|
École Des Arts Industriels Et Des Mines
École des arts industriels et des mines is the name used during the Second French Empire to designate the French engineering school established in 1854 in Lille, North of France. It succeeded to the municipal chairs of experimental physics, applied chemistry and mechanics that were established in 1817. Its heir as a graduate engineering school is École Centrale de Lille. History École des arts industriels et des mines de Lille was founded in 1854, the same year when Louis Pasteur became the dean of Faculté des sciences de Lille and pioneered applied research with industry cooperations, with support of scientists such as Frédéric Kuhlmann. Between 1854 and 1871, students attending the two-year/three-year curriculum grew to 90 per annum. Baccalaureate was a prerequisite to admission to the engineering school. The school delivered engineering degrees. The curriculum during the first two years of engineering education included manufacturing and textile industry, engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department, and the main city of the Métropole Européenne de Lille, European Metropolis of Lille. The city of Lille proper had a population of 234,475 in 2019 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its French suburbs and exurbs the Lille metropolitan area (French part only), which extends over , had a population of 1,510,079 that same year (Jan. 2019 census), the fourth most populated in France after Paris, Lyon, and Marseille. The city of Lille and 94 suburban French municipalities have formed since 2015 the Métropole Européenne de Lille, European Metropolis of Lille, an Indirect election, indirectly elected Métropole, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude-Auguste Lamy
Claude Auguste Lamy (; 15 June 1820 – 20 March 1878) was a French chemist who discovered the element thallium independently from William Crookes in 1862. Life Lamy was born in the commune of Ney in the department of Jura, France in 1820. He studied at the École Normale Supérieure, Paris. After he graduated from University in 1842 he became a teacher at Lille then at Limoges and again in Lille. In 1851 he received his Ph.D. In 1854 he became professor at the faculty of sciences of Lille (Université Lille Nord de France) and taught at École des arts industriels et des mines (École centrale de Lille Located in the campus of Science and Technology (Cité Scientifique) of the University of Lille in Villeneuve-d'Ascq ( European Metropolis of Lille - Hauts-de-France); École Centrale de Lille is a renowned graduate engineering school, with ro ...). In 1866 he changed to the École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures (École centrale de Paris). Lamy died in 1878. Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Schools In France
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Buildings In Lille
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education History of education, originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational aims and objectives, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the Philosophy of education#Critical theory, liberation of learners, 21st century skills, skills needed fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Lille Nord De France
The Community of Universities and Institutions (COMUE) Lille Nord de France (formerly Université Lille Nord de France) was a French Groups of Universities and Institutions ( COMUE) spread over multiple campuses and centered in Lille (North - Hauts-de-France). It included a European Doctoral College and federated universities, engineering schools and research centers. With more than one hundred thousand students, it was one of the largest university federations in France. The University of Lille, with nearly 70,000 students, was its main component. The COMUE stopped its activity in 2019 and its activities were transferred to its founding institutions. History Founded as University of Douai in 1562, the university was renamed ''Université impériale de Douai-Lille'' in 1808, then as ''Université de Lille'' with faculty expansion in the Lille region from mid-19th century onwards. * The roots of the faculties in law and humanities date back from the 16th century; * The school of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Universities And Colleges In France
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on particular areas of applied mathematics, applied science, and types of application. See glossary of engineering. The term ''engineering'' is derived from the Latin ''ingenium'', meaning "cleverness" and ''ingeniare'', meaning "to contrive, devise". Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD, the predecessor of ABET) has defined "engineering" as: The creative application of scientific principles to design or develop structures, machines, apparatus, or manufacturing processes, or works utilizing them singly or in combination; or to construct or operate the same with full cognizance of their design; or to forecast their behavior under specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compagnie Des Mines D'Anzin
The Compagnie des mines d'Anzin (Anzin Mining Company) was a large French mining company in the coal basin of Nord-Pas-de-Calais in northern France. It was established in 1756 and operated for almost 200 years. The company used innovative pumping technology to support deep mining operations in the rich bituminous coalfield. At its peak in the mid-19th century it was one of the largest industrial enterprises in France, with about 12,000 miners. Émile Zola visited the region during a strike in 1884 which he used as the basis for his novel ''Germinal (novel), Germinal''. The work was dangerous and unhealthy, but the company paid the miners well compared to other industries, provided housing, welfare and pensions, and sponsored social activities. The mines reached their peak of prosperity before World War I (1914–18), but were badly damaged during the war. They struggled to regain profitability in period leading up to World War II (1939–45). The mines were nationalized in 1946. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
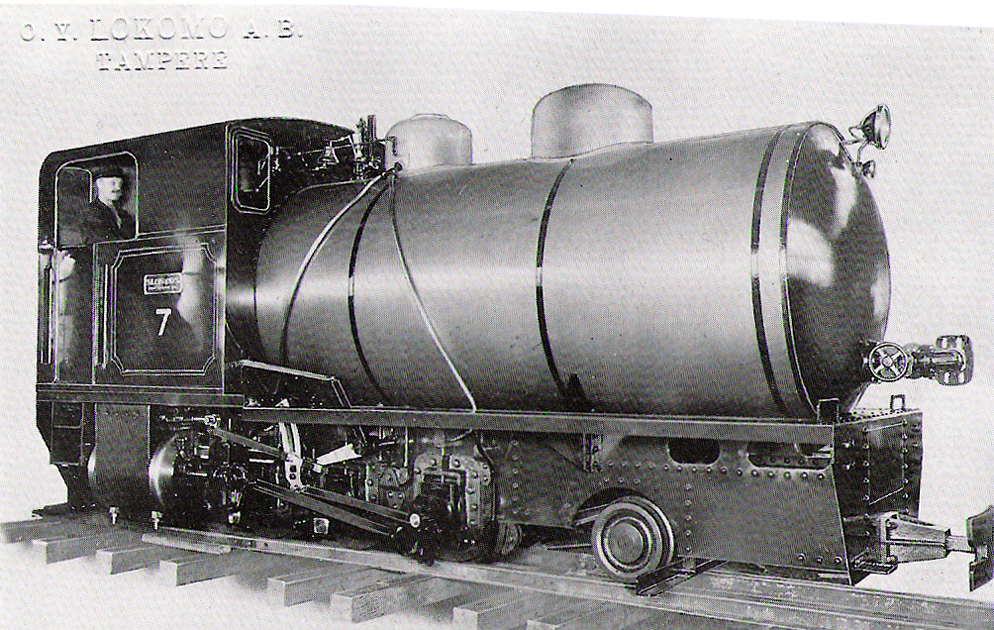
Fireless Locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of locomotive which uses reciprocating engines powered from a reservoir of compressed air or steam, which is filled at intervals from an external source. They offer advantages over conventional steam locomotives of lower cost per unit, cleanliness, and decreased risk from fire or boiler explosion; these are counterbalanced by the need for a source to refill the locomotive, and by the limited range afforded by the reservoir. They were desirable in situations where smoke from a firebox would be too noxious, or where there was risk of fire or explosion. Typical usage was in a mine, or a food or chemical factory. They were also used where a source of air or steam was readily available, and for moving loads within limited areas, such as a switch yard or within an industrial factory. They were eventually replaced for most uses by diesel and battery electric locomotives fitted with protective appliances; these are described as flame-proof locomotives. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. It is the only fixed link between the island of Great Britain and the European mainland. At its lowest point, it is deep below the sea bed and below sea level. At , it has the longest underwater section of any tunnel in the world, and is the third longest railway tunnel in the world. The speed limit for trains through the tunnel is . The tunnel is owned and operated by the company Getlink, formerly "Groupe Eurotunnel". The tunnel carries high-speed Eurostar passenger trains, the Eurotunnel Shuttle for road vehicles and international freight trains. It connects end-to-end with the high-speed railway lines of the LGV Nord in France and High Speed 1 in England. In 2017, through rail services carried 10.3 million passengers and 1.22 milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Amand-les-Eaux
Saint-Amand-les-Eaux (; former nl, Sint-Amands-aan-de-Skarpe, link=no) is a commune in the Nord department, northern France. It lies on the river Scarpe, 12 km northwest of Valenciennes. In French, the town people are named ''Amandinois'' (m), ''Amandinoise'' (f). The composer Robert Lannoy (1915–1979) was born in Saint-Amand-les-Eaux. Saint-Amand Abbey, formerly Elnon Abbey, was located here from its foundation in the 630s by Saint Amand until its dissolution in 1789. Population Heraldry Local culture and heritage Industries Saint Amand has an industrial belt, casino, shopping centre, thermal baths, and several springs. The Tower The tower on the Grand'Place standing 82 metres tall is the symbol of this town. It is one of the remaining structures of the former Saint-Amand Abbey, and it was the west façade of the former abbey church, which has been demolished. It has a carillon with 48 bells and a museum devoted to faience. The abbey was founded in the 7th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Désiré Blanquart-Evrard
Louis Désiré Blanquart-Evrard (2 August 1802 – 28 April 1872) was a French inventor, photographer and photo publisher. Being a cloth merchant by trade, in the 1840s he developed interest in photography and focused on technical and economical issues of mass production of photo prints. Biography He was born and raised in Lille where he studied chemistry with Charles Frédéric Kuhlmann and miniature painting on porcelain.Encyclopedia of nineteenth-century photography: A-I Volume 1, edited by John Hannavy. New York: Taylor & Francis, 2007, pp. 167–168. After Louis Daguerre solved the problem of long exposure time and introduced Daguerreotype, daguerreotypy, a practical p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut Industriel Du Nord
The Institut industriel du Nord (IDN) was the engineering school and research institute at École Centrale de Lille from 1872 to 1991, within the campus of the Lille University of Science and Technology (France). History École des arts industriels et des mines (École Centrale de Lille) was a college of engineering founded in Lille in 1854 during the Second French Empire. On the eve of the French Third Republic, lectures and research activities were reorganised into a comprehensive three-year curriculum and developed in 1872, embodied by its newly built Institut industriel du Nord de la France (IDN). Education initially focused on civil engineering, mechanical engineering, chemistry and manufacturing engineering. Electrical engineering full courses were added in 1892, automobile design has been taught from 1899 onwards. More than 200 students graduated in year 1914. Aerodynamics studies started in 1930. A focus on automatic control and computers was initiated in 1957. Later c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1860.png)