|
1624 In France
Events from the year 1624 in France. Incumbents *Monarch: Louis XIII Events * Winter – The Rhône and the vineyards of Languedoc freeze. * January 2 – Disgrace of Nicolas Brûlart de Sillery and Pierre Brûlart, marquis de Sillery. * January 6 – Étienne Ier d'Aligre becomes Keeper of the Seals of France. * April 29 – Louis XIII appoints Cardinal Richelieu to the '' Conseil du Roi'' (Royal Council). * May – Croquant rebellions in Quercy, suppressed on June 7 by Marshal de Thémines. * June 10 – Treaty of Compiègne is signed between the Kingdom of France and the Dutch Republic. * August 13 – Cardinal Richelieu is appointed by Louis XIII to be his chief minister, having intrigued against Charles de La Vieuville, Superintendent of Finances, arrested for corruption the previous day. * October 3 – Étienne Ier d'Aligre becomes Grand Chancellor of France. * October 21 – Edict of Saint-Germain-en-Laye establishes a Chamber of Justice for the investigation of financi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
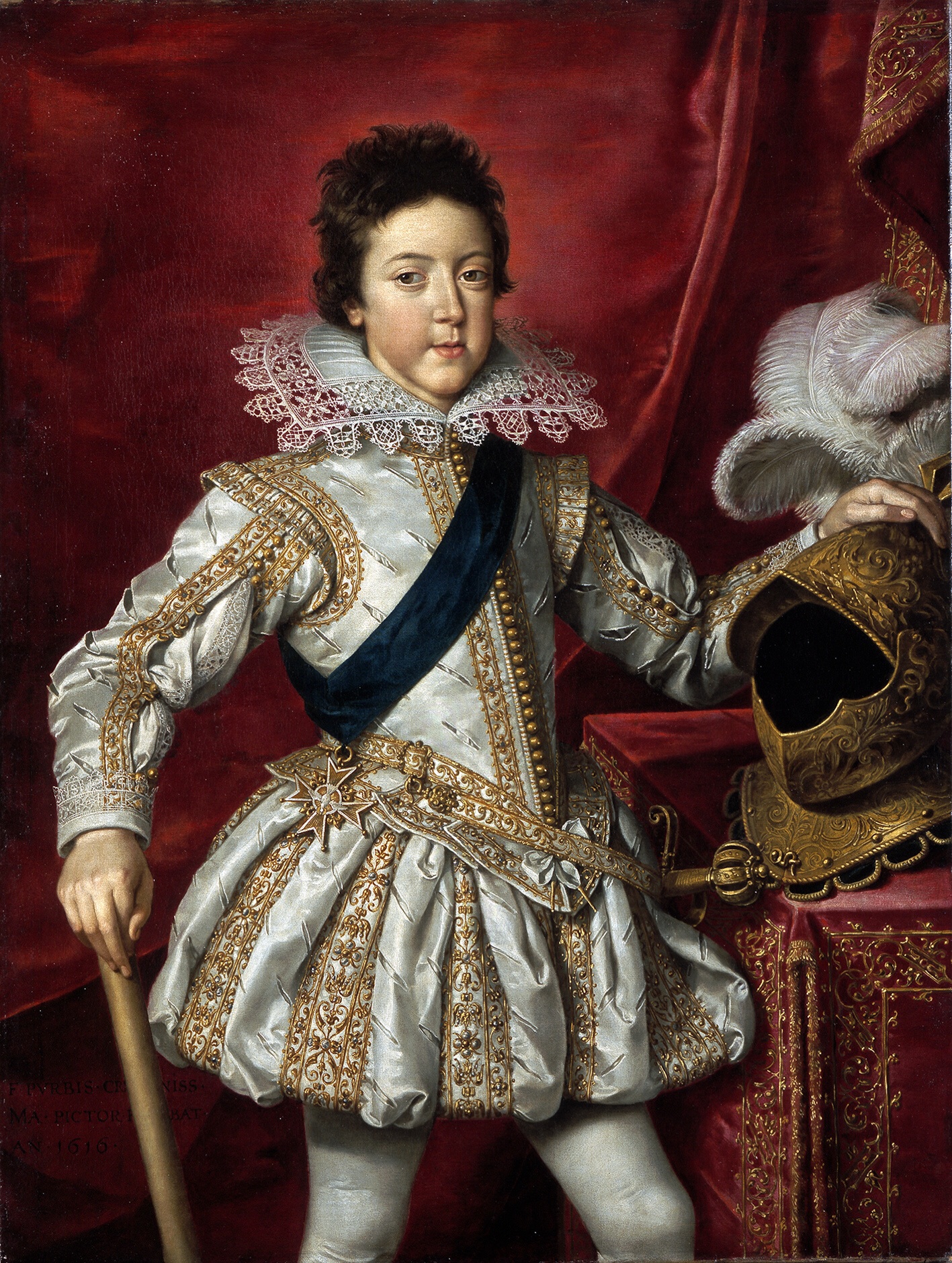
Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown. Shortly before his ninth birthday, Louis became king of France and Navarre after his father Henry IV was assassinated. His mother, Marie de' Medici, acted as regent during his minority. Mismanagement of the kingdom and ceaseless political intrigues by Marie and her Italian favourites led the young king to take power in 1617 by exiling his mother and executing her followers, including Concino Concini, the most influential Italian at the French court. Louis XIII, taciturn and suspicious, relied heavily on his chief ministers, first Charles d'Albert, duc de Luynes and then Cardinal Richelieu, to govern the Kingdom of France. The King and the Cardinal are remembered for establishing the ''Académie française'', and ending the revolt of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
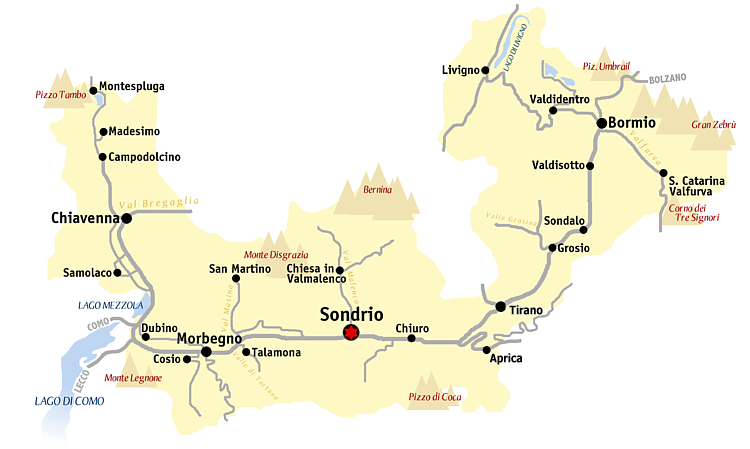
Valtellina
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the Lombardy region of northern Italy, bordering Switzerland. Today it is known for its ski center, hot spring spas, bresaola, cheeses (in particular Bitto, named after the river Bitto) and wines. In past centuries it was a key alpine pass between northern Italy and Germany and control of the Valtellina was much sought after, particularly during the Thirty Years' War as it was an important part of the Spanish Road. Geography The most important comune of the valley is Sondrio; the others major centers are Aprica, Morbegno, Tirano, Bormio and Livigno. Although Livigno is on the northern side of the alpine watershed, it is considered part of Valtellina as it falls within the province of Sondrio. History Antiquity and the middle ages The region was conquered in 16 BC by the Romans. By the 5th century i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François De La Chaise
François de la Chaise (August 25, 1624 – January 20, 1709) was a French Jesuit priest, the father confessor of King Louis XIV of France. Biography François de la Chaise was born at the Château of Aix in Aix-la-Fayette, Puy-de-Dôme, Auvergne, being the son of Georges d'Aix, seigneur de La Chaise, and of Renée de Rochefort. On his mother's side he was a grandnephew of Pierre Coton, the confessor of Henry IV. He became a novice of the Society of Jesus before completing his studies at Lyon, where, after taking final vows, he lectured on philosophy to students attracted by his fame from all parts of France. Through the influence of Camille de Villeroy, Archbishop of Lyon, Père de la Chaise was in 1674 nominated confessor of Louis XIV, who entrusted him during the lifetime of Harlay de Champvallon, archbishop of Paris, with the administration of the ecclesiastical patronage of the crown. The confessor united his influence with that of Madame de Maintenon to induce the king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Regnault De Segrais
Jean Regnault de Segrais (22 August 1624, Caen – 25 March 1701) was a French poet and novelist born in Caen. He was elected a member of the Académie française An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ... in 1662. {{DEFAULTSORT:Regnault De Segrais, Jean 1624 births 1701 deaths Writers from Caen Mayors of Caen Members of the Académie Française French poets 17th-century French male writers 17th-century French novelists French male poets French male novelists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Du Hamel
Jean-Baptiste Du Hamel, Duhamel or du Hamel (11 June 1624 – 6 August 1706) was a French cleric and natural philosopher of the late seventeenth century, and the first secretary of the Academie Royale des Sciences. As its first secretary, he influenced the initial work of the Académie, but his legacy and influence on the Académie and the growth of science in France is mixed. Early life and education He was born at Vire, Normandy (now in the department of Calvados), the son of Vire lawyer Nicolas Du Hamel. The family also included two other brothers, Georges, who would become a lawyer like his father and go onto great success as a member of the Grand Conseil in Paris, and Guillaume, who became a priest and served in the court of the King of France. He began his formal studies at Caen, moving to Paris in 1642. Du Hamel demonstrated an early aptitude for scholarly work, and at the age of eighteen published an explanation of the work of Theodosius of Bithynia called ''Sphéri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Pagi
Antoine Pagi (31 March 1624 – 5 June 1699) was a French ecclesiastical historian. Pagi was born in Rognes. After studying with the Jesuits in Aix, he entered the monastery of the Conventual Franciscans in Arles and made solemn profession on 31 January 1641. At the age of twenty-nine years, he was elected provincial, an office which he held four times. He died, aged 75, in Aix-en-Provence. Works He devoted his spare time to the study of history. Discerning numerous chronological errors, and frequently misstatements of facts in the ''Annales ecclesiastici'' of Baronius, he made it his life-work to correct them and otherwise elucidate the work. Pagi's first volume was printed during his lifetime (Paris, 1689); the remaining three volumes, reaching till the year 1198, the last year in the work of Baronius, were completed in manuscript shortly before his death. The whole work was edited in four volumes by his nephew François Pagi: ''Critica historico-chronologica in universos ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Roberday
François Roberday (21 March 1624 – 13 October 1680) was a French Baroque organist and composer. One of the last exponents of the French polyphonic music tradition established by Jean Titelouze and Louis Couperin, Roberday is best remembered today for his ''Fugues et caprices'', a collection of four-part contrapuntal organ pieces. Life He was born in Paris in 1624, most probably in March. His family was one of goldsmiths and musicians: his father, a renowned goldsmith, owned a pipe organ and François himself was the brother-in-law of Jean-Henri d'Anglebert, one of the most famous French composers and harpsichordist to the King of France. After his father's death, Roberday was appointed King's goldsmith, and in 1659 he bought the job of the official manservant to the Queen. Unfortunately, Roberday's business gradually declined and by the time of his death he was quite poor. He died in 1680 in Auffargis, a village south of Paris, during an epidemic. Roberday was organist of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Lambert De La Motte
Pierre Lambert de la Motte, MEP (16 January 1624 – 15 January 1679) was a French bishop. He was a founding member of the Paris Foreign Missions Society and became a missionary in Asia. Biography Lambert de la Motte was born 16 January 1624 in La Boissière, Calvados. He was ordained a priest on 27 December 1655 and was recruited by Alexander de Rhodes, SJ, as a secular clergy volunteer to become a missionary in Asia, together with François Pallu and Ignace Cotolendi. These were sent to the Far East as Apostolic vicars. On 29 July 1658 Pope Alexander VII appointed him as the first Apostolic Vicar of Cochin and as titular bishop of Beirut. On 11 June 1660 he was consecrated bishop by Victor Le Bouthillier, Archbishop of Tours. The three bishops left France (1660–62) to go to their respective missions, and crossed Persia and India on foot, since Portugal would have refused to take non-Padroado missionaries by ship, and the Dutch and the English refused to take Catholic mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Renndaandi Senegaali); Arabic: جمهورية السنغال ''Jumhuriat As-Sinighal'') is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. Senegal is bordered by Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds the Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's economic and political capital is Dakar. Senegal is notably the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. It owes its name to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. It borders Brazil to the east and south and Suriname to the west. With a land area of , French Guiana is the second-largest Regions of France, region of France (more than one-seventh the size of Metropolitan France) and the largest Special member state territories and the European Union, outermost region within the European Union. It has a very low population density, with only . (Its population is less than that of Metropolitan France.) Half of its 294,436 inhabitants in 2022 lived in the metropolitan area of Cayenne, its Prefectures in France, capital. 98.9% of the land territory of French Guiana is covered by forests, a large part of which is Old-growth forest, primeval Tropical r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French Colonial Empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French Colonial Empire", which began with the conquest of Algiers in 1830. At its apex between the two world wars, the second French colonial empire was the second-largest colonial empire in the world behind the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India in the 17th century but lost most of its possessions following its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain but the latter returned Louisiana (New France) to France in 1800. The territory was then sold to the United States in 1803. France rebuilt a new empire mostly after 1850, concentrating chiefly in Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congregation Of The Mission
, logo = , image = Vincentians.png , abbreviation = CM , nickname = Vincentians, Paules, Lazarites, Lazarists, Lazarians , established = , founder = Vincent de Paul , founding_location = Paris, France , type = Society of Apostolic Life of Pontifical Right (for Men) , members = 3,100 as of 2021 , headquarters = General MotherhouseVia dei Capasso 30, 00164 Rome, Italy , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Evangelizare pauperibus misit me English:''He sent me to bring Good News to the poor'' , leader_title2 = Superior General , leader_name2 = Tomaž Mavrič, CM , leader_title3 = Patron , leader_name3 = Saint Vincent de Paul, CM , main_organ = Nuntia and Vincentiana , website = The Congregation of the Mission ( la, Congregatio Missionis) abbreviated CM and commonly called the Vincentians or La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |