|
├İster Voldgade
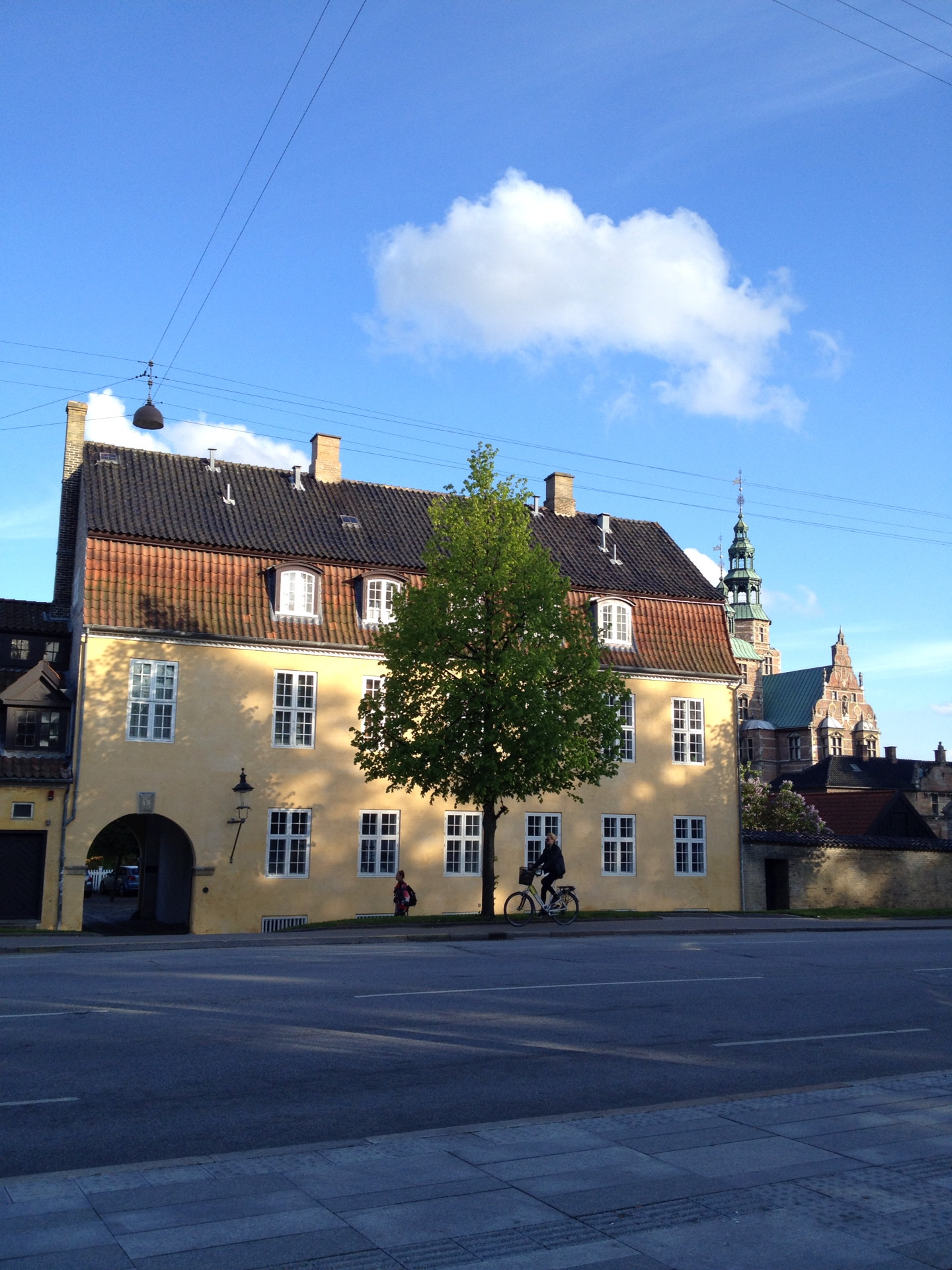
├İster Voldgade ( lit. "East Rampart Street"), together with Vester Voldgade and N├©rre Voldgade, forms a succession of large streets which arches around the central and oldest part of the Zealand side of Copenhagen, Denmark. It runs north-east from Gothersgade at N├©rreport Station to Georg Brandes Plads, between the Copenhagen Botanical Gardens and Rosenborg Castle Gardens, and continues straight to a large junction at the southern end of Oslo Plads, near ├İsterport Station, where it turns into Folke Bernadotte All├®. History ├İster Voldgade was originally a smaller street which ran on the inside of the new East Rampart, built in the 1650s to replace the old East Rampart which followed present day Gothersgade. The alley was expanded when the ramparts were removed in the 1850s. Notable buildings and residents The long, Neoclassical building on the corner of ├İster Voldgade and Gothersgade, opposite the entrance to Copenhagen Botanical Gardens, is Rosenborg Barracks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, K├©benhavn ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan area has 2,057,142 people. Copenhagen is on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malm├Â, Sweden, by the ├İresund strait. The ├İresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Vikings, Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. Beginning in the 17th century, it consolidated its position as a regional centre of power with its institutions, defences, and armed forces. During the Renaissance the city served as the de facto capital of the Kalmar Union, being the seat of monarchy, governing the majority of the present day Nordic countries, Nordic region in a personal union with Sweden and N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folke Bernadotte All├®
Folke is a parish in the county of Dorset in southern England, situated in the Blackmore Vale, approximately south-east of Sherborne. The parish has an area of and is made of the villages of Folke and Alweston, and the hamlet of Bishops Down. Dorset County Council's 2013 estimate of the population of Folke parish is 270. In the 2011 census figures have been published for the population of Folke parish combined with the small parish of North Wootton to the north; this was 339. The Manor House in the hamlet of Folke dates from about 1500 and adjoins the early 17th-century parish church. The house of Font le Roi, sited by the road towards Sturminster Newton, was built as a gatehouse in the 15th century. Folke Wood Folke Wood is a wood near Folke in Dorset, England. It was planted by the Woodland Trust in 1985. It consists of native broadleaved trees as well as apple and ash trees. The apple trees are the remains of an orchard which existed in the 19th c ... is nearby. Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rundetårn
The Round Tower ( Danish: Rundetårn) is a 17th-century tower in Copenhagen, Denmark, one of the many architectural projects of Christian IV of Denmark. Built as an astronomical observatory, it is noted for its equestrian staircase, a 7.5-turn helical corridor leading to the platform at the top (34.8 meters above ground), and its views over Copenhagen. The tower is part of the ''Trinitatis Complex'' which also includes a chapel, the Trinitatis Church, and an academic library, which were the first facilities of the Copenhagen University Library founded in 1482. History Background Astronomy had grown in importance in 17th-century Europe. Countries had begun competing with each other in establishing colonies, creating a need for accurate navigation across the oceans. Many national observatories were therefore established, the first in 1632 at Leiden in the Dutch Republic. Only five years later the Round Tower Observatory, first referred to as STELLÆBURGI REGII HAUNIENSIS, woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
├İstervold Observatory
├İstervold Observatory (or Copenhagen University Observatory; da, K├©benhavns Universitet Astronomisk Observatorium) is a former astronomical observatory (IAU code 035) in Copenhagen, Denmark owned and operated by the University of Copenhagen (K├©benhavns Universitet). It opened in 1861 as a replacement for the University's old observatory at Rundet├Ñrn. History The first astronomical observatory operated by the University of Copenhagen was Rundet├Ñrn. It had been inaugurated in 1642 as a replacement for Tycho Brahe's Stjerneborg, but during the early 19th century had become outdated as astronomical instruments grew bigger and bigger while the tower could not be expanded. In the same time, light pollution from the surrounding city as well as vibrations caused by the still increasing traffic in the streets below had made the observations inaccurate. In 1861 the observatory was moved to ├İstervold, where a new observatory was constructed on the old bastioned fortifications of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosenborg Castle
Rosenborg Castle ( da, Rosenborg Slot) is a renaissance castle located in Copenhagen, Denmark. The castle was originally built as a country summerhouse in 1606 and is an example of Christian IV's many architectural projects. It was built in the Dutch Renaissance style, typical of Danish buildings during this period, and has been expanded several times, finally evolving into its present condition by the year 1624. Architects Bertel Lange and Hans van Steenwinckel the Younger are associated with the structural planning of the castle. History The castle was used by Danish regents as a royal residence until around 1710. After the reign of Frederik IV, Rosenborg was used as a royal residence only twice, and both these times were during emergencies. The first time was after Christiansborg Palace burned down in 1794, and the second time was during the British attack on Copenhagen in 1801. Architecture Long Hall Located on the third floor, the Long Hall was completed in 1624. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Life Guards (Denmark)
The Royal Life Guards ( da, Den Kongelige Livgarde) is a mechanized infantry regiment of the Danish Army, founded in 1658 by King Frederik III. The primary task is to provide a number of soldiers from the Guard Company to serve as a guard/ceremonial unit to the Danish monarchy, while training the Royal Guards for various functions in the mobilisation force. Until its disbandment, the Royal Horse Guards ( da, Livgarden til Hest), served the role as the mounted guard/ceremonial unit, afterwards the role was taken over by Guard Hussar Regiment Mounted Squadron. During the time period 1684-1867, the Royal Life Guards were called The Royal Foot Guard ( da, Den Kongelige Livgarde til Fods), in order to distinguish between the regiment and the Royal Horse Guards. History Role Organisation The regiment itself has two battalions, the Guard Company and a Musical Corps: * 1st Battalion ÔÇô Founded 1658. Mechanized Infantry Battalion, part of 1st Brigade. ''Plus Ultra'' (Even further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Cornelius Krieger
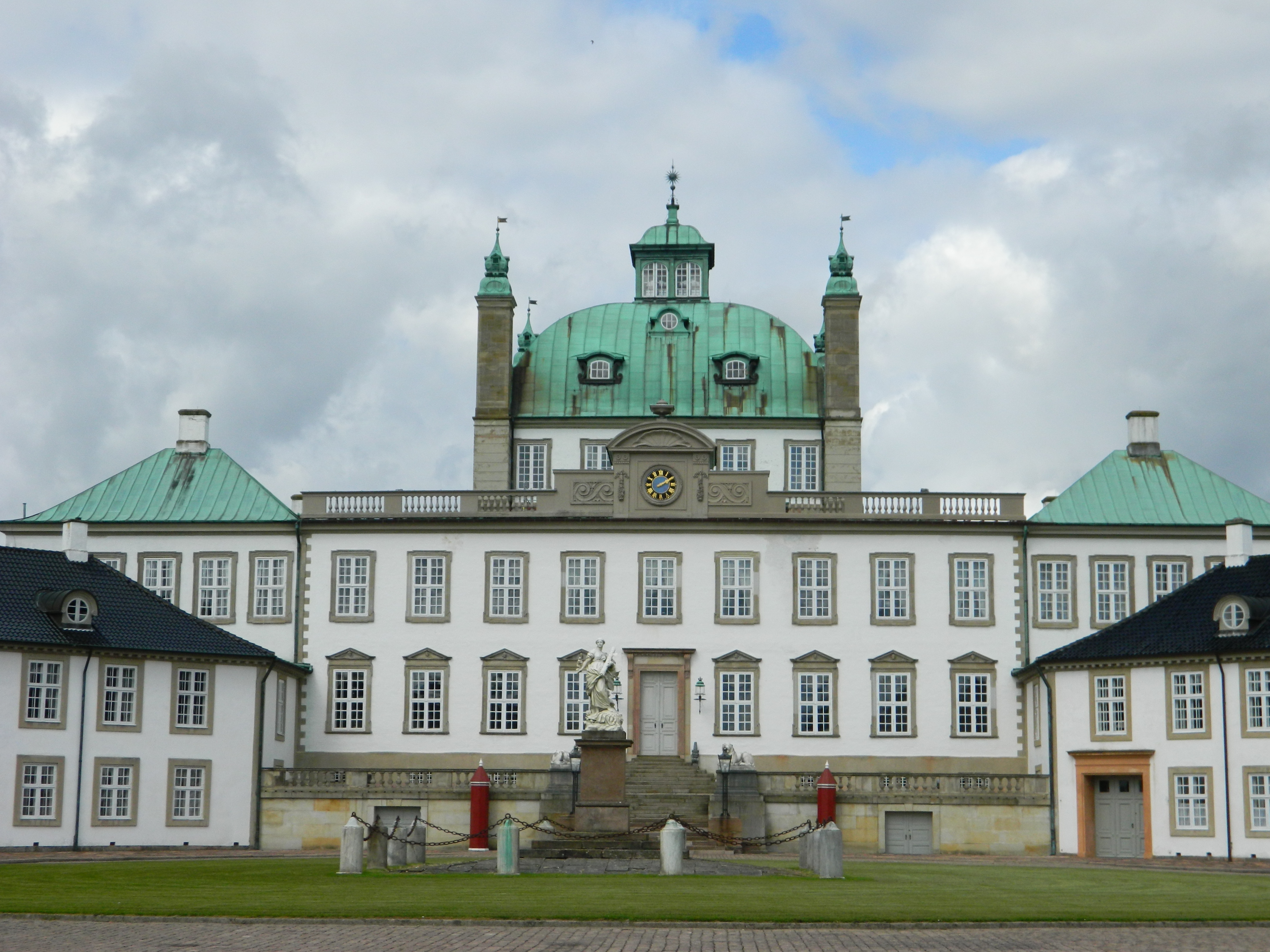
Johan Cornelius Krieger (1683ÔÇô1755) was a Danish architect and landscape architect, who from the 1720s served as both the country's chief architect, and head of the royal gardens. Krieger oversaw the construction of Fredensborg Palace and its gardens, as well as an expansion of Frydenlund Manor. He also designed or redeveloped the gardens of Frederiksberg Palace (now Frederiksberg Park), Clausholm Castle, Rosenborg Castle, Hirschholm Palace, and Odense Palace. Following the Copenhagen Fire of 1728, he was involved in the plan to reconstruct the city using brick-faced houses, establishing by March 1729 a brick works and, in partnership with Vice Admiral Ulrich Kaas, a lime kiln and a sawmill in Christianshavn He was an exponent of the baroque architecture and was influenced by the French formal garden style of Andr├® Le N├┤tre. Personal life On 8 March 1712, he married Anna Matthisen (1692ÔÇô1760). He died on 21 September 1755 in Copenhagen. Selected buildings * Batzke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
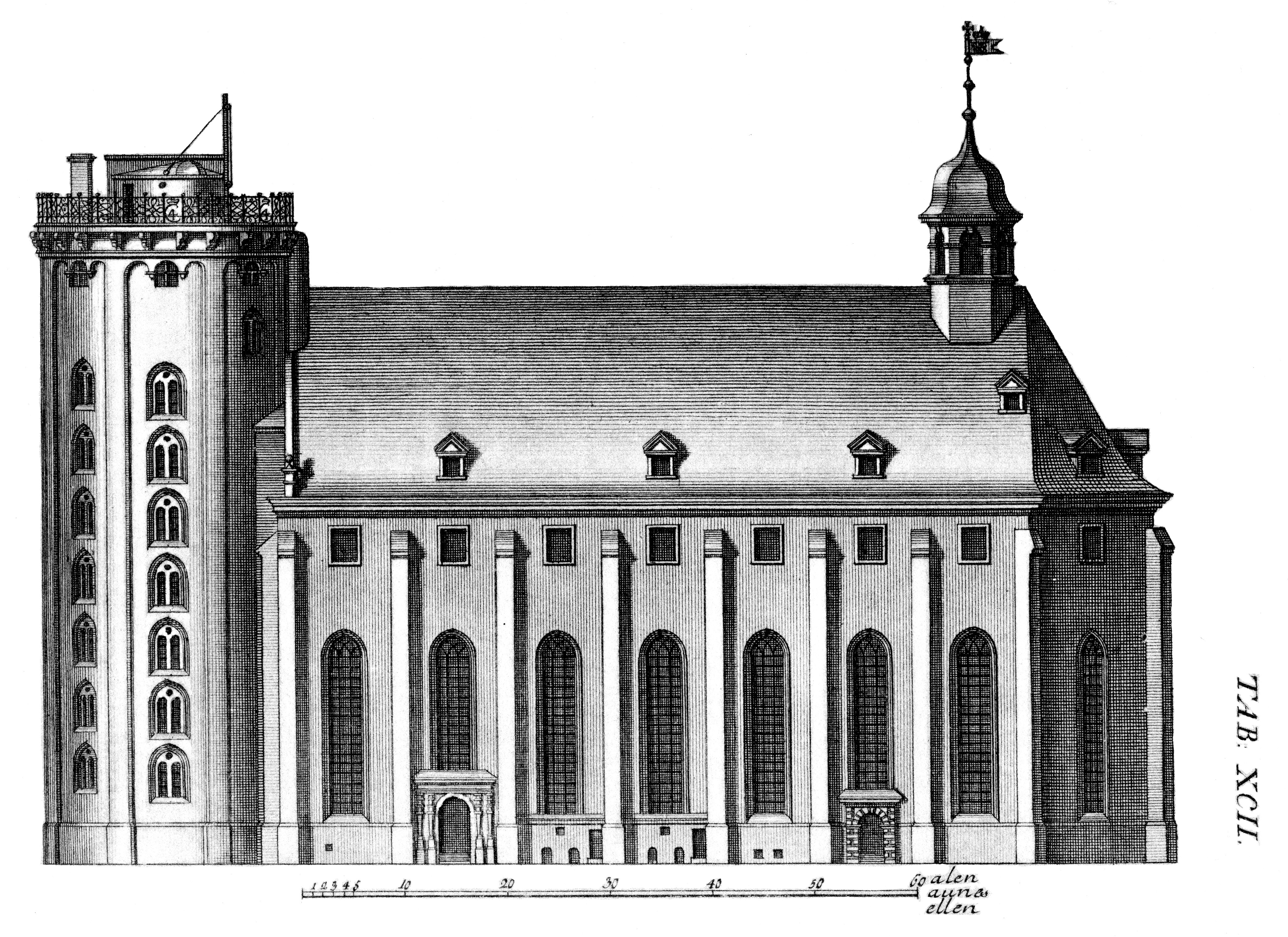
Rosenborg Barracks
Rosenborg Barracks ( Danish: ''Livgardens Kaserne ved Rosenborg''), one of two barracks of the Royal Danish Life Guard, is located next to Rosenborg Castle in Copenhagen, Denmark. Its address is Gothersgade but it has a long facade along ├İster Voldgade. History Christian V's orangery The building originates in King Christian V's pavilion which was built in 1670 with the assistance of architect Lambert van Haven. It was flanked by two long orangerie wings, one on each side, which ran parallel to the new Eastern Rampart which had been constructed in the 1650s. The central pavilion was often used for royal banquets, supplementing Christian IB's old pavilion which the king converted into a more intimate Hermitage. The Laurel House In 1709, the entire complex was interconnected to form one long building, known as the ''Orangerie''. In 1743 the building was adapted into the Baroque style by Johan Cornelius Krieger and the name was changed to ''Laurierhuset'' (English: The Laurel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)