|
Laurentia
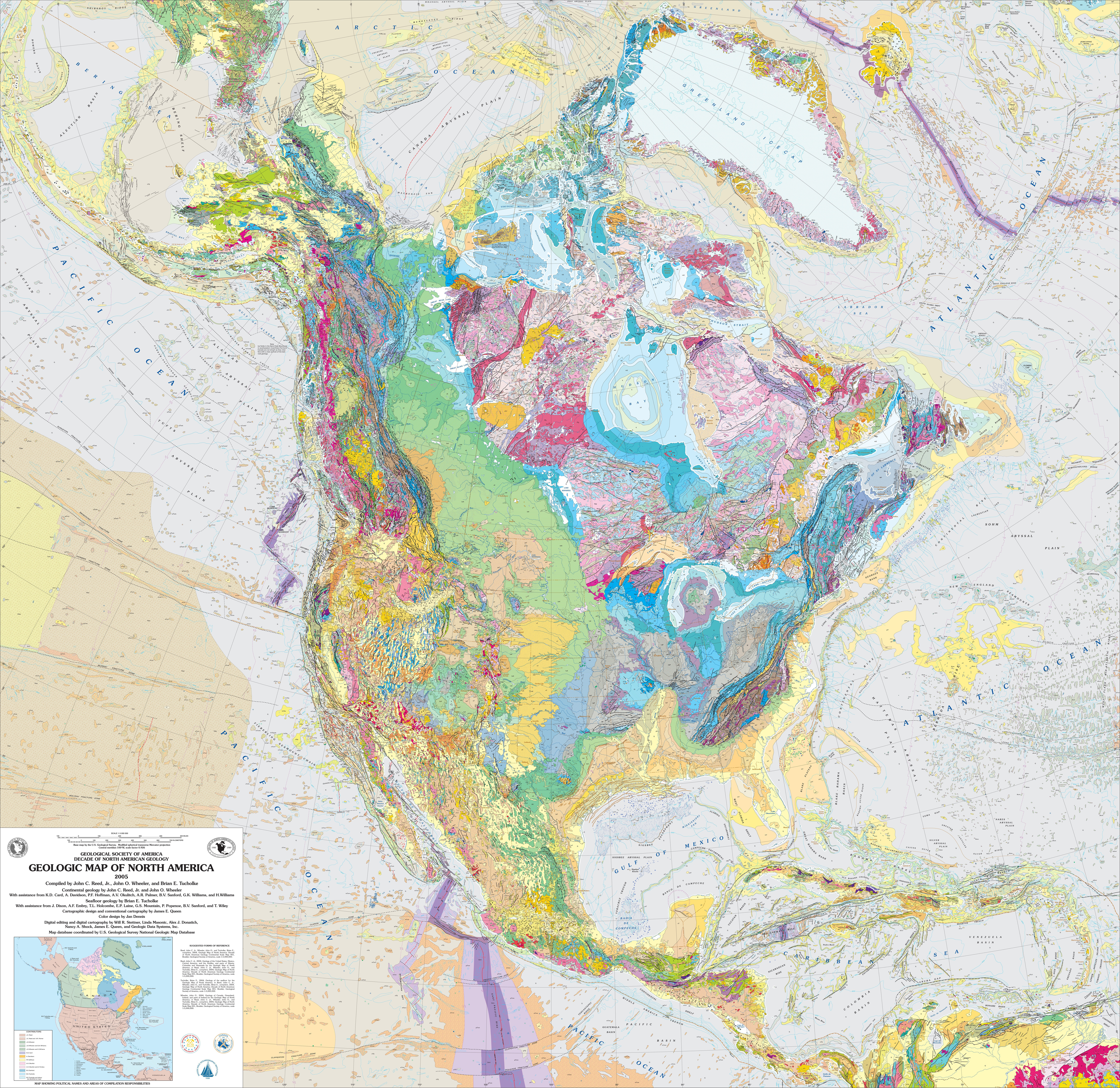
Laurentia or the North American craton is a large continental craton that forms the Geology of North America, ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and the Hebridean terrane in northwest Scotland. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of early Proterozoic Orogenic belt, orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and Suture (geology), sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today. Etymology The craton is named after the Laurentian Shield, through the Laurentian Mountains, which received their name from the St. Lawrence River, named after Saint Lawrence of Rome. Interior platform In eastern and centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting further north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau of Laurentia and Eurasia. Laurentia, Avalonia, Baltica, and a series of smaller terranes, collided in the Caledonian orogeny c. 400 Mya to form Laurussia. Laurussia then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea. Kazakhstania and Siberia were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Mya to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia. Terminology and origin of the concept Laurentia, the Palaeozoic core of North America and continental fragments that now make up part of Europe, collided with Baltica and Aval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentian Mountains
The Laurentian Mountains, also known as the Laurentians or Laurentides, are a mountain range in Canada. The range is long and ranges in height from with peaks over . The Laurentian Mountains extend across Labrador and Quebec within the Laurentian Upland, which contains foothills in northeastern Ontario. The range is located near the rivers of Ottawa River, Ottawa, St. Lawrence River, St. Lawrence, and Saguenay River, Saguenay. The Laurentian Mountains primarily stretch across multiple regions in Quebec, with geologic formations such as the Jacques-Cartier Massif located within the range. The Laurentians Mountains are one of the oldest mountain ranges on earth. The range formed around one billion years ago during the Grenville orogeny, in which the Grenville Province formed, a subdivision of the Canadian Shield. During that time, Laurentia, the geologic core of the Canadian Shield, collided with other continents and formed Precambrian rocks which extend across the range. The mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentia (other)
Laurentia may refer to: ;Geography * Laurentia, the continental craton at the heart of North America ** Laurentia, a former continent * North America, the continent * Laurentian Shield, the shield at the heart of the craton * Laurentian Mountains * Saint Lawrence River basin * Laurentia (bioregion) * Laurentia, a proposed deep-water container terminal at the Port of Quebec * Laurentie (concept), a poetic name given to Quebec, and a name for the idea of an independent Quebec, from the 1930s to the 1950s ;Media * ''Laurentie'' (magazine), a magazine of the Alliance laurentienne, a Quebec independence organization in the 1950s * ''Laurentia'' (film), also known as ''Laurentie'', a film directed by Mathieu Denis ;People * surname "Laurentia", see Laurentius * Saint Laurentia, see Palatias and Laurentia * Pierre-Sébastien Laurentie ;Biology * ''Laurentia'' (moth), a moth genus of the family Pyralidae * '' Doxocopa laurentia'', a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae * '' Amaxia l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield ( ), also called the Laurentian Shield or the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the continental United States. Geographical extent The Canadian Shield is a physiographic division comprising four smaller physiographic provinces: the Laurentian Upland, Kazan Region, Davis and James. The shield extends into the United States as the Adirondack Mountains ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentian Shield
The Canadian Shield ( ), also called the Laurentian Shield or the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the continental United States. Geographical extent The Canadian Shield is a physiographic division comprising four smaller physiographic provinces: the Laurentian Upland, Kazan Region, Davis and James. The shield extends into the United States as the Adirondack Mountains (conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adirondack Mountains
The Adirondack Mountains ( ) are a massif of mountains in Northeastern New York which form a circular dome approximately wide and covering about . The region contains more than 100 peaks, including Mount Marcy, which is the highest point in New York at . The Adirondack High Peaks, a traditional list of 46 peaks over , are popular hiking destinations. There are over 200 named lakes with the number of smaller lakes, ponds, and other bodies of water reaching over 3,000. Among the named lakes around the mountains are Lake George, Lake Placid, and Lake Tear of the Clouds. The region has over of river. Although the mountains are formed from ancient rocks more than 1 billion years old, geologically, the mountains are relatively young and were created during recent periods of glaciation. Because of this, the Adirondacks have been referred to as "new mountains from old rocks." It is theorized that there is a hotspot beneath the region, which causes continued uplift at the rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of North America
The geology of North America is a subject of regional geology and covers the North American continent, the third-largest in the world. Geologic units and processes are investigated on a large scale to reach a synthesized picture of the geological development of the continent. The divisions of regional geology are drawn in different ways, but are usually outlined by a common geologic history, geographic vicinity or political boundaries. The regional geology of North America usually encompasses the geographic regions of Alaska, Canada, Greenland, the continental United States, Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. The parts of the North American Plate that are not occupied by North American countries are usually not discussed as part of the regional geology. The regions that are not geographically North American but reside on the North American Plate include parts of Siberia (see the Geology of Russia), and Geology of Iceland, Iceland, and Bermuda. A discussion of Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence (; 31 December 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, persecution of the Christians that the Roman Empire, Roman emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian ordered in 258. Life Lawrence is thought to have been born on 31 December AD 225, in Huesca (or less probably, in Valencia), the town from which his parents came in the later region of Aragon that was then part of the Roman province of Hispania Tarraconensis. The martyrs Orentius (Modern Spanish: ) and Patientia (Modern Spanish: ) are traditionally held to have been his parents.Sts. Orentius and Patientia Catholic Online Lawrence encountered the future Pope Sixtus II, a famous teacher born in Greece, in Caesa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suture (geology)
In structural geology, a suture is a joining along a major fault zone, of separate terranes, tectonic units that have different plate tectonic, metamorphic and paleogeographic histories. The suture is often represented on the surface by an orogen or mountain range. Overview In plate tectonics, sutures are the remains of subduction zones, and the terranes that are joined are interpreted as fragments of different palaeocontinents or tectonic plates. Outcrops of sutures can vary in width from a few hundred meters to a couple of kilometers. They can be networks of mylonitic shear zones or brittle fault zones, but are usually both. Sutures are usually associated with igneous intrusions and tectonic lenses with varying kinds of lithologies from plutonic rocks to ophiolitic fragments. An example from Great Britain is the Iapetus Suture which, though now concealed beneath younger rocks, has been determined by geophysical means to run along a line roughly parallel wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craton
A craton ( , , or ; from "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots extending several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: a continental '' shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, and a '' platform'' which o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
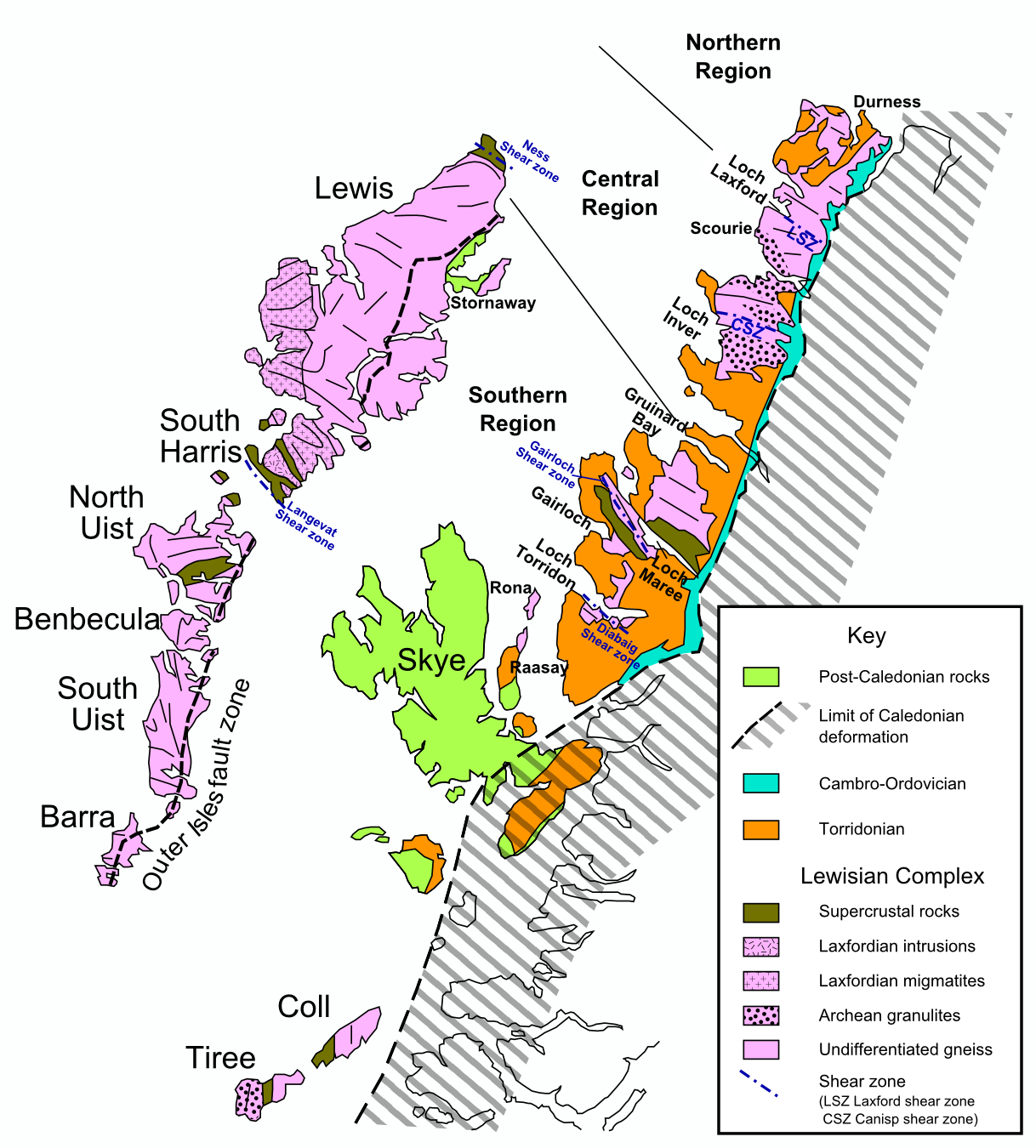
Hebridean Terrane
The Hebridean terrane is one of the terranes that form part of the Caledonian orogenic belt in northwest Scotland. Its boundary with the neighbouring Northern Highland terrane is formed by the Moine Thrust Belt. The basement is formed by Archaean and Paleoproterozoic gneisses of the Lewisian complex, unconformably overlain by the Neoproterozoic Torridonian sediments, which in turn are unconformably overlain by a sequence of Cambro–Ordovician sediments. It formed part of the Laurentian foreland during the Caledonian continental collision. Extent The Hebridean terrane forms the westernmost strip of mainland Scotland, most of the Inner Hebrides and all of the Outer Hebrides. Similar rocks are also thought to be present in Shetland and have been proved west and north of the Outer Hebrides by BGS shallow boreholes and hydrocarbon exploration wells. The full extent of this terrane to the west is obscured by the effects of Mesozoic rifting. Rock units Lewisian complex Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |