|
155 K 83
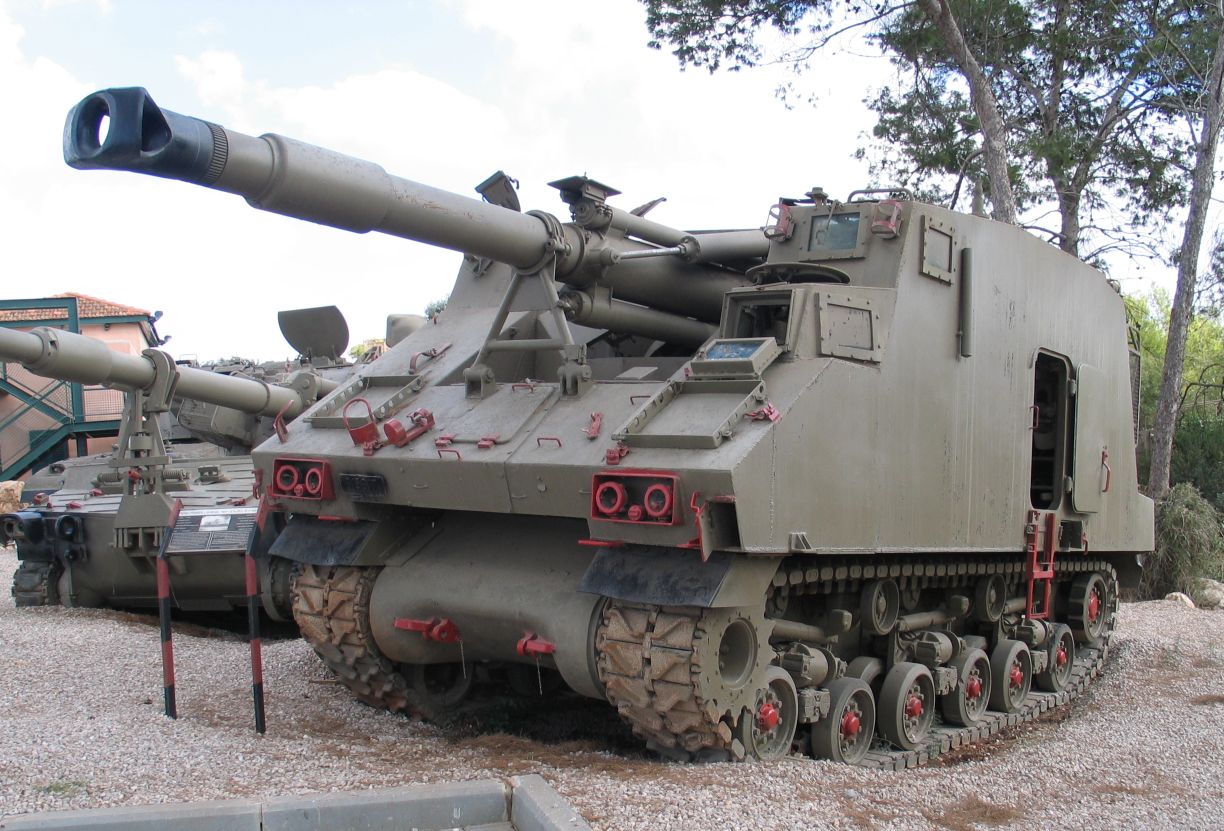
The Tampella 155 K 83 is a Finnish towed 155 mm field gun (Finnish designation; technically it is a gun-howitzer), manufactured in the 1980s by Tampella. History The development process for the 155 K 83 began in 1960 when Tampella presented their concept of a new 122 mm gun for the Finnish Army. It was a sound concept, but quite a heavy gun. It was only ordered in small numbers. In order to take advantage of the design, a decision was made to further develop this into a 155 mm gun. Through a number of development stages the 155 K 83 was born. The drawings were also used to develop the Israeli Soltam M-68, which, after improvements, became the Soltam M-71 (designated the G4 in South Africa). Some guns have been modernized to 155 K 83-97 standard. The gun design was further modified in the late 1990s. The gun, called 155 GH 52 APU (or 155 K 98 in Finnish Army service), was given a longer, 52 calibre barrel and an auxiliary power unit, enabling it to move by its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Gun
A field gun is a field artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march, that when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances ( field artillery), as opposed to guns installed in a fort (garrison artillery or coastal artillery), or to siege cannons and mortars which are too large to be moved quickly, and would be used only in a prolonged siege. Perhaps the most famous use of the field gun in terms of advanced tactics was Napoleon Bonaparte's use of very large wheels on the guns that allowed them to be moved quickly even during a battle. By moving the guns from point-to-point during a battle, enemy formations could be broken up to be handled by the infantry or cavalry wherever they were massing, dramatically increasing the overall effectiveness of the attack. World War I As the evolution of artillery continued, almost all guns of any size became capable of being moved at some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun-howitzer
Gun-howitzer (also referred to as gun howitzer) is a type of artillery weapon that is intended to fulfill both the role of ordinary cannon or field gun, and that of a howitzer. It is thus able to convey both direct and indirect fire. Modern gun-howitzers are usually identified just as howitzers. To be able to serve as a howitzer, gun-howitzers are typically built to achieve at least 60° to 70° of elevation. For effective direct fire, the gun-howitzers typically employ a fairly long gun barrel, usually not shorter than 30 calibres. Its ammunition also has a high muzzle velocity and usually of large calibre ( calibre and greater). History Historically the first gun-howitzer was the French ''canon obusier'' of the mid-19th century. The smooth-bore Canon obusier de 12 was a versatile weapon that quickly replaced both ordinary cannons and howitzers in French service, and became one of the basic types of artillery used by both sides of the American Civil War. Owing to their versal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Bleed
Base bleed is a system used on some artillery shells to increase range, typically by about 20–35%. It expels gas into the low pressure area behind the shell to reduce base drag (it does not produce thrust). Since base bleed extends the range by a percentage, it is more useful on longer range artillery where an increase of approximately can be achieved. Until the late 1980s the small gains in range were not considered worthwhile for field artillery. Base bleed shells are becoming more common in units equipped with modern artillery with far greater range than older guns, but are usually only used when the longer range is required, due to their higher cost. Function Most (50–60%) of the drag on an artillery shell comes from the nose of the shell, as it pushes the air out of its way at supersonic speeds. Shaping the shell properly can reduce this drag. However, another powerful source of drag is the low-pressure area left behind the shell due to its blunt base. Base blee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Gun
