Utility function
Consider a set of alternatives among which a person has a preference ordering. A utility function represents that ordering if it is possible to assign aApplications
Utility can be represented through sets of indifference curve, which are level curves of the function itself and which plot the combination of commodities that an individual would accept to maintain a given level of satisfaction. Combining indifference curves with budget constraints allows for individual demand curves derivation. A diagram of a general indifference curve is shown below (Figure 1). The vertical and horizontal axes represent an individual's consumption of commodity Y and X respectively. All the combinations of commodity X and Y along the same indifference curve are regarded indifferently by individuals, which means all the combinations along an indifference curve result in the same utility value. Individual and social utility can be construed as the value of a utility function and a social welfare function, respectively. When coupled with production or commodity constraints, by some assumptions, these functions can be used to analyze
Individual and social utility can be construed as the value of a utility function and a social welfare function, respectively. When coupled with production or commodity constraints, by some assumptions, these functions can be used to analyze Preference
While preferences are the conventional foundation of choice theory inRevealed preference
It was recognized that utility could not be measured or observed directly, so instead economists devised a way to infer relative utilities from observed choice. These 'revealed preferences', as termed byUtility is assumed to be correlative to Desire or Want. It has been argued already that desires cannot be measured directly, but only indirectly, by the outward phenomena which they cause: and that in those cases with which economics is mainly concerned the measure is found by the price which a person is willing to pay for the fulfillment or satisfaction of his desire.
Utility functions, expressing utility as a function of the amounts of the various goods consumed, are treated as either ''cardinal'' or ''ordinal'', depending on whether they are or are not interpreted as providing more information than simply the rank ordering of preferences among bundles of goods, such as information concerning the strength of preferences.
Cardinal
Cardinal utility states that the utilities obtained from consumption can be measured and ranked objectively and are representable by numbers. There are fundamental assumptions of cardinal utility. Economic agents should be able to rank different bundles of goods based on their preferences or utilities and sort different transitions between two bundles of goods. A cardinal utility function can be transformed to another utility function by a positive linear transformation (multiplying by a positive number, and adding some other number); however, both utility functions represent the same preferences. When cardinal utility is assumed, the magnitude of utility differences is treated as an ethically or behaviorally significant quantity. For example, suppose a cup of orange juice has utility of 120 "utils", a cup of tea has a utility of 80 utils, and a cup of water has a utility of 40 utils. With cardinal utility, it can be concluded that the cup of orange juice is better than the cup of tea by the same amount by which the cup of tea is better than the cup of water. This means that if a person has a cup of tea, they would be willing to take any bet with a probability, p, greater than .5 of getting a cup of juice, with a risk of getting a cup of water equal to 1-p. One cannot conclude, however, that the cup of tea is two-thirds of the goodness of the cup of juice because this conclusion would depend not only on magnitudes of utility differences but also on the "zero" of utility. For example, if the "zero" of utility were located at -40, then a cup of orange juice would be 160 utils more than zero, a cup of tea 120 utils more than zero. Cardinal utility can be considered as the assumption that quantifiable characteristics, such as height, weight, temperature, etc can measure utility.Ordinal
Instead of giving actual numbers over different bundles, ordinal utilities are only the rankings of utilities received from different bundles of goods or services. For example, ordinal utility could tell that having two ice creams provide a greater utility to individuals in comparison to one ice cream but could not tell exactly how much extra utility received by the individual. Ordinal utility, it does not require individuals to specify how much extra utility they received from the preferred bundle of goods or services in comparison to other bundles. They are only needed to tell which bundles they prefer. When ordinal utilities are used, differences in utils (values assumed by the utility function) are treated as ethically or behaviorally meaningless: the utility index encodes a full behavioral ordering between members of a choice set, but tells nothing about the related ''strength of preferences''. For the above example, it would only be possible to say that juice is preferred to tea to water. Thus, ordinal utility utilizes comparisons, such as "preferred to", "no more", "less than", etc. If a function is ordinal and non-negative, it is equivalent to the function , because taking the square is an increasing monotone (or monotonic) transformation. This means that the ordinal preference induced by these functions is the same (although they are two different functions). In contrast, if is cardinal, it is not equivalent to .Examples
In order to simplify calculations, various alternative assumptions have been made concerning details of human preferences, and these imply various alternative utility functions such as: * CES (''constant elasticity of substitution''). * Isoelastic utility * Exponential utility * Quasilinear utility * Homothetic preferences * Stone–Geary utility function * Gorman polar form ** Greenwood–Hercowitz–Huffman preferences ** King–Plosser–Rebelo preferences * Hyperbolic absolute risk aversion Most utility functions used for modeling or theory are well-behaved. They are usually monotonic and quasi-concave. However, it is possible for rational preferences not to be representable by a utility function. An example is lexicographic preferences which are not continuous and cannot be represented by a continuous utility function.Marginal utility
Economists distinguish between total utility and marginal utility. Total utility is the utility of an alternative, an entire consumption bundle or situation in life. The rate of change of utility from changing the quantity of one good consumed is termed the marginal utility of that good. Marginal utility therefore measures the slope of the utility function with respect to the changes of one good. Marginal utility usually decreases with consumption of the good, the idea of "diminishing marginal utility". In calculus notation, the marginal utility of good X is . When a good's marginal utility is positive, additional consumption of it increases utility; if zero, the consumer is satiated and indifferent about consuming more; if negative, the consumer would pay to reduce his consumption.Law of diminishing marginal utility
Rational individuals only consume additional units of goods if it increases the marginal utility. However, the law of diminishing marginal utility means an additional unit consumed brings a lower marginal utility than that carried by the previous unit consumed. For example, drinking one bottle of water makes a thirsty person satisfied; as the consumption of water increases, he may feel begin to feel bad which causes the marginal utility to decrease to zero or even become negative. Furthermore, this is also used to analyze progressive taxes as the greater taxes can result in the loss of utility.Marginal rate of substitution (MRS)
Marginal rate of substitution is the absolute value of the slope of the indifference curve, which measures how much an individual is willing to switch from one good to another. Using a mathematic equation, keeping ''U''(''x''1,''x''2) constant. Thus, MRS is how much an individual is willing to pay for consuming a greater amount of ''x''1. MRS is related to marginal utility. The relationship between marginal utility and MRS is: :Expected utility
Expected utility theory deals with the analysis of choices among risky projects with multiple (possibly multidimensional) outcomes. The St. Petersburg paradox was first proposed by Nicholas Bernoulli in 1713 and solved by Daniel Bernoulli in 1738, although the Swiss mathematician Gabriel Cramer proposed taking the expectation of a square-root utility function of money in an 1728 letter to N. Bernoulli. D. Bernoulli argued that the paradox could be resolved if decision-makers displayedVon Neumann–Morgenstern
Von Neumann and Morgenstern addressed situations in which the outcomes of choices are not known with certainty, but have probabilities associated with them. A notation for a '' lottery'' is as follows: if options A and B have probability ''p'' and 1 − ''p'' in the lottery, we write it as a linear combination: : More generally, for a lottery with many possible options: : where . By making some reasonable assumptions about the way choices behave, von Neumann and Morgenstern showed that if an agent can choose between the lotteries, then this agent has a utility function such that the desirability of an arbitrary lottery can be computed as a linear combination of the utilities of its parts, with the weights being their probabilities of occurring. This is termed the ''expected utility theorem''. The required assumptions are four axioms about the properties of the agent's preference relation over 'simple lotteries', which are lotteries with just two options. Writing to mean 'A is weakly preferred to B' ('A is preferred at least as much as B'), the axioms are: # completeness: For any two simple lotteries and , either or (or both, in which case they are viewed as equally desirable). # transitivity: for any three lotteries , if and , then . # convexity/continuity (Archimedean property): If , then there is a between 0 and 1 such that the lottery is equally desirable as . # independence: for any three lotteries and any probability ''p'', if and only if . Intuitively, if the lottery formed by the probabilistic combination of and is no more preferable than the lottery formed by the same probabilistic combination of and then and only then . Axioms 3 and 4 enable us to decide about the relative utilities of two assets or lotteries. In more formal language: A von Neumann–Morgenstern utility function is a function from choices to the real numbers: : which assigns a real number to every outcome in a way that represents the agent's preferences over simple lotteries. Using the four assumptions mentioned above, the agent will prefer a lottery to a lottery if and only if, for the utility function characterizing that agent, the expected utility of is greater than the expected utility of : :. Of all the axioms, independence is the most often discarded. A variety ofIndirect utility
An indirect utility function gives the optimal attainable value of a given utility function, which depends on the prices of the goods and the income or wealth level that the individual possesses.Money
One use of the indirect utility concept is the notion of the utility of money. The (indirect) utility function for money is a nonlinear function that is bounded and asymmetric about the origin. The utility function is concave in the positive region, representing the phenomenon of diminishing marginal utility. The boundedness represents the fact that beyond a certain amount money ceases being useful at all, as the size of any economy at that time is itself bounded. The asymmetry about the origin represents the fact that gaining and losing money can have radically different implications both for individuals and businesses. The non-linearity of the utility function for money has profound implications in decision-making processes: in situations where outcomes of choices influence utility by gains or losses of money, which are the norm for most business settings, the optimal choice for a given decision depends on the possible outcomes of all other decisions in the same time-period.Budget constraints
Individuals' consumptions are constrained by their budget allowance. The graph of budget line is a linear, downward-sloping line between X and Y axes. All the bundles of consumption under the budget line allow individuals to consume without using the whole budget as the total budget is greater than the total cost of bundles (Figure 2). If only considers prices and quantities of two goods in one bundle, a budget constraint could be formulated as , where and are prices of the two goods, and are quantities of the two goods.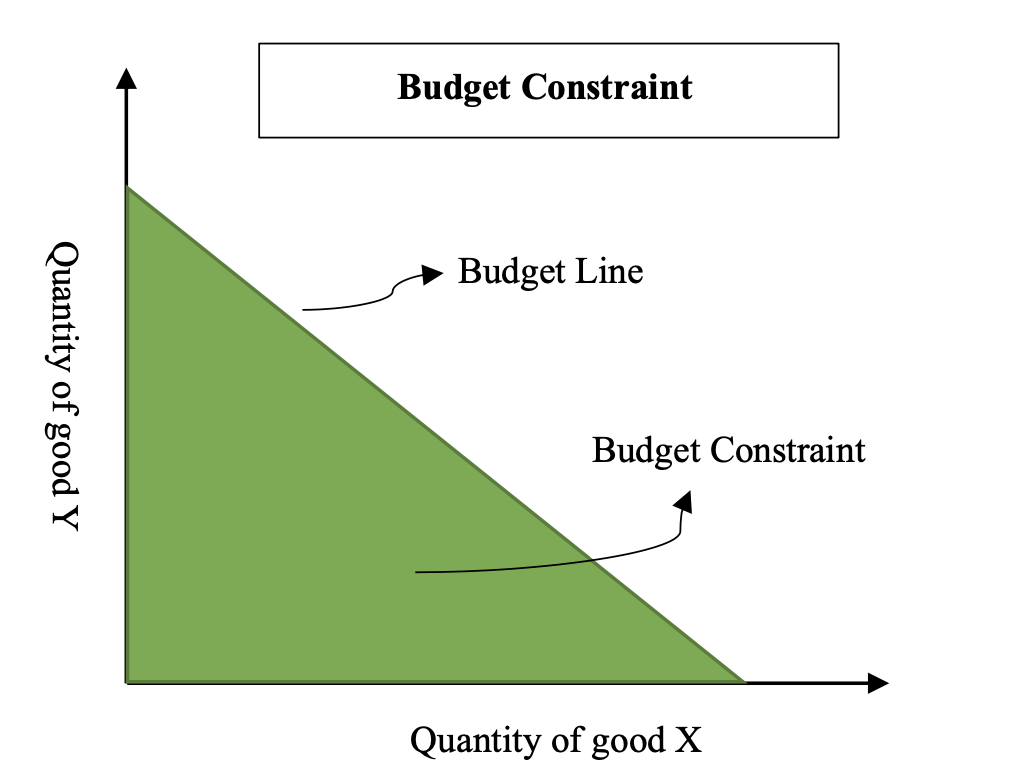 :
:
Constrained utility optimisation
Rational consumers wish to maximise their utility. However, as they have budget constraints, a change of price would affect the quantity of demand. There are two factors could explain this situation: * Purchasing power. Individuals obtain greater purchasing power when the price of a good decreases. The reduction of the price allows individuals to increase their savings so they could afford to buy other products. * Substitution effect. If the price of good A decreases, then the good becomes relatively cheaper with respect to its substitutes. Thus, individuals would consume more of good A as the utility would increase by doing so.Discussion and criticism
Cambridge economist Joan Robinson famously criticized utility for being a circular concept: "Utility is the quality inMeasuring utility functions
There are many empirical works trying to estimate the form of utility functions of agents with respect to money.See also
*References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * Viner, Jacob (1925). "The Utility Concept in Value Theory and Its Critics". ''Journal of Political Economy''. 33 (4): 369–387. * Viner, Jacob (1925). "The Utility Concept in Value Theory and Its Critics". ''Journal of Political Economy''. 33 (6): 638–659.External links
Definition of Utility by Investopedia
and perhaps als
{{Authority control Choice modelling Concepts in ethics Value (ethics)