingdom period, ruling c.1294 or 1290 BC to 1279 BC. He was the son of Ramesses I and Sitre, and the father of Ramesses II. The name 'Seti' means "of Set", which indicates that he was consecrated to the god Set (also termed "Sutekh" or "Seth"). As with most pharaohs, Seti had several names. Upon his ascension, he took the prenomen "mn-m3't-r' ", usually vocalized in Egyptian as ''Menmaatre (''Established is the Justice of Re). His better known nomen, or birth name, is transliterated as "''sty mry-n-ptḥ"'' or ''Sety Merenptah'', meaning "Man of Set, beloved of Ptah". Manetho incorrectly considered him to be the founder of the 19th Dynasty, and gave him a reign length of 55 years, though no evidence has ever been found for so long a reign. Reign After the enormous social upheavals generated by Akhenaten's religious reform, Horemheb, Ramesses I and Seti I's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mejit Island
Mejit ( Marshallese: , , or , ) is an island in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. Unlike most of the other islands of the Marshall Islands, Mejit is a stony island rather than a coral atoll, although it is surrounded by a fringing coral reef enclosing a narrow lagoon. It is located east of the main line of the Ratak chain, approximately northeast from Wotje. With an estimated population of 348 people, the island is lush in pandanus, breadfruit and taro. To the residents, this island is known as 'Paradise". It has a freshwater lake (rare in the Marshall Islands) with indigenous ducks. Mejit is famous for its pandanus leaf mats. An airstrip, Mejit Airport, bisects the island. It is served by Air Marshall Islands. History First recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish expedition of Miguel López de Legazpi on 9 January 1565. It was charted as ''Los Barbudos'' (The Bearded in Spanish) because of the long beards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Von Kotzebue
Otto von Kotzebue (russian: О́тто Евста́фьевич Коцебу́, tr. ; – ) was a Russian officer and navigator in the Imperial Russian Navy. He was born in Reval. He was known for his explorations of Oceania. Early life and education Born into the Kotzebue family of Brandenburgish origin, originating in Kossebau in Altmark, he was the second son of writer and diplomat August von Kotzebue and his wife, he was born in Reval (now Tallinn, Estonia), then part of the Russian Empire. After attending the Saint Petersburg school of cadets, he accompanied Adam Johann von Krusenstern on his voyage of 1803–1806. Both attested to the prominence of Baltic Germans in Imperial Russia's naval expeditions around 1800. Naval career On promotion to lieutenant, Kotzebue was placed in command of an expedition, fitted out at the expense of the imperial chancellor, Count Nikolay Rumyantsev, in the brig ''Rurik''. In this vessel, with only twenty-seven men, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
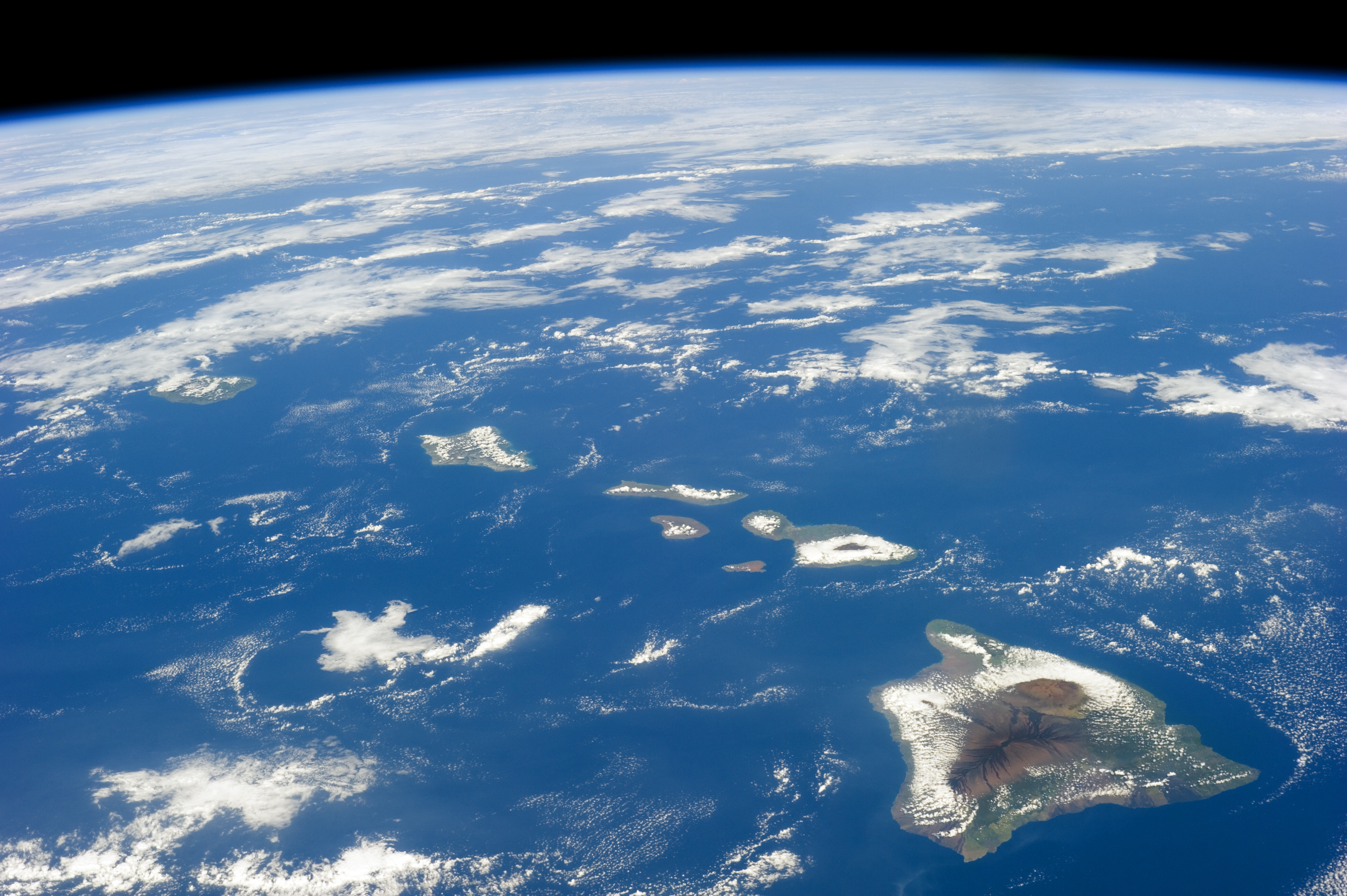
Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly the group was known to Europeans and Americans as the Sandwich Islands, a name that James Cook chose in honor of the 4th Earl of Sandwich, the then First Lord of the Admiralty. Cook came across the islands by chance when crossing the Pacific Ocean on his Third Voyage in 1778, on board HMS ''Resolution''; he was later killed on the islands on a return visit. The contemporary name of the islands, dating from the 1840s, is derived from the name of the largest island, Hawaii Island. Hawaii sits on the Pacific Plate and is the only U.S. state that is not geographically connected to North America. It is part of the Polynesia subregion of Oceania. The state of Hawaii occupies the archipelago almost in its entirety (includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stelae
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. The city developed from a Canaanite Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. According to accounts by Timaeus of Tauromenium, she purchased from a local tribe the amount of land that could be covered by an oxhide. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule the colonies. The ancient city was destroyed in the nearly-three year siege of Carthage by the Roman Republic during the Third Punic War in 146 BC and then re-developed as Roman Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tophet
In the Hebrew Bible, Tophet or Topheth ( hbo, תֹּפֶת, Tōp̄eṯ; grc-gre, Ταφέθ, taphéth; la, Topheth) is a location in Jerusalem in the Valley of Hinnom (Gehenna), where worshipers engaged in a ritual involving "passing a child through the fire", most likely child sacrifice. Traditionally, the sacrifices have been ascribed to a god named Moloch. The Bible condemns and forbids these sacrifices, and the tophet is eventually destroyed by king Josiah, although mentions by the prophets Jeremiah, Ezekiel, and Isaiah suggest that the practices associated with the tophet may have persisted. Most scholars agree that the ritual performed at the tophet was child sacrifice, and they connect it to similar episodes throughout the Bible and recorded in Phoenicia (whose inhabitants were referred to as Canaanites in the Bible) and Carthage by Hellenistic sources. There is disagreement about whether the sacrifices were offered to a god named "Moloch". Based on Phoenician and Carthagin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Caviglia
Giovanni Battista Caviglia (1770 in Genoa – September 7, 1845, in Paris) was an Italian explorer, navigator and Egyptologist. He was one of the pioneers of Egyptian archeology of his time. He was influential in the excavation of the Sphinx of Giza near Cairo. Early life He was born in Genoa in 1770 at a time when the city was the capital of the Republic of Genoa. He spent most of his life sailing in the Mediterranean in which he became a merchant captain. Career in Egypt When he decided to start his career as an explorer, he left his ship moored in Alexandria and offered his services to various collectors. Most of his excavations were carried out on behalf of the British Consul General Henry Salt. Between 1816 and 1817, he explored the Great Pyramid of Giza where he made important discoveries, including the descending corridor, the bottom of the well service and unfinished underground room. In 1817, Salt hired him to excavate the Great Sphinx at Giza, which over the cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |