Uinta Mountain Group on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Uinta Mountains ( ) are an east-west trending
/ref> (between about 700 million and 760 million years old) and consist primarily of
 The south and east sides of the range are largely within the
The south and east sides of the range are largely within the
 The Uinta Mountains are part of the Wasatch and Uinta montane forests
The Uinta Mountains are part of the Wasatch and Uinta montane forests
''The Geologic Story of the Uinta Mountains''
Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office, 1969
mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
in northeastern Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
extending a short distance into northwest Colorado and slightly into southwestern Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. As a subrange of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
, they are unusual for being the highest range in the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The te ...
running east to west, and lie approximately east of Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in the state. The city is the core of the Salt Lake Ci ...
. The range has peaks ranging from , with the highest point being Kings Peak, also the highest point in Utah. The Mirror Lake Highway
State Route 150, also known as the Mirror Lake Highway, is a state highway in the U.S. state of Utah. It is named for Mirror Lake, a picturesque lake that the highway passes along the way. It is also a USDA Forest Service Scenic Byway.
Route d ...
crosses the western half of the Uintas on its way to Wyoming. Utah State Route 44
State Route 44 (SR-44) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Utah that runs from US-191 (UT), US-191 at Greendale Junction, Utah, Greendale Junction, southwest of Dutch John, Utah, Dutch John, to SR-43 (UT), SR-43 in Manila, Utah, Manila. Th ...
crosses the east end of the Uintas between Vernal and Manila
Manila, officially the City of Manila, is the Capital of the Philippines, capital and second-most populous city of the Philippines after Quezon City, with a population of 1,846,513 people in 2020. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay on ...
.
Etymology
The name "Uinta" derives from theUte
Ute or UTE may refer to:
* Ute people, a Native American people of the Great Basin
* Ute Indian Tribe of the Uintah and Ouray Reservation, Utah
* Ute Mountain Ute Tribe, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah
* Southern Ute Indian Tribe of the Southern ...
word ''Yoov-we-teuh'', meaning "pine forest" or "pine tree".
Geology
The Uinta Mountains are Laramide upliftedmetasediment
In geology, metasedimentary rock is a type of metamorphic rock. Such a rock was first formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occu ...
ary rocks deposited in an intracratonic basin in southwest Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American craton is a large continental craton that forms the Geology of North America, ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of ...
during the time of the breakup of the supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). wer ...
. The marine and fluvial metasedimentary rocks in the core of the Uinta Mountains are of Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
agePaleomagnetic results from the Neoproterozoic Uinta Mountain Group/ref> (between about 700 million and 760 million years old) and consist primarily of
quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tecton ...
, slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic ro ...
, and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of Clay mineral, clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g., Kaolinite, kaolin, aluminium, Al2Silicon, Si2Oxygen, O5(hydroxide, OH)4) and tiny f ...
. These rocks comprise the Uinta Mountain Group, and reach thicknesses of . Most of the high peaks are outcrops of the Uinta Mountain Group. Many of the peaks are ringed with bands of cliffs, rising to form broad or flat tops. The mountains are bounded to the north and south by reverse fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic f ...
s that meet below the range, on the north by the North Flank fault and on the south by the Uinta Basin boundary fault.
The Uinta Mountain Group, from oldest to youngest, includes Uinta Mountain undivided quartz arenite
A quartz arenite or quartzarenite is a sandstone composed of greater than 90% detrital quartz. Quartz arenites are the most mature sedimentary rocks possible, and are often referred to as ultra- or super-mature, and are usually cemented by sil ...
, overlain by the Moosehorn Lake, Mount Watson, Hades Peak, and Red Shale formations. The flanks of the east-west trending Uinta Mountains contain a sequence of Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
strata ranging from the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
Lodore Formation
''Lodore'', also published under the title ''The Beautiful Widow'', is the penultimate novel by Romantic novelist Mary Shelley, completed in 1833 and published in 1835.
Plot and themes
In ''Lodore'', Shelley focused her theme of power and res ...
to the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
Mancos Shale
The Mancos Shale or Mancos Group is a Late Cretaceous (Upper Cretaceous) geologic formation of the Western United States.
The Mancos Shale was first described by Cross and Purington in 1899 and was named for exposures near the town of Mancos, C ...
, all of which have been tilted during the uplift of the mountain range.
The uplift of the range dates to the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 80 to 70 million years ago, and ended 55 to 35 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
, about 70 to 50 million years ago, when compressive forces produced high-angle reverse fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic f ...
s on both the north and south sides of the present mountain range. The east-west orientation of the Uintas is anomalous compared to most of the ranges of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
; it may relate to changing stress patterns and rotation of the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. This plateau covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within w ...
. The Green River used to flow into the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
, but changed to the Colorado River by going through the Uintas in ways not fully understood.
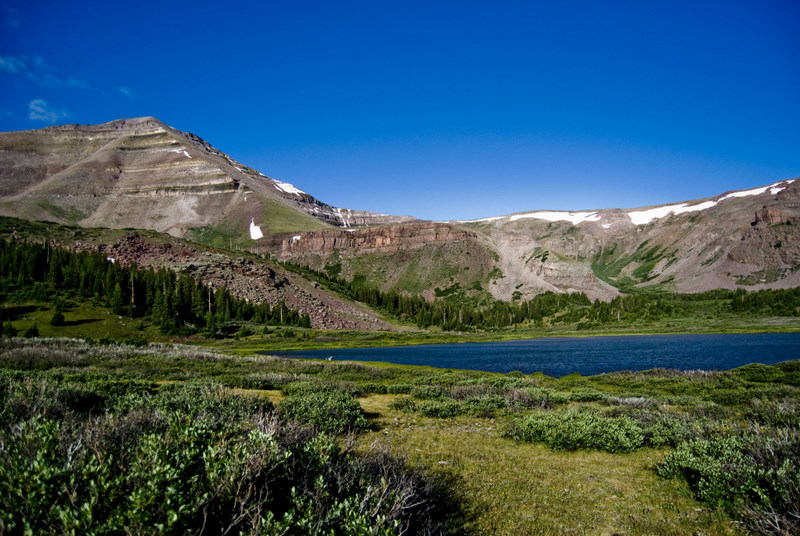
The high Uintas were extensively glaciated during the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
, and most of the large stream valleys on both the north and south sides of the range held long valley glaciers. However, despite reaching to over in elevation, the climate today is sufficiently dry that no glaciers survived even before the rapid current glacial retreat began in the middle nineteenth century. The Uintas are the most poleward mountain range in the world to reach over without modern glaciers, and are in fact the highest mountain range in the contiguous United States with no modern glaciers. Permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
occurs at elevations above and at times forms large rock glacier
Rock glaciers are distinctive geomorphological landforms that consist either of angular rock debris frozen in interstitial ice, former "true" glaciers overlain by a layer of talus, or something in between. Rock glaciers are normally found at hi ...
s.
Soils in the Uinta Mountains are acidic to varying degrees, in contrast to the neutral or alkaline pH readings which prevail at lower elevations across most of Utah.
Between the summits and ridgelines are wide, level basins with around 500 small lakes. One of the most popular lakes is Mirror Lake because of its good fishing, scenic views, and easy road access.
Hydrology
 The south and east sides of the range are largely within the
The south and east sides of the range are largely within the Colorado River
The Colorado River () is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The river, the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), 5th longest in the United St ...
watershed, including the Blacks Fork
Blacks Fork (also referred to as Blacks Fork of the Green River) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. , accessed March 18, 2011 tributary of the Green River in Utah and Wyoming in the United ...
and the Duchesne River
The Duchesne River ( ), located in the Uintah Basin region of Utah in the western United States, is a tributary of the Green River. The watershed of the river covers the Northeastern corner of Utah. The Duchesne River is long,U.S. Geological S ...
, which are tributaries of the Green River. The Green is the major tributary of the Colorado River and flows in a tight arc around the eastern side of the range. (Indeed, John Wesley Powell said the Green was the "master stream" where it and the Colorado River came together.)
The Bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats ...
and Weber
Weber may refer to:
Places United States
* Weber, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Weber City, Virginia, a town
* Weber City, Fluvanna County, Virginia, an unincorporated community
* Weber County, Utah
* Weber Canyon, Utah
* Weber R ...
rivers, the two largest tributaries of Great Salt Lake
The Great Salt Lake is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere and the eighth-largest terminal lake in the world. It lies in the northern part of the U.S. state of Utah and has a substantial impact upon the local climate, partic ...
, are born on the west slope of the range. The Provo River
The Provo River (Ute people, Ute: Timpanoquint, “Rock River) is located in Utah County, Utah, Utah County and Wasatch County, Utah, Wasatch County, Utah, in the United States. It rises in the Uinta Mountains at Wall Lake and flows about southw ...
, the largest tributary to Utah Lake
Utah Lake is a shallow freshwater lake in the center of Utah County, Utah, United States. It lies in Utah Valley, surrounded by the Provo- Orem metropolitan area. The lake's only river outlet, the Jordan River, is a tributary of the Great Sa ...
, begins on the southern side of the range and flows west to Utah Lake, which itself drains via the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead ...
into Great Salt Lake.
Large portions of the mountain range receive over of precipitation annually. The high Uintas are snowcapped most of the year except for late July through early September. The Uinta Mountains have more than of streams and 1,000 lakes and ponds.
The Uintas have a continental snowpack leading to high avalanche danger in the winter.
Ecology
 The Uinta Mountains are part of the Wasatch and Uinta montane forests
The Uinta Mountains are part of the Wasatch and Uinta montane forests ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
. Nearly the entire range lies within Uinta-Wasatch-Cache National Forest (on the north and west) and Ashley National Forest
Ashley National Forest is a United States National Forest, National Forest located in northeastern Utah and southwestern Wyoming. Within the Forest's bounds are (with in Utah and in Wyoming) of vast forests, lakes, and mountains, with elevati ...
(on the south and east). The range's highest peaks are protected as part of the High Uintas Wilderness
The High Uintas Wilderness is a wilderness area located in northeastern Utah, United States. The wilderness covers the Uinta Mountains, encompassing parts of Duchesne and Summit counties. Designated as a wilderness in 1984, the area is located ...
. The forests contain many species of trees, including lodgepole pine
''Pinus contorta'', with the common names lodgepole pine and shore pine, and also known as twisted pine, and contorta pine, is a common tree in western North America. It is common near the ocean shore and in dry montane forests to the subalpin ...
, subalpine fir
''Abies lasiocarpa'', the subalpine fir or Rocky Mountain fir, is a western North American fir tree.
Description
''Abies lasiocarpa'' is a medium-sized evergreen conifer with a very narrow conic crown, growing to tall, exceptionally , with a t ...
, Engelmann spruce
''Picea engelmannii'', with the common names Engelmann spruce, white spruce, mountain spruce, and silver spruce, is a species of spruce native to western North America. It is highly prized for producing distinctive tone wood for acoustic guitars ...
, Douglas-fir
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is the tallest tree in the Pinaceae family. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Or ...
, and quaking aspen
''Populus tremuloides'' is a deciduous tree native to cooler areas of North America, one of several species referred to by the common name aspen. It is commonly called quaking aspen,
. There are also many species of grasses, shrubs, and forb
A forb or phorb is a herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in botany and in vegetation ecology especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically, these are eudicots without woo ...
s growing in the Uinta Mountains.
Fauna is typical of the central Rocky Mountains. Large grazing and browsing animals include the Rocky Mountain elk, mule deer, moose, pronghorn antelope, mountain goats, and Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep. Mammalian predators include the American black bear, mountain lion, coyotes, red fox, badger, wolverine, marten, and the long-tailed weasel. A gray wolf pack has been observed at the eastern end of the range, in Moffat County, Colorado. Raptors include bald and golden eagles, turkey vultures, various hawks and harriers, and owls including the great horned owl, great grey owl, and barn owls. Other notable large birds include the sage grouse and white-tailed ptarmigan.
Points of interest
The Uintas are home to Camp Steiner, the highestBoy Scout
A Scout, Boy Scout, Girl Scout or, in some countries, a Pathfinder is a participant in the Scout Movement, usually aged 10–18 years, who engage in learning scoutcraft and outdoor and other special interest activities. Some Scout organizatio ...
camp in the U.S., at . The camp is near mile marker 33 of the Mirror Lake Highway.
The Uinta Highline Trail
The Uinta Highline Trail is a trail in the Uinta Mountains of Utah that traverses the range from east to west. The trail passes through expansive alpine landscapes dominated by metasedimentary rocks sculpted by past glaciers. The broad glacial b ...
traverses the entire range and is a popular backpacking trail.
Dinosaur National Monument
Dinosaur National Monument is an American national monument located on the southeast flank of the Uinta Mountains on the border between Colorado and Utah at the confluence of the Green River (Colorado River tributary), Green and Yampa River, Y ...
is on the Uintas' southeast flank, on the border between Colorado and Utah.
See also
*List of mountain ranges
This is a list of mountain ranges on Earth and a few other astronomical object, astronomical bodies. First, the highest and longest mountain ranges on Earth are listed, followed by more comprehensive alphabetical lists organized by continent. Rang ...
* Mountain ranges of Utah
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
* High Uintas Wilderness
The High Uintas Wilderness is a wilderness area located in northeastern Utah, United States. The wilderness covers the Uinta Mountains, encompassing parts of Duchesne and Summit counties. Designated as a wilderness in 1984, the area is located ...
References
Further reading
* Davis, Mel, and Veranth, John, ''High Uinta Trails'', Salt Lake City: Wasatch Publishers, 1988 (3rd edition) * Hansen, Wallace R''The Geologic Story of the Uinta Mountains''
Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office, 1969
External links
* - an interactive map for exploring the high Uinta lakes {{Authority control 01 Ranges of the Rocky Mountains Mountain ranges of Utah Mountain ranges of Wyoming Colorado Plateau Mountain ranges of Duchesne County, Utah Mountain ranges of Summit County, Utah Mountain ranges of Wasatch County, Utah Ashley National Forest Wasatch-Cache National Forest Mountain ranges of Daggett County, Utah