|
╩┐─Ćd
╩┐─Ćd (, ') was an ancient tribe in pre-Islamic Arabia. 'Ad is best known for being mentioned two dozen times in the Quran, often in conjunction with Thamud. Recently, it has been shown that 'Ad was a tribe that existed two millennia ago in the Wadi Rum region of the southern Jordan. The tribe's members, referred to as ╩┐─Ćdites, formed a prosperous nation until they were destroyed in a violent storm. According to Islamic mythology, Islamic tradition, the storm came after they had rejected the teachings of a Tawhid, monotheistic prophet named ''Hud (prophet), Hud''. 'Ad is regarded as one of the original tribes of Arabia, "The Extinct Arabs". Etymology There is a possibility that the tribal name ''╩┐─Ćd'' represents misinterpretation of a common noun: the expression ''min al-╩┐─üd'' is today understood to mean "since the time of ╩┐─Ćd", but ''╩┐─üd'' might originally have been a common noun meaning 'antiquity', which was reinterpreted as a proper noun, inspiring of the tribe 'A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hud (prophet)
H┼½d (), sometimes called Eber, is believed in Islam to have been a Prophets and messengers in Islam, messenger sent to pre-Islamic Arabia, ancient Arabia before Muhammad. Hud is repeatedly mentioned in the Quran, whose eleventh Surah, chapter is also Hud (surah), named after him (although a small portion of it is actually about him). Historical context Hud has sometimes been identified with Eber, an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites who is mentioned in the Old Testament. Hud is said to have been a subject of a ''mulk'' () named after its founder, ╩┐─Ćd, 'Ad, a fourth-generation descendant of Noah (his father being Uz, son of Aram, Uz, the son of Aram, son of Shem, Aram, who was the son of Shem, who in turn was a son of Noah): The other tribes said to be present at this Pre-Islamic Arabia, time in Arabia, were the Thamud, Jurhum, Tasam, Jadis, Amim, Midian, Amalek Imlaq, Jasim, Qahtanite, Qahtan, Banu Yaqtan and others. The Quran gives the location of ╩┐─Ć ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iram Of The Pillars
Iram of the Pillars (; an alternative translation is ''Iram of the tentpoles''), also called "Irum", "Irem", "Erum", or the "City of the pillars", is a lost city mentioned in the Quran. Iram in the Quran The Quran mentions Iram in connection with (pillars): There are several explanations for the reference to "Iram ŌĆō who had lofty pillars". Some see this as a geographic location, either a city or an area, others as the name of a tribe. Those identifying it as a city have made various suggestions as to where or what city it was, ranging from Alexandria or Damascus to a city which actually moved or a city called Ubar. Ubar, according to ancient and medieval authors, was a land instead of a city. As an area, it has been identified with the biblical region known as Aram. A more plausible candidate for Iram is Wadi Ramm in Jordan, as the Temple of al-Lat at the foot of Jabal Ramm has some ancient inscriptions mentioning Iram and possibly the tribe of ╩┐─Ćd. It has also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ╩┐─Ćd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Islamic Arabia
Pre-Islamic Arabia is the Arabian Peninsula and its northern extension in the Syrian Desert before the rise of Islam. This is consistent with how contemporaries used the term ''Arabia'' or where they said Arabs lived, which was not limited to the peninsula. Pre-Islamic Arabia included both nomadic and settled populations. Several settled populations developed distinctive civilizations. From around the second half of the 2nd millennium BCE, South Arabia, Southern Arabia was the home to a number of kingdoms, such as the Sabaeans and the Minaeans, and Eastern Arabia was inhabited by Semitic-speaking peoples who presumably migrated from the southwest, such as the so-called Samad Late Iron Age, Samad population.Kenneth A. Kitchen The World of "Ancient Arabia" Series. Documentation for Ancient Arabia. Part I. Chronological Framework and Historical Sources p.110 From 106 CE to 630 CE, Arabia's most northwestern areas were controlled by the Roman Empire, which governed it as Arabia Petrae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ahqaf
Al-Ahqaf (, ; "the sand dunes" or "the winding sand tracts") is the 46th chapter (''surah'') of the Qur'an with 35 verses ('' ayat''). This is the seventh and last chapter starting with the Muqattaʿat letters '' Hāʼ Mīm''. Regarding the timing and contextual background of the believed revelation ('' asbāb al-nuzūl''), it is one of the late Meccan chapters, except for verse 10 and possibly a few others which Muslims believe were revealed in Medina. The chapter covers various topics: It warns against those who reject the Quran, and reassures those who believe; it instructs Muslims to be virtuous towards their parents; it tells of the Prophet Hud and the punishment that befell his people, and it advises Muhammad to be patient in delivering his message of Islam. A passage in verse 17, which talks about a child's gestation and weaning, became the basis by which some Islamic jurists determined that the minimum threshold of fetal viability in Islamic law would be about 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
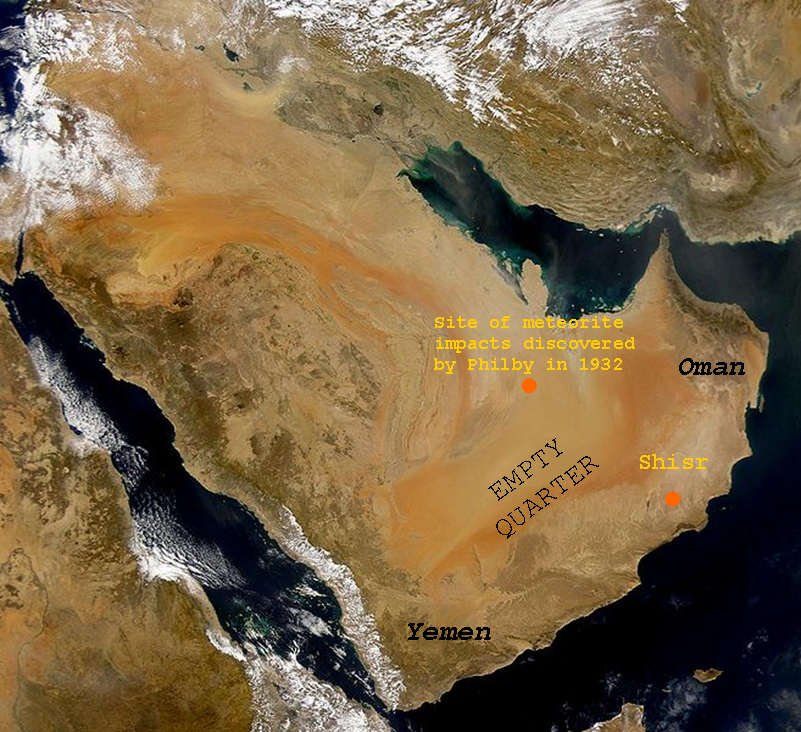
Atlantis Of The Sands
Atlantis of the Sands refers to a legendary lost place in the southern deserts of the Arabian Peninsula, known as Ūbār/Awbār () or Wabār/Wubār () in Arabic, thought to have been destroyed by a natural disaster or as a punishment by God. The English name is commonly attributed to T. E. Lawrence in the 20th century, but it never appears in Lawrence's published works, and neither Bertram Thomas who made "Atlantis of the Sands" public (and was probably the real coiner of this term) nor Ranulph Fiennes and Nicholas Clapp who made this term popular have ever attributed this term to Lawrence. Ubar is often said to be mentioned in the Quran and ''One Thousand and One Nights'', but that is not the case. The misconception is due to the equation of Ubar with Iram by Nicholas Clapp, but such equation is not generally accepted by scholars. Introduction In modern times, the mystery of the lost city of Atlantis has generated several books, films, articles, and web pages. (See Atl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thamud
The Thamud () were an ancient tribe or tribal confederation in pre-Islamic Arabia that occupied the northwestern Arabian Peninsula. They are attested in contemporaneous Mesopotamian and Classical inscriptions, as well as Arabic ones from the eighth century BCE, all the way until the fifth century CE, when they served as Roman auxiliaries. They are also later remembered in pre-Islamic Arabic poetry and Islamic-era sources, including the Quran. Prominently, they appear in the Ruwafa inscriptions discovered in a temple constructed circa 165ŌĆō169 CE in honor of the local deity, ╩Šlh╩Š. Islamic sources state that the Thamud were an early Arab tribe that had gone extinct in ancient days. Thamud appears twenty-six times in the Quran, where the tribe is presented as an example of an ancient polytheistic people destroyed by God for their rejection of God's prophet Salih. In the Quran, Thamud is associated with a pattern of rebellion and destruction of past groups of people. This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribes Of Arabia
The tribes of Arabia () have inhabited the Arabian Peninsula for thousands of years and traditionally trace their ancestry to one of two forefathers: Adnan, whose descendants originate from Hejaz, West Arabia, Syrian Desert, North Arabia, East Arabia, and Najd#History, Central Arabia; or Qahtanite, Qahtan, whose descendants originate from South Arabia. Further, it is held in the Abrahamic religionsŌĆöparticularly IslamŌĆöthat the Arab people are descended from Abraham through his son Ishmael. From the 7th century onward, concurrent with the spread of Islam, many of these tribes' members began migrating and settling in the various regions that were subdued during the early Muslim conquests, including the Arab migrations to the Levant, Levant, Arab conquest of Mesopotamia, Mesopotamia, Arab conquest of Egypt, Egypt, Muslim conquest of Khuzestan, Khuzestan, the Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Maghreb, and Islamization of the Sudan region, Sudan. This phenomenon triggered a process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories to the west. The Jordan River, flowing into the Dead Sea, is located along the country's western border within the Jordan Rift Valley. Jordan has a small coastline along the Red Sea in its southwest, separated by the Gulf of Aqaba from Egypt. Amman is the country's capital and List of cities in Jordan, largest city, as well as the List of largest cities in the Levant region by population, most populous city in the Levant. Inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period, three kingdoms developed in Transjordan (region), Transjordan during the Iron Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered in Petra. The Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman period saw the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Of The Qur'an
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.B├®joint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30ŌĆō31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacular language), size (few or many volumes), intent (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen, as well as southern Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula was also considered a part of Arabia. The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the north-east, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Arab world and globally due to its vast reserves of petroleum, oil and natural gas. Before the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |