|
1,2,4-Triazole
1,2,4-Triazole (as ligand in coordination compounds, Htrz abbreviation is sometimes used) is one of a pair of isomeric chemical compounds with molecular formula CHN, called triazoles, which have a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms. 1,2,4-Triazole and its derivatives find use in a wide variety of applications. Structure and properties 1,2,4-Triazole is a planar molecule. The C-N and N-N distances fall into a narrow range 136 - 132 picometers, consistent with the aromaticity. Although two tautomers can be envisioned, only one exists practically speaking. 1,2,4-Triazole is amphoteric, being susceptible to both N-protonation and deprotonation in aqueous solution. The pKa of 1,2,4-triazolium (C2N3H4+) is 2.45. The pKa of the neutral molecule is 10.26. Synthesis and occurrence 1,2,4-Triazoles can be prepared using the Einhorn–Brunner reaction or the Pellizzari reaction. Unsubstituted 1,2,4-triazole can be prepared from thiosemicarbazide by acylation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
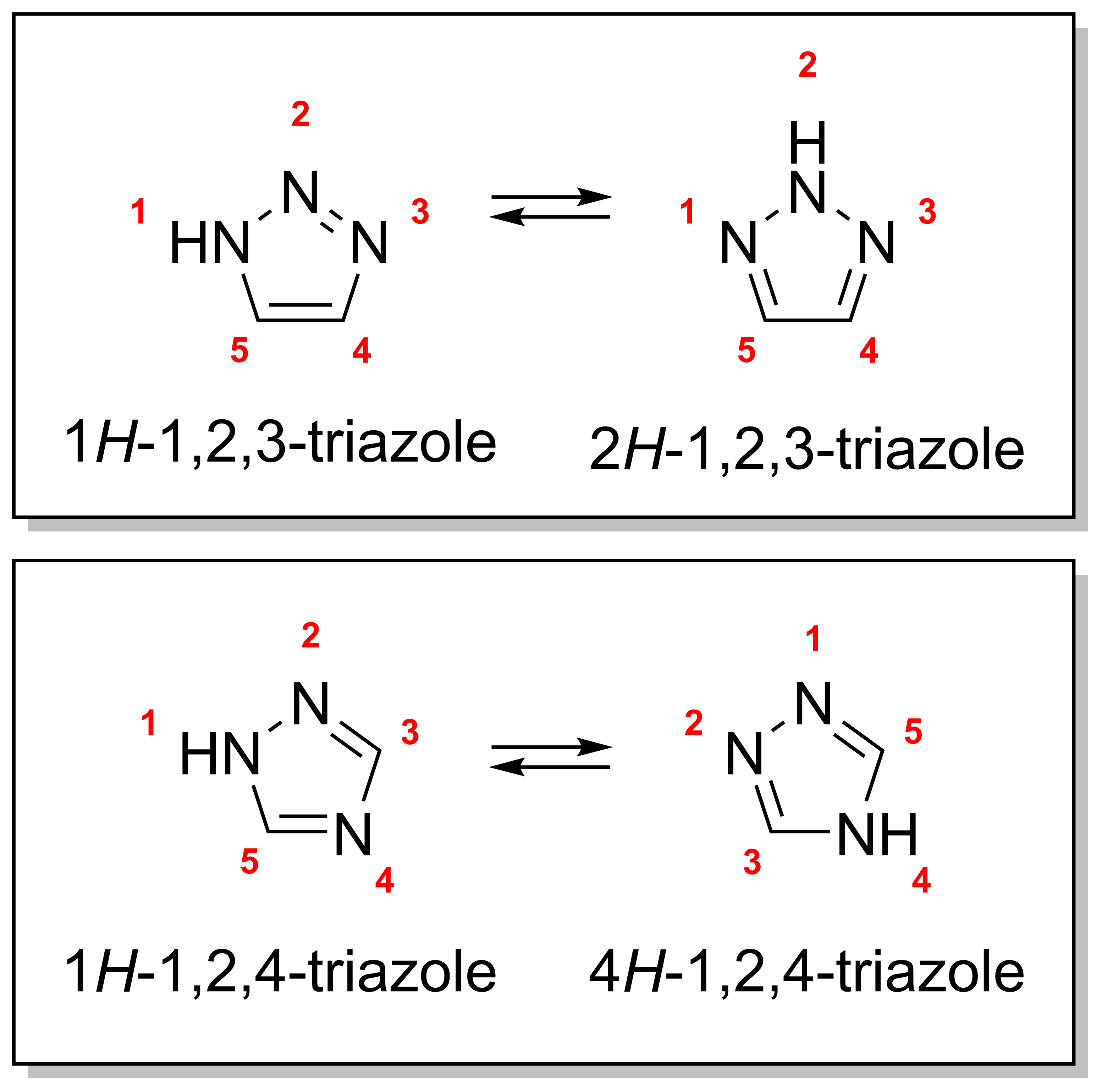
Triazole
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einhorn–Brunner Reaction
The Einhorn–Brunner reaction is the designation for the chemical reaction of imides with alkyl hydrazines to form an isomeric mixture of 1,2,4-triazoles. It was initially described by the German chemist Alfred Einhorn in a paper, published in 1905, describing N-methylol compounds of amides. In 1914 chemist Karl Brunner published a paper expanding on Einhorn's research of the reaction pictured below, thus resulting in the naming as the Einhorn-Brunner. Substituted 1,2,4-triazole have been prepared from diverse imides and hydrazines.* Regioselectivity In the case that the R groups of the imide are different, the reaction has regioselectivity. In their research on the synthesis of 1,2,4-triazoles, Potts determined that the strongest acidic group attached to the side of the imide will be favored for the 3 position on the triazole ring. In the diagram below, if one considers the blue R group to be more acidic in respect to the green, the favored product would be the isomer o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiosemicarbazide
Thiosemicarbazide is the chemical compound with the formula H2NC(S)NHNH2. A white, odorless solid, it is related to thiourea (H2NC(S)NH2) by the insertion of an NH center. They are commonly used as ligands for transition metals. Many thiosemicarbazides are known. These feature an organic substituent in place of one or more H's of the parent molecule. 4-Methyl-3-thiosemicarbazide is a simple example. According to X-ray crystallography, the CSN3 core of the molecule is planar as are the three H's nearest the thiocarbonyl group. Reactions Thiosemicarbazides are precursors to thiosemicarbazones. They are precursors to heterocycle A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and ...s. Formylation of thiosemicarbazide provides access to triazole. References {{Authority control Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paclobutrazol
Paclobutrazol (PBZ) is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a plant growth retardant and triazole fungicide. It is a known antagonist of the plant hormone gibberellin, acting by inhibiting gibberellin biosynthesis, reducing internodal growth to give stouter stems, increasing root growth, causing early fruitset and increasing seedset in plants such as tomato and pepper. PBZ has also been shown to reduce frost sensitivity in plants. Moreover, paclobutrazol can be used as a chemical approach for reducing the risk of lodging in cereal crops. PBZ has been used by arborists to reduce shoot growth and shown to have additional positive effects on trees and shrubs. Among those are improved resistance to drought stress, darker green leaves, higher resistance against fungi and bacteria, and enhanced development of roots. Cambial growth, as well as shoot growth, has been shown to be reduced in some tree species. Structure and synthesis The first synthesis of paclobut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Growth Regulator
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in higher plants. Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones affect gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given by mouth or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, and headache. Severe side effects may include liver problems, heart failure, Stevens–Johnson syndrome and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. It is in the triazole family of medications. It stops fungal growth by affecting the cell membrane or affecting their metabolism. Itraconazole was patented in 1978 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1992. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Recent research works suggest itraconazole (ITZ) could also be used in the treatment of cancer by inhibiting the hedgehog pathway in a similar way to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prevent candidiasis in those who are at high risk such as following organ transplantation, low birth weight babies, and those with neutropenia, low blood neutrophil counts. It is given either by mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and elevated transaminases, increased liver enzymes. Serious side effects may include liver problems, QT prolongation, and seizures. During pregnancy it may increase the risk of miscarriage while large doses may cause birth defects. Fluconazole is in the azole antifungal family of medication. It is believed to work by affecting the fungal cellular membrane. Fluconazole was patented in 1981 and came into commercial use in 1988. It is on the WHO Model Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal Drug
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple conjugated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as pigments in inks and dyes. Nitric acid is also commonly used as a strong oxidizing agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellizzari Reaction
The Pellizzari reaction was discovered in 1911 by Guido Pellizzari, and is the organic reaction of an amide and a hydrazide to form a 1,2,4-triazole. The product is similar to that of the Einhorn-Brunner reaction, but the mechanism itself is not regioselective. : Mechanism The mechanism begins by the nitrogen in the hydrazide attacking the carbonyl carbon on the amide to form compound 3. The negatively charged oxygen then abstracts two hydrogens from neighboring nitrogens in order for a molecule of water to be released to form compound 5. The nitrogen then performs an intramoleculer attack on the carbonyl group to form the five-membered ring of compound 6. After another proton migration from the nitrogens to the oxygen, another water molecule is released to form the 1,2,4-triazole 8. : Uses The synthesis of the 1,2,4-triazole has a wide range of biological functions. 1,2,4-triazoles have antibacterial, antifungal, antidepressant and hypoglycemic Hypoglycemia, also called low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3_(FIBCEA01).png)