A field gun is a field artillery piece. Originally the term referred to smaller guns that could accompany a field army on the march, that when in combat could be moved about the battlefield in response to changing circumstances ( field artillery), as opposed to guns installed in a fort (garrison artillery or coastal artillery), or to siege cannons and mortars which are too large to be moved quickly, and would be used only in a prolonged siege. Perhaps the most famous use of the field gun in terms of advanced tactics was Napoleon Bonaparte's use of very large wheels on the guns that allowed them to be moved quickly even during a battle. By moving the guns from point-to-point during a battle, enemy formations could be broken up to be handled by the infantry or cavalry wherever they were massing, dramatically increasing the overall effectiveness of the attack. World War I As the evolution of artillery continued, almost all guns of any size became capable of being moved at some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun-howitzer
Gun-howitzer (also referred to as gun howitzer) is a type of artillery weapon that is intended to fulfill both the role of ordinary cannon or field gun, and that of a howitzer. It is thus able to convey both direct and indirect fire. Modern gun-howitzers are usually identified just as howitzers. To be able to serve as a howitzer, gun-howitzers are typically built to achieve at least 60° to 70° of elevation. For effective direct fire, the gun-howitzers typically employ a fairly long gun barrel, usually not shorter than 30 calibres. Its ammunition also has a high muzzle velocity and usually of large calibre ( calibre and greater). History Historically the first gun-howitzer was the French ''canon obusier'' of the mid-19th century. The smooth-bore Canon obusier de 12 was a versatile weapon that quickly replaced both ordinary cannons and howitzers in French service, and became one of the basic types of artillery used by both sides of the American Civil War. Owing to their versal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tampella
Oy Tampella Ab was a Finnish heavy industry manufacturer, a maker of paper machines, locomotives, military weaponry, as well as wood-based products such as packaging. The company was based mainly in the Naistenlahti district of the city of Tampere. Until 1963 the company was called Tampereen Pellava- ja Rauta-Teollisuus Osake-Yhtiö (The Flax and Iron Industry of Tampere Stock Company). In Swedish it was called Tammerfors Linne-&Jern-Manufakt.A.B.. In 1993 the company’s forest and packaging business was bought by Enso-Gutzeit Oy. Tampereen Pellava- ja Rautateollisuus Oy was a company based on the merger in 1861 of two factories - a linen mill and foundry - situated by the Tammerkoski rapids. After a modest start it grew to become an institution employing thousands of people in the centre of Tampere alone, and more in its other units. In the 1950s the company's name was shortened to Tampella. The company went into decline during the 1980s and eventually went bankrupt in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soltam M-68
The M-68 was a 155 mm L33 caliber towed gun howitzer manufactured by Soltam Systems of Israel, and used by the Israeli Defense Force. Design The M-68 is based on the Finnish designed 122 K 60 and 155 K 68 cannon series, first developed in the mid-1960s by the company Tampella Oy. Twelve Finnish cannons were built between 1970-1975, with more guns later built of later designs. These Tampella guns formed the basis for Soltam's production of the M-68 and later "Tampella series" guns. Before the 155 K 68 (Tampella), the 155HX prototype was shipped to Soltam for trials. The first prototype was completed in 1968 for trials and evaluations by the Israeli Defense Force (IDF), who were satisfied with the performance of the howitzer. Subsequently, an order was placed with Soltam and a production line was initiated in 1970. The gun entered IDF service in time to serve IDF artillery corps during the Yom Kippur War of 1973. In addition to Israel, the M-68 has also been exported to Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soltam M-71
The M-71 is a 155 mm 39 caliber towed howitzer manufactured by Israeli company Soltam Systems. Design The weapon was based on the earlier Soltam M-68 and uses the same recoil system, breech and carriage but had a longer gun barrel (39 calibre versus 33 calibre of M-68). It is fitted with a compressed air-driven rammer to permit rapid and easy loading at all angles of elevation as well as having a rechargeable battery mounted on the right trail for auxiliary power. It can fire a high-explosive shell up to a maximum range of at a muzzle velocity of . Deployment In addition to Israel, this weapon is in service with Chile, Singapore, Thailand, Philippines, South Africa, Slovenia and Myanmar. A version of this weapon was developed to mount on a modified Centurion chassis (M-72), but this vehicle never reached production. Operators * *: 8 *: 60 howitzers used by the Chilean Army, 36 Soltam M-68s acquired in the 1970s later upgraded to Soltam M-71 standard and 24 Soltam M-71 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
155 GH 52 APU
The 155 GH 52 APU (which stands for ''155 mm gun-howitzer, 52 calibers, auxiliary power unit''), Finnish designation 155 K 98 (''155 mm kenttäkanuuna 1998'' or "155 mm field gun 1998"; FDF terminology doesn't recognise gun-howitzers), is a Finnish towed artillery piece developed in 1998. It is largely based on the 155 K 83 with some major enhancements. It can be moved on the field short distances with its own auxiliary diesel engine, which is used in all 56 units used by the Finnish defence forces, is a 78-kilowatt Deutz diesel engine. The Egyptian units are not equipped with the APU. The 155 GH 52 is considered to be one of the most modern field artillery cannons to date and was originally manufactured by Oy Tampella AB industries (today a part of Patria, Patria Vammas Systems Oy). It has a high rate of fire (6 rounds per minute) and can fire all types of 155 mm ammunition. Domestic operators The Kainuu Artillery Regiment of Kainuu Brigade in Vuosanka shooting range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
155 K 98
The 155 GH 52 APU (which stands for ''155 mm gun-howitzer, 52 calibers, auxiliary power unit''), Finnish designation 155 K 98 (''155 mm kenttäkanuuna 1998'' or "155 mm field gun 1998"; FDF terminology doesn't recognise gun-howitzers), is a Finnish towed artillery piece developed in 1998. It is largely based on the 155 K 83 with some major enhancements. It can be moved on the field short distances with its own auxiliary diesel engine, which is used in all 56 units used by the Finnish defence forces, is a 78-kilowatt Deutz diesel engine. The Egyptian units are not equipped with the APU. The 155 GH 52 is considered to be one of the most modern field artillery cannons to date and was originally manufactured by Oy Tampella AB industries (today a part of Patria, Patria Vammas Systems Oy). It has a high rate of fire (6 rounds per minute) and can fire all types of 155 mm ammunition. Domestic operators The Kainuu Artillery Regiment of Kainuu Brigade in Vuosanka shooting range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Power Unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115 V AC voltage at 400 Hz (rather than 50/60 Hz in mains supply), to run the electrical systems of the aircraft; others can produce 28 V DC voltage. APUs can provide power through single or three-phase systems. Transport aircraft History During World War I, the British Coastal class blimps, one of several types of airship operated by the Royal Navy, carried a ABC auxiliary engine. These powered a generator for the craft's radio transmitter and, in an emergency, could power an auxiliary air blower. One of the first military fixed-wing aircraft to use an APU was the British, World War 1, Supermarine Nighthawk, an anti-Zeppelin night fighter.Andrews and Morgan 1987, p. 21. During World War II, a number of large Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Artillery
Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement. Until the early 20th century, field artillery were also known as foot artillery, for while the guns were pulled by beasts of burden (often horses), the gun crews would usually march on foot, thus providing fire support mainly to the infantry. This was in contrast to horse artillery, whose emphasis on speed while supporting cavalry units necessitated lighter guns and crews riding on horseback. Whereas horse artillery has been superseded by self-propelled artillery, field artillery has survived to this day both in name and mission, albeit with motor vehicles towing the guns (this towed artillery arrangement is often called mobile artillery), carrying the crews and transporting the ammunition. Modern artillery has also advanced to rapidly deployable wheeled a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |