North America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
North America is a
 The Americas are usually accepted as having been named after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci by the German cartographers Martin Waldseemüller and Matthias Ringmann. Vespucci, who explored South America between 1497 and 1502, was the first
The Americas are usually accepted as having been named after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci by the German cartographers Martin Waldseemüller and Matthias Ringmann. Vespucci, who explored South America between 1497 and 1502, was the first
 The
The
Africa, America, Asia, Europe, and Oceania
). with North America a subcontinent). North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Before the Central American isthmus formed, the region had been underwater. The islands of the
Before the Central American isthmus formed, the region had been underwater. The islands of the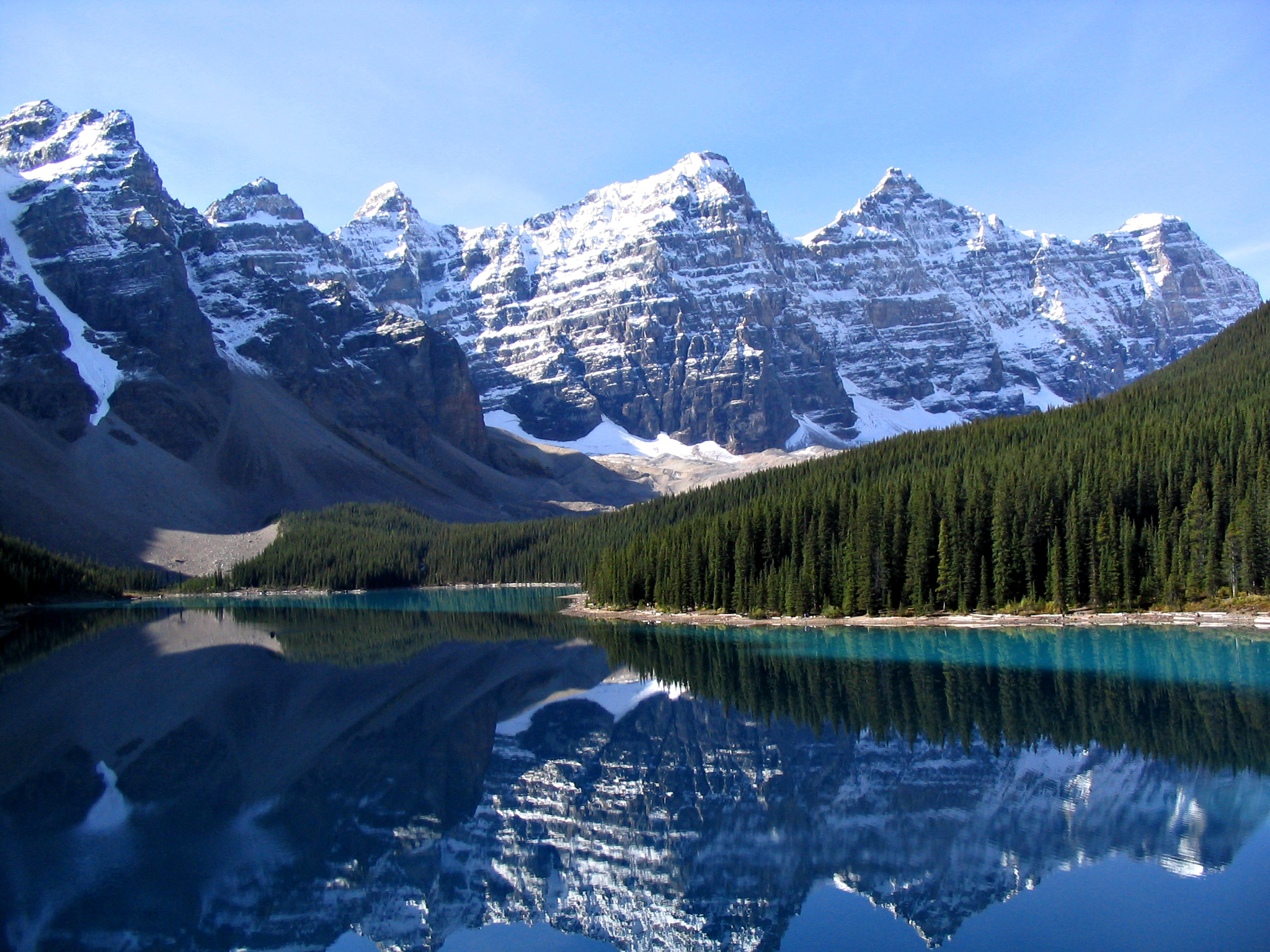  The vast majority of North America is on the North American Plate. Parts of western Mexico, including Baja California, and of
The vast majority of North America is on the North American Plate. Parts of western Mexico, including Baja California, and of  The western mountains are split in the middle into the main range of the Rockies and the coast ranges in California,
The western mountains are split in the middle into the main range of the Rockies and the coast ranges in California,
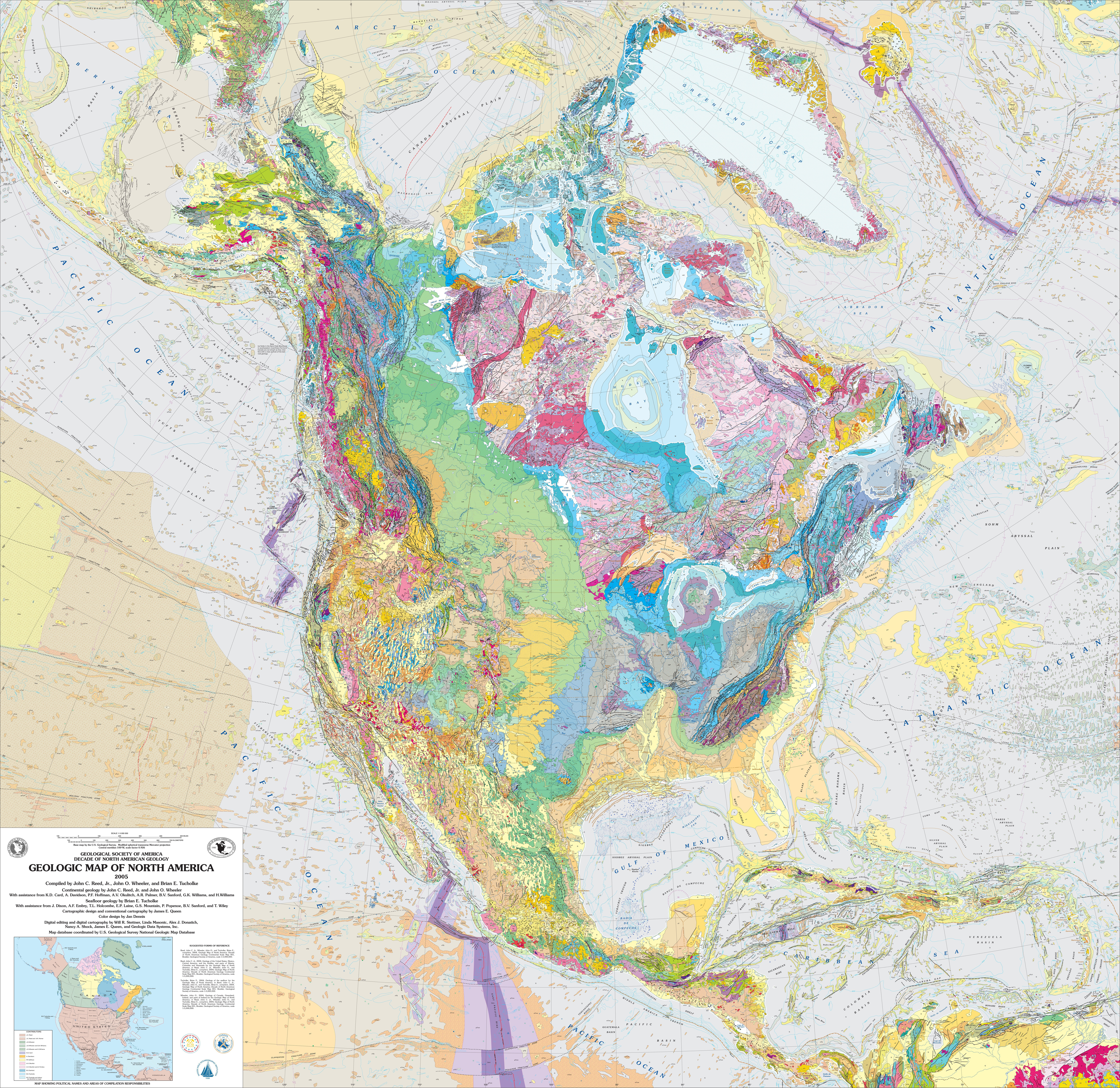
 Laurentia is an ancient craton which forms the geologic core of North America; it formed between 1.5 and 1.0 billion years ago during the
Laurentia is an ancient craton which forms the geologic core of North America; it formed between 1.5 and 1.0 billion years ago during the
 Geologically, Canada is one of the oldest regions in the world, with more than half of the region consisting of
Geologically, Canada is one of the oldest regions in the world, with more than half of the region consisting of
 Central America is geologically active with volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occurring from time to time. In 1976 Guatemala was hit by a major earthquake, killing 23,000 people; Managua, the capital of Nicaragua, was devastated by earthquakes in 1931 and 1972, the last one killing about 5,000 people; three earthquakes devastated El Salvador, one in 1986 and two in 2001; one
Central America is geologically active with volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occurring from time to time. In 1976 Guatemala was hit by a major earthquake, killing 23,000 people; Managua, the capital of Nicaragua, was devastated by earthquakes in 1931 and 1972, the last one killing about 5,000 people; three earthquakes devastated El Salvador, one in 1986 and two in 2001; one
 North America is a very large continent that extends from north of the Arctic Circle to south of the
North America is a very large continent that extends from north of the Arctic Circle to south of the
 The
The
 During the so-called
During the so-called
 Economically, Canada and the U.S. are the wealthiest and most developed nations in the continent, followed by Mexico, a newly industrialized country. The countries of Central America and the Caribbean are at various levels of economic and human development. For example, small Caribbean island-nations, such as Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and Antigua and Barbuda, have a higher GDP (PPP) per capita than Mexico due to their smaller populations. Panama and Costa Rica have a significantly higher
Economically, Canada and the U.S. are the wealthiest and most developed nations in the continent, followed by Mexico, a newly industrialized country. The countries of Central America and the Caribbean are at various levels of economic and human development. For example, small Caribbean island-nations, such as Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and Antigua and Barbuda, have a higher GDP (PPP) per capita than Mexico due to their smaller populations. Panama and Costa Rica have a significantly higher
 The dominant languages in North America are English, Spanish, and French. Danish is prevalent in Greenland alongside Greenlandic, and Dutch is spoken side by side local languages in the
The dominant languages in North America are English, Spanish, and French. Danish is prevalent in Greenland alongside Greenlandic, and Dutch is spoken side by side local languages in the

Greenland has a small population of 55,984 for its massive size (2,166,000 km2 or 836,300 mi2), and therefore, it has the world's lowest population density at 0.026 pop./km2 (0.067 pop./mi2). While the U.S., Canada, and Mexico maintain the largest populations, large city populations are not restricted to those nations. There are also large cities in the Caribbean. The largest cities in North America, by far, are Mexico City and New York. These cities are the only cities on the continent to exceed eight million, and two of three in the Americas. Next in size are Los Angeles,
 Canada shows significant growth in the sectors of services, mining and manufacturing. Canada's per capita GDP (PPP) was estimated at $44,656 and it had the 11th largest GDP (nominal) in 2014. Canada's services sector comprises 78% of the country's GDP (estimated in 2010), industry comprises 20% and agriculture comprises 2%. Mexico has a per capita GDP (PPP) of $16,111 and as of 2014 is the 15th largest GDP (nominal) in the world. Being a newly industrialized country, Mexico maintains both modern and outdated industrial and agricultural facilities and operations. Its main sources of income are oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, banking and financial services.
The North American economy is well defined and structured in three main economic areas. These areas are those under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), the
Canada shows significant growth in the sectors of services, mining and manufacturing. Canada's per capita GDP (PPP) was estimated at $44,656 and it had the 11th largest GDP (nominal) in 2014. Canada's services sector comprises 78% of the country's GDP (estimated in 2010), industry comprises 20% and agriculture comprises 2%. Mexico has a per capita GDP (PPP) of $16,111 and as of 2014 is the 15th largest GDP (nominal) in the world. Being a newly industrialized country, Mexico maintains both modern and outdated industrial and agricultural facilities and operations. Its main sources of income are oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, banking and financial services.
The North American economy is well defined and structured in three main economic areas. These areas are those under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), the  The Caribbean trade bloc (CARICOM) came into agreement in 1973 when it was signed by 15 Caribbean nations. As of 2000, CARICOM trade volume was US$96 billion. CARICOM also allowed for the creation of a common passport for associated nations. In the past decade the trade bloc focused largely on free-trade agreements and under the CARICOM Office of Trade Negotiations free-trade agreements have been signed into effect.
Integration of Central American economies occurred under the signing of the Central American Common Market agreement in 1961; this was the first attempt to engage the nations of this area into stronger financial cooperation. The 2006 implementation of the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) left the future of the CACM unclear. The Central American Free Trade Agreement was signed by five Central American countries, the Dominican Republic, and the U.S. The focal point of CAFTA is to create a free trade area similar to that of NAFTA. In addition to the U.S., Canada also has relations in Central American trade blocs.
These nations also take part in inter-continental trade blocs. Mexico takes a part in the
The Caribbean trade bloc (CARICOM) came into agreement in 1973 when it was signed by 15 Caribbean nations. As of 2000, CARICOM trade volume was US$96 billion. CARICOM also allowed for the creation of a common passport for associated nations. In the past decade the trade bloc focused largely on free-trade agreements and under the CARICOM Office of Trade Negotiations free-trade agreements have been signed into effect.
Integration of Central American economies occurred under the signing of the Central American Common Market agreement in 1961; this was the first attempt to engage the nations of this area into stronger financial cooperation. The 2006 implementation of the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) left the future of the CACM unclear. The Central American Free Trade Agreement was signed by five Central American countries, the Dominican Republic, and the U.S. The focal point of CAFTA is to create a free trade area similar to that of NAFTA. In addition to the U.S., Canada also has relations in Central American trade blocs.
These nations also take part in inter-continental trade blocs. Mexico takes a part in the
 The First Transcontinental Railroad in the U.S. was built in the 1860s, linking the railroad network of the eastern U.S. with California on the Pacific coast. Finished on 10 May 1869 at the famous golden spike event at Promontory Summit, Utah, it created a nationwide mechanized transportation network that revolutionized the population and economy of the
The First Transcontinental Railroad in the U.S. was built in the 1860s, linking the railroad network of the eastern U.S. with California on the Pacific coast. Finished on 10 May 1869 at the famous golden spike event at Promontory Summit, Utah, it created a nationwide mechanized transportation network that revolutionized the population and economy of the
 The cultures of North America are diverse. The .S. and English Canada have many cultural similarities, while French Canada has a distinct culture from Anglophone Canada, which is protected by law. Since the U.S. was formed from portions previously part of the Spanish Empire and then independent Mexico, and there has been considerable and continuing immigration of Spanish speakers from south of the U.S.–Mexico border. In the southwest of the U.S. there are many Hispanic cultural traditions and considerable bilingualism. Mexico and Central America are part of
The cultures of North America are diverse. The .S. and English Canada have many cultural similarities, while French Canada has a distinct culture from Anglophone Canada, which is protected by law. Since the U.S. was formed from portions previously part of the Spanish Empire and then independent Mexico, and there has been considerable and continuing immigration of Spanish speakers from south of the U.S.–Mexico border. In the southwest of the U.S. there are many Hispanic cultural traditions and considerable bilingualism. Mexico and Central America are part of
"MLS vs the major leagues: can soccer compete when it comes to big business?"
, Guardian.com, 12 March 2014. Canada has a separate
Houghton Mifflin Company, "North America"
* Interactive SVG version of Non-Native American Nations Control over N America 1750–2008 animation {{Authority control Continents
continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, th ...
. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
, to the southeast by South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
and the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
. Because it is on the North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
is included as a part of North America geographically.
North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and the fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography that studies spatial relationships between human communities, cultures, economies, and their interactions with the environment. It analyzes spatial interdependencies between social i ...
and in the English-speaking world
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest languag ...
outside the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, particularly in Canada, "North America" and "North American" can refer to just Canada and the United States together.
North America was reached by its first human populations during the Last Glacial Period, via crossing the Bering land bridge approximately 20,000 to 17,000 years ago. The so-called Paleo-Indian period is taken to have lasted until about 10,000 years ago (the beginning of the Archaic or Meso-Indian period). The classic stage spans roughly the 6th to 13th centuries. The first recorded Europeans to visit North America (other than Greenland) were the Norse around 1000 AD. Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
's arrival in 1492 sparked a transatlantic exchange which included migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
, African slaves
Slavery has historically been widespread in Africa. Systems of servitude and slavery were common in parts of Africa in ancient times, as they were in much of the rest of the ancient world. When the trans-Saharan slave trade, Indian Ocean sl ...
, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and the descendants of these groups.
Owing to Europe's colonization of the Americas, most North Americans speak European languages such as English, Spanish or French, and their cultures commonly reflect Western traditions. However, in parts of Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, there are indigenous populations continuing their cultural traditions and speaking native languages.
Name
 The Americas are usually accepted as having been named after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci by the German cartographers Martin Waldseemüller and Matthias Ringmann. Vespucci, who explored South America between 1497 and 1502, was the first
The Americas are usually accepted as having been named after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci by the German cartographers Martin Waldseemüller and Matthias Ringmann. Vespucci, who explored South America between 1497 and 1502, was the first Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an to suggest that the Americas were not the East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and aroun ...
, but a different landmass previously unknown by Europeans. In 1507, Waldseemüller produced a world map, in which he placed the word "America" on the continent of South America. What was known about the continent was referred to as ''Parias'' above what is today Mexico''.'' On a 1553 world map published by Petrus Apianus, North America was called ''Baccalearum'', meaning "realm of the Cod fish", in reference to the abundance of Cod fish on the east coast.
Waldseemüller used the Latinized version of Vespucci's name (Americus Vespucius), but in its feminine form "America", following the examples of "Europa", "Asia" and "Africa". Later mapmakers extended the name ''America'' to the northern continent. In 1538, Gerard Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represente ...
used ''America'' on his map of the world for the entire Western Hemisphere.
Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
on his map called North America "America or New India" (''America sive India Nova''). The Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
called its territories in North and South America "Las Indias"; the state body overseeing them was the Council of the Indies
The Council of the Indies ( es, Consejo de las Indias), officially the Royal and Supreme Council of the Indies ( es, Real y Supremo Consejo de las Indias, link=no, ), was the most important administrative organ of the Spanish Empire for the Am ...
.
Extent
 The
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
formally recognizes "North America" as comprising three areas: Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America (including the Caribbean and Central America).Gonzalez, Joseph. ...
, Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, and the Caribbean. This has been formally defined by the UN Statistics Division.
"Northern America", as a term distinct from "North America", excludes Central America, which itself may or may not include Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
. In the limited context of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), the term covers Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which are the three signatories of that treaty.
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, and the countries of Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
use a six-continent model, with the Americas viewed as a single continent and ''North America'' designating a subcontinent comprising Canada, the U.S., Mexico, and Saint Pierre et Miquelon (politically part of France), and often Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is ...
, and Bermuda
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, ...
.
North America has been historically referred to by other names. Spanish North America (New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
) was often referred to as ''Northern America
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America (including the Caribbean and Central America).Gonzalez, Joseph. ...
'', and this was the first official name given to Mexico.
Regions
Geographically, the North American continent has many regions and subregions. These include cultural, economic, and geographic regions. Economic regions included those formed by trade blocs, such as those of the NAFTA and Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA). Linguistically and culturally, the continent could be divided into Anglo-America and Latin America. Anglo-America includes most of Northern America,Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
, and Caribbean islands with English-speaking populations (though sub-national entities, such as Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a U.S. state, state in the Deep South and South Central United States, South Central regions of the United States. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-smal ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
, have large Francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the ...
populations; in Quebec, French is the sole official language).
The southern part of the North American continent is composed of two regions. These are Central America and the Caribbean. The north of the continent maintains recognized regions as well. In contrast to the common definition of "North America", which encompasses the whole continent, the term "North America" is sometimes used to refer only to Mexico, Canada, the U.S., and Greenland.
The term Northern America refers to the northernmost countries and territories of North America: the U.S., Bermuda, St. Pierre and Miquelon, Canada, and Greenland. Although the term does not refer to a unified region, Middle America—not to be confused with the Midwestern U.S.—groups the regions of Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean.
North America's largest countries by land area, Canada and the U.S., also have well-defined and recognized regions. In the case of Canada, these are (from east to west) Atlantic Canada, Central Canada
Central Canada (french: Centre du Canada, sometimes the Central provinces) is a region consisting of Canada's two largest and most populous provinces: Ontario and Quebec. Geographically, they are not at the centre of Canada but instead overlap ...
, Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie Provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These pro ...
, the British Columbia Coast
, settlement_type = Region of British Columbia
, image_skyline =
, nickname = "The Coast"
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 = British ...
, and Northern Canada. These regions also contain many subregions. In the case of the U.S.—and in accordance with the U.S. Census Bureau definitions—these regions are: New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
, Mid-Atlantic, South Atlantic states
The South Atlantic United States form one of the nine Census Bureau Division
This is a list of some of the ways ''regions'' is defined in the United States. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the federal government; others by ...
, East North Central states, West North Central states
The West North Central states form one of the nine geographic subdivisions within the United States that are officially recognized by the U.S. Census Bureau.
Seven states compose the division: Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North ...
, East South Central states, West South Central states, Mountain states, and Pacific states. Regions shared between both nations include the Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canada, Canadian–United States, American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York (state), New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania ...
. Megalopolises have formed between both nations in the case of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
and the Great Lakes Megaregion.
Countries, dependencies, and other territories
Natural characteristics
Geography
North America occupies the northern portion of the landmass generally referred to as the New World, theWestern Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, th ...
, the Americas, or simply America (which, in many countries is considered as a single continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven ...
The five rings of the Olympic flag represent the five inhabited, participating continentsAfrica, America, Asia, Europe, and Oceania
). with North America a subcontinent). North America is the third-largest continent by area, following
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. North America's only land connection to South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
is at the Isthmus of Darian/Isthmus of Panama. The continent is delimited on the southeast by most geographers at the Darién watershed along the Colombia-Panama border, placing almost all of Panama within North America. Alternatively, some geologists physiographically locate its southern limit at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico, with Central America extending southeastward to South America from this point. The Caribbean islands, or West Indies, are considered part of North America. The continental coastline is long and irregular. The Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
is the largest body of water indenting the continent, followed by Hudson Bay. Others include the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
, image = Baie de la Tour.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Gulf of St. Lawrence from Anticosti National Park, Quebec
, image_bathymetry = Golfe Saint-Laurent Depths fr.svg
, alt_bathymetry = Bathymetry ...
and the Gulf of California.
 Before the Central American isthmus formed, the region had been underwater. The islands of the
Before the Central American isthmus formed, the region had been underwater. The islands of the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Great ...
delineate a submerged former land bridge, which had connected North and South America via what are now Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in ...
.
There are numerous islands off the continent's coasts; principally, the Arctic Archipelago, the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archi ...
, Turks & Caicos, the Greater and Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
, the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin, "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, ...
(some of which are in the Eastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to po ...
proper), the Alexander Archipelago, the many thousand islands of the British Columbia Coast, and Newfoundland. Greenland, a self-governing Danish island, and the world's largest, is on the same tectonic plate (the North American Plate) and is part of North America geographically. In a geologic sense, Bermuda is not part of the Americas, but an oceanic island that was formed on the fissure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge over 100 million years ago (mya). The nearest landmass to it is Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape located at a pronounced bend in Hatteras Island, one of the barrier islands of North Carolina.
Long stretches of beach, sand dunes, marshes, and maritime forests create a unique environment where wind and waves shap ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia a ...
. However, Bermuda is often thought of as part of North America, especially given its historical, political and cultural ties to Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
and other parts of the continent.
 The vast majority of North America is on the North American Plate. Parts of western Mexico, including Baja California, and of
The vast majority of North America is on the North American Plate. Parts of western Mexico, including Baja California, and of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
, including the cities of San Diego
San Diego ( , ; ) is a city on the Pacific Ocean coast of Southern California located immediately adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a 2020 population of 1,386,932, it is the eighth most populous city in the United States ...
, Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the wor ...
, and Santa Cruz, lie on the eastern edge of the Pacific Plate, with the two plates meeting along the San Andreas fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly through California. It forms the tectonic boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate, and its motion is right-lateral strike-slip (horizontal) ...
. The southernmost portion of the continent and much of the West Indies lie on the Caribbean Plate, whereas the Juan de Fuca and Cocos plates border the North American Plate on its western frontier.
The continent can be divided into four great regions (each of which contains many subregions): the Great Plains stretching from the Gulf of Mexico to the Canadian Arctic; the geologically young, mountainous west, including the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
, the Great Basin, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
and Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
; the raised but relatively flat plateau of the Canadian Shield in the northeast; and the varied eastern region, which includes the Appalachian Mountains, the coastal plain along the Atlantic seaboard, and the Florida peninsula. Mexico, with its long plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
s and cordilleras, falls largely in the western region, although the eastern coastal plain does extend south along the Gulf.
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idah ...
, Washington, and British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
, with the Great Basin—a lower area containing smaller ranges and low-lying deserts—in between. The highest peak is Denali
Denali (; also known as Mount McKinley, its former official name) is the highest mountain peak in North America, with a summit elevation of above sea level. With a topographic prominence of and a topographic isolation of , Denali is the thi ...
in Alaska.
The U.S. Geographical Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and ...
(USGS) states that the geographic center of North America is "6 miles 0 kmwest of Balta, Pierce County, North Dakota" at about , about from Rugby, North Dakota. The USGS further states that "No marked or monumented point has been established by any government agency as the geographic center of either the 50 states, the conterminous United States, or the North American continent." Nonetheless, there is a field stone obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by An ...
in Rugby claiming to mark the center. The North American continental pole of inaccessibility is located from the nearest coastline, between Allen and Kyle, South Dakota at .
Geology
Geologic history
 Laurentia is an ancient craton which forms the geologic core of North America; it formed between 1.5 and 1.0 billion years ago during the
Laurentia is an ancient craton which forms the geologic core of North America; it formed between 1.5 and 1.0 billion years ago during the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
eon. The Canadian Shield is the largest exposure of this craton. From the Late Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
to Early Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Creta ...
eras, North America was joined with the other modern-day continents as part of the supercontinent Pangaea, with Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
to its east. One of the results of the formation of Pangaea was the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
, which formed some 480 mya, making it among the oldest mountain ranges in the world. When Pangaea began to rift around 200 mya, North America became part of Laurasia, before it separated from Eurasia as its own continent during the mid-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period. The Rockies and other western mountain ranges began forming around this time from a period of mountain building called the Laramide orogeny, between 80 and 55 mya. The formation of the Isthmus of Panama that connected the continent to South America arguably occurred approximately 12 to 15 mya, and the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
(as well as many other northern freshwater lakes and rivers) were carved by receding glaciers about 10,000 years ago.
North America is the source of much of what humanity knows about geologic time periods. The geographic area that would later become the United States has been the source of more varieties of dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s than any other modern country. According to paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of foss ...
Peter Dodson, this is primarily due to stratigraphy, climate and geography, human resources, and history. Much of the Mesozoic Era is represented by exposed outcrops in the many arid regions of the continent. The most significant Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987.
In European lithostratigraphy, the ...
dinosaur-bearing fossil deposit in North America is the Morrison Formation of the western U.S.
Canada
 Geologically, Canada is one of the oldest regions in the world, with more than half of the region consisting of
Geologically, Canada is one of the oldest regions in the world, with more than half of the region consisting of Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
rocks that have been above sea level since the beginning of the Palaeozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
era. Canada's mineral resources are diverse and extensive. Across the Canadian Shield and in the north there are large iron, nickel, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic t ...
, copper, gold, lead, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with le ...
, and uranium reserves. Large diamond concentrations have been recently developed in the Arctic, making Canada one of the world's largest producers. Throughout the Shield, there are many mining towns extracting these minerals. The largest, and best known, is Sudbury Sudbury may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sudbury Reef, Queensland
Canada
* Greater Sudbury, Ontario (official name; the city continues to be known simply as Sudbury for most purposes)
** Sudbury (electoral district), one of the city's federal e ...
, Ontario. Sudbury is an exception to the normal process of forming minerals in the Shield since there is significant evidence that the Sudbury Basin is an ancient meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object en ...
impact crater. The nearby, but less known Temagami Magnetic Anomaly has striking similarities to the Sudbury Basin. Its magnetic anomalies are very similar to the Sudbury Basin, and so it could be a second metal-rich impact crater. The Shield is also covered by vast boreal forests that support an important logging industry.
United States
The lower 48 U.S. states can be divided into roughly five physiographic provinces: # The American cordillera # The Canadian Shield Northern portion of the upper midwestern U.S. # The stable platform # The coastal plain # The Appalachian orogenic belt The geology ofAlaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
is typical of that of the cordillera, while the major islands of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
consist of Neogene volcanics
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic r ...
erupted over a hot spot
Hotspot, Hot Spot or Hot spot may refer to:
Places
* Hot Spot, Kentucky, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Hot Spot (comics), a name for the DC Comics character Isaiah Crockett
* Hot Spot (Tra ...
.
Central America
 Central America is geologically active with volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occurring from time to time. In 1976 Guatemala was hit by a major earthquake, killing 23,000 people; Managua, the capital of Nicaragua, was devastated by earthquakes in 1931 and 1972, the last one killing about 5,000 people; three earthquakes devastated El Salvador, one in 1986 and two in 2001; one
Central America is geologically active with volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occurring from time to time. In 1976 Guatemala was hit by a major earthquake, killing 23,000 people; Managua, the capital of Nicaragua, was devastated by earthquakes in 1931 and 1972, the last one killing about 5,000 people; three earthquakes devastated El Salvador, one in 1986 and two in 2001; one earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
devastated northern and central Costa Rica in 2009, killing at least 34 people; in Honduras a powerful earthquake killed seven people in 2009.
Volcanic eruptions are common in the region. In 1968 the Arenal Volcano, in Costa Rica, erupted and killed 87 people. Fertile soils from weathered volcanic lavas have made it possible to sustain dense populations in agriculturally productive highland areas.
Central America has many mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s; the longest are the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, the Cordillera Isabelia, and the Cordillera de Talamanca
The Cordillera de Talamanca is a mountain range that lies in the southeast half of Costa Rica and the far west of Panama. Much of the range and the area around it is included in La Amistad International Park, which also is shared between the two ...
. Between the mountain ranges lie fertile valleys that are suitable for the people; in fact, most of the population of Honduras, Costa Rica, and Guatemala live in valleys. Valleys are also suitable for the production of coffee, beans, and other crops.
Climate
Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, which is also referred to as the Northern Tropic, is the most northerly circle of latitude on Earth at which the Sun can be directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted tow ...
. Greenland, along with the Canadian Shield, is tundra with average temperatures ranging from , but central Greenland is composed of a very large ice sheet. This tundra radiates throughout Canada, but its border ends near the Rocky Mountains (but still contains Alaska) and at the end of the Canadian Shield, near the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five la ...
.
Climate west of the Cascade Range is described as being temperate weather with average precipitation .
Climate in coastal California is described to be Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
, with average temperatures in cities like San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of Ca ...
ranging from over the course of the year.
Stretching from the East Coast to eastern North Dakota, and stretching down to Kansas, is the humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
featuring intense seasons, with a large amount of annual precipitation, with places like New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the U ...
averaging .
Starting at the southern border of the humid continental climate and stretching to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
(whilst encompassing the eastern half of Texas) is the humid subtropical climate. This area has the wettest cities in the contiguous U.S., with annual precipitation reaching in Mobile, Alabama.
Stretching from the borders of the humid continental and subtropical climates, and going west to the Sierra Nevada, south to the southern tip of Durango
Durango (), officially named Estado Libre y Soberano de Durango ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Durango; Tepehuán: ''Korian''; Nahuatl: ''Tepēhuahcān''), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated i ...
, north to the border with tundra climate, the steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslan ...
/ desert climates are the driest in the United States. Highland climates cut from north to south of the continent, where subtropical or temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
s occur just below the tropics, as in central Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
and Guatemala. Tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the cool ...
s appear in the island
An island or isle is a piece of subcontinental land completely surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be ...
regions and in the subcontinent's bottleneck. Precipitation patterns vary across the region, and as such rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
, monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
, and savanna types can be found, with rains and high temperatures throughout the year. Found in countries and states bathed by the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
or to the south of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
.
Ecology
Notable North American fauna include thebison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North ...
, black bear, jaguar, cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large cat native to the Americas. Its range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. I ...
, prairie dog, turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, pronghorn, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight o ...
, coyote and monarch butterfly.
Notable plants that were domesticated in North America include tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ch ...
, maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
, squash, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , ...
, sunflower, blueberry, avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerica, Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Pre-Columb ...
, cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor p ...
, chile pepper
and vanilla.
History
Pre-Columbian
 The
The indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
have many creation myth
A creation myth (or cosmogonic myth) is a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop ...
s by which they assert that they have been present on the land since its creation, but there is no evidence that humans evolved there. The specifics of the initial settlement of the Americas
The settlement of the Americas began when Paleolithic hunter-gatherers entered North America from the North Asian Mammoth steppe via the Beringia land bridge, which had formed between northeastern Siberia and western Alaska due to the lower ...
by ancient Asians are subject to ongoing research and discussion. The traditional theory has been that hunters entered the Bering Land Bridge between eastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
and present-day Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
from 27,000 to 14,000 years ago. A growing viewpoint is that the first American inhabitants sailed from Beringia some 13,000 years ago, with widespread habitation of the Americas during the end of the Last Glacial Period, in what is known as the Late Glacial Maximum, around 12,500 years ago. The oldest petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s in North America date from 15,000 to 10,000 years before present. Genetic research and anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
indicate additional waves of migration from Asia via the Bering Strait during the Early-Middle Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
.
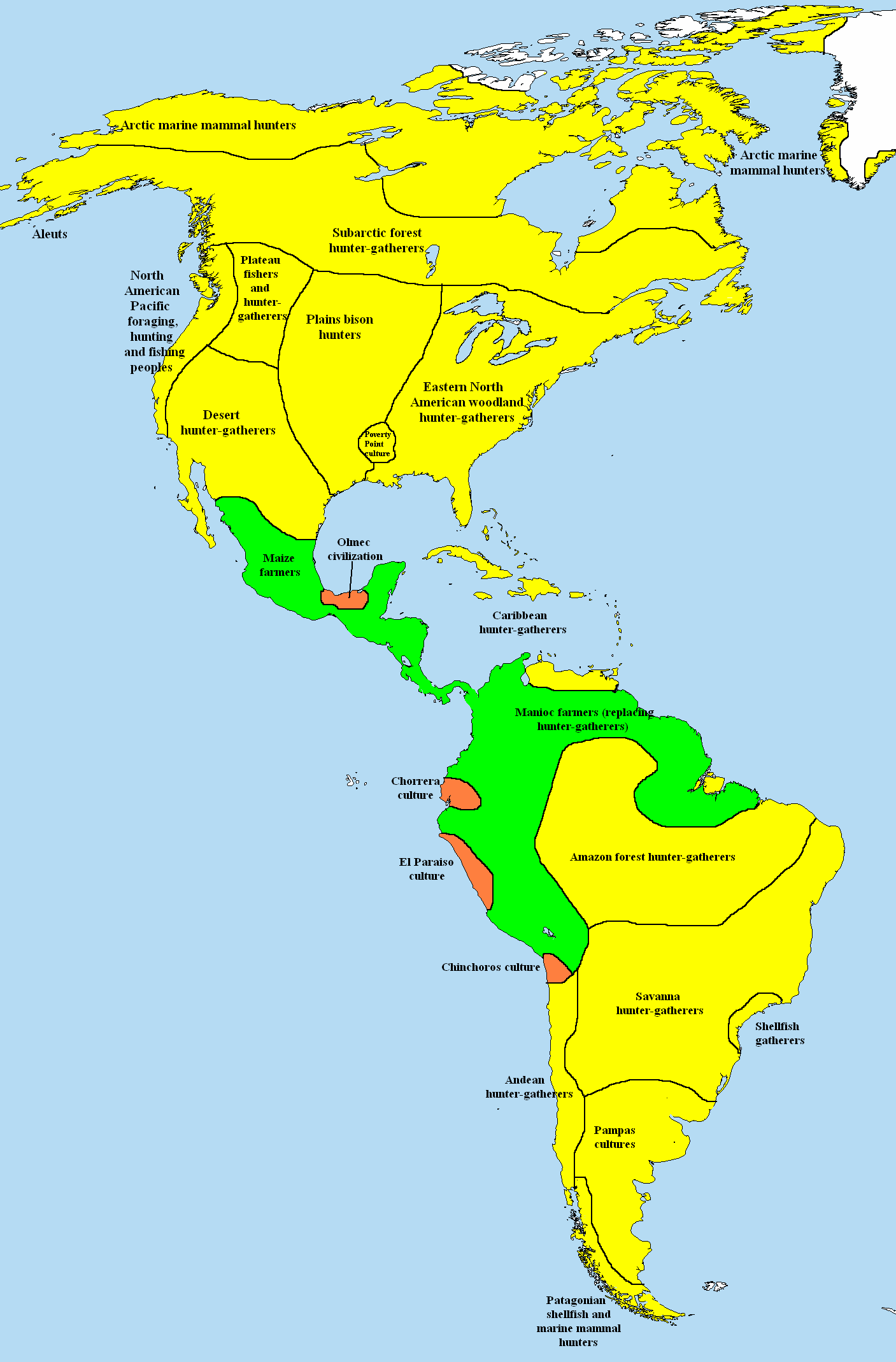
Before contact with Europeans, the natives of North America were divided into many different polities, from small bands of a few families to large empires. They lived in several " culture areas", which roughly correspond to geographic and biological zones and give a good indication of the main way of life of the people who lived there (e.g., the bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North ...
hunters of the Great Plains, or the farmers of Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
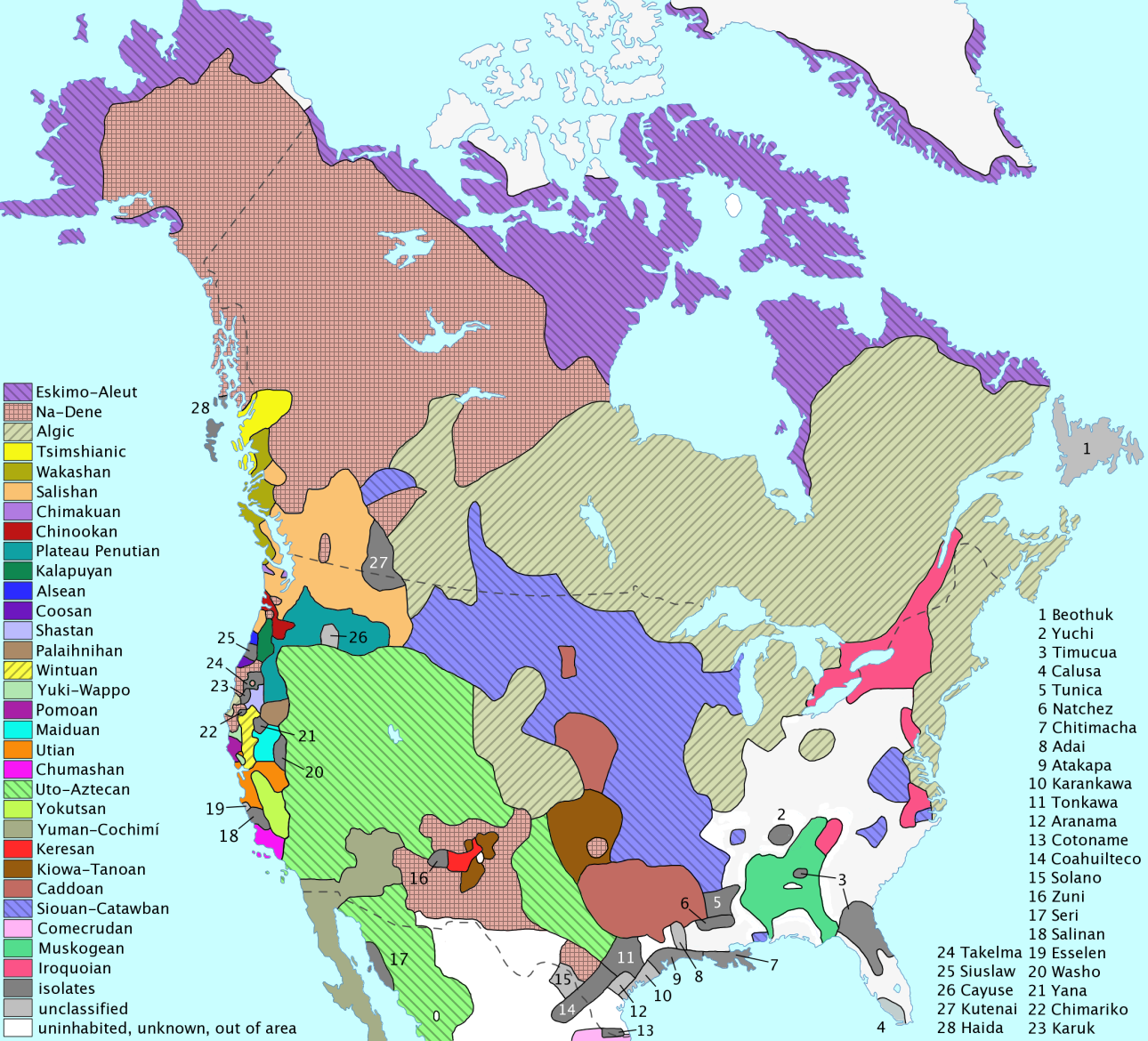
). Native groups can also be classified by their language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in his ...
(e.g., Athapascan or ). Peoples with similar languages did not always share the same material culture
Material culture is the aspect of social reality grounded in the objects and architecture that surround people. It includes the usage, consumption, creation, and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms, and rituals that the objects crea ...
, nor were they always allies. Anthropologists think that the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, ...
of the high Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada ( Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm ( Greenland), Finland, Iceland ...
came to North America much later than other native groups, as evidenced by the disappearance of Dorset culture artifacts from the archaeological record
The archaeological record is the body of physical (not written) evidence about the past. It is one of the core concepts in archaeology, the academic discipline concerned with documenting and interpreting the archaeological record. Archaeological ...
, and their replacement by the Thule people.
During the thousands of years of native habitation on the continent, cultures changed and shifted. One of the oldest yet discovered is the Clovis culture (c. 9550–9050 BCE) in modern New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
. Later groups include the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, ear ...
and related Mound building cultures, found in the Mississippi river
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
valley and the Pueblo culture
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, ...
of what is now the Four Corners. The more southern cultural groups of North America were responsible for the domestication
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
of many common crops now used around the world, such as tomatoes, squash, and maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
. As a result of the development of agriculture in the south, many other cultural advances were made there. The Mayans developed a writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable for ...
, built huge pyramids and temples, had a complex calendar, and developed the concept of zero around 400 CE.
The first recorded European references to North America are in Norse sagas where it is referred to as Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland ( non, Vínland ᚠᛁᚾᛚᛅᚾᛏ) was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and Jo ...
. The earliest verifiable instance of pre-Columbian trans-oceanic contact by any European culture with the North America mainland has been dated to around 1000 CE. The site, situated at the northernmost extent of the island named Newfoundland, has provided unmistakable evidence of Norse
Norse is a demonym for Norsemen, a medieval North Germanic ethnolinguistic group ancestral to modern Scandinavians, defined as speakers of Old Norse from about the 9th to the 13th centuries.
Norse may also refer to:
Culture and religion
* Nor ...
settlement. Norse explorer Leif Erikson
Leif Erikson, Leiv Eiriksson, or Leif Ericson, ; Modern Icelandic: ; Norwegian: ''Leiv Eiriksson'' also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to have set foot on continental Nort ...
(c. 970–1020 CE) is thought to have visited the area. Erikson was the first European to make landfall on the continent (excluding Greenland).
The Mayan culture was still present in southern Mexico and Guatemala when the Spanish conquistadors arrived, but political dominance in the area had shifted to the Aztec Empire, whose capital city Tenochtitlan was located further north in the Valley of Mexico. The Aztecs were conquered in 1521 by Hernán Cortés.Bernard Grunberg, ''"La folle aventure d'Hernan Cortés''", in '' L'Histoire'' n°322, July–August 2007
Post-contact, 1492–1910
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
, Europeans explored overseas and staked claims to various parts of North America, much of which was already settled by indigenous peoples. Upon Europeans' arrival in the "New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
", indigenous peoples had a variety of reactions, including curiosity, trading, cooperation, resignation, and resistance. The indigenous population declined substantially following European arrival, primarily due to the introduction of Eurasian diseases, such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
, to which the indigenous peoples lacked immunity, and because of violent conflicts with Europeans. Indigenous culture changed significantly and their affiliation with political and cultural groups also changed. Several linguistic groups died out, and others changed quite quickly.
On the southern eastcoast of North America, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León (, , , ; 1474 – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Florida and for serving as the first governor of Puerto Rico. He was born in Santerv ...
, who had accompanied Columbus's second voyage, visited and named in 1513 '' La Florida''. As the colonial period unfolded, Spain, England, and France appropriated and claimed extensive territories in North America eastern and southern coastlines. Spain established permanent settlements on the Caribbean islands of Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and t ...
and Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
in the 1490s, building cities, putting the resident indigenous populations to work, raising crops for Spanish settlers and panning gold to enrich the Spaniards. Much of the indigenous population died due to disease and overwork, spurring the Spaniards on the claim new lands and peoples. An expedition under the command of Spanish settler, Hernán Cortés, sailed westward in 1519 to what turned out to be the mainland in Mexico. With local indigenous allies, the Spanish conquered the Aztec empire in central Mexico in 1521. Spain then established permanent cities in Mexico, Central America, and Spanish South America in the sixteenth century. Once Spaniards conquered the high civilization of the Aztecs and Incas, the Caribbean was a backwater of the Spanish empire.
Other European powers began to intrude on areas that Spain had claimed, including the Caribbean islands. France took the western half of Hispaniola and developed Saint-Domingue as a cane sugar producing colony worked by black slave labor. Britain took Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate ...
and Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispan ...
; the Dutch and Danes also took islands previous claimed by Spain. Britain did not begin settling on the North American mainland until a hundred years after the first Spanish settlements, since it sought first to control nearby Ireland. The first permanent English settlement was in Jamestown, Virginia in 1607, and then further settler colonial establishments on the east coast of the continent from is now Georgia up to Massachusetts, forming the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th cent ...
. The English did not establish settlements north, east of the St. Lawrence Valley in what would become Canada until well after the war of independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which resi ...
. English early permanent settlements were St. John's, Newfoundland in 1630 and Halifax, Nova Scotia
Halifax is the capital and largest municipality of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the largest municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of the 2021 Census, the municipal population was 439,819, with 348 ...
in 1749. The first permanent French settlement was in Quebec City, Quebec in 1608. In the British victory the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754– ...
, France ceded to Britain its claims east of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it ...
in 1763. Spain gained rights to the territories west of Mississippi now acting as a border. French so-called "colonists" that had first settled the Illinois Country after several generations of experience on the new continent migrated over the Mississippi in the absence of Spanish occupants while leveraging earlier Louisiana French settlements around the Gulf of Mexico. These early French settlers partnering with midwest indigenous tribes and their mixed ancestry descendants would precede the westward push and guide through waves of followers all the way to the Pacific.
In the late 18th and early the Thirteen Colonies on the North Atlantic coast declared independence in 1776, fighting a protracted war of independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which resi ...
with the aid of Britain's enemies France and Spain, becoming the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territor ...
. The new nation steadily attempted to increase its territory. By that time, Russians were already well established on the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
northern coastline with Maritime Fur Trade
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in e ...
activities supported by active settlements. As a result, Spanish were showing more interest in controlling the trade on the Pacific coast and mapped most of its coastline. The first Spanish settlements were attempted in Alta California during that period. Numerous overland explorations associated with Voyageurs, Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mo ...
, and U.S. led expeditions (e.g. Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* " Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohe ...
, Fremont and Wilkes) were reaching the Pacific at various latitudes around the turn of the century. In 1803 Napoleon Bonaparte sold France's remaining claims in North America, west of the Mississippi River, to the U.S., in a deal named the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
. Spain and the U.S. settled their western boundary dispute in 1819 in the Adams-Onís Treaty. Mexico fought a lengthy war for independence from Spain, winning it for Mexico and Central American in 1821. The U.S. sought further westward expansion and fought the Mexican-American War, gaining a vast territory that first Spain and then Mexico claimed but which they did not effectively control. Much of the area was in fact dominated by indigenous peoples, which did not recognize the claims of Spain, France, or the U.S.. Russia sold its North American claims, which included Alaska, to the U.S. in 1867. Also in 1867, settler colonies in eastern North America, were unified as the dominion of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
. The U.S. sought to dig a canal across the Isthmus of Panama, a part of Colombia, and aided Panamanians in a war to separate it from Colombia. The U.S. carved out the Panama Canal Zone
The Panama Canal Zone ( es, Zona del Canal de Panamá), also simply known as the Canal Zone, was an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the Isthmus of Panama, that existed from 1903 to 1979. It was located within the terr ...
, over which it claimed sovereignty. After decades of work on the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a Channel ( ...
was completed, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific oceans in 1913.
Demographics
 Economically, Canada and the U.S. are the wealthiest and most developed nations in the continent, followed by Mexico, a newly industrialized country. The countries of Central America and the Caribbean are at various levels of economic and human development. For example, small Caribbean island-nations, such as Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and Antigua and Barbuda, have a higher GDP (PPP) per capita than Mexico due to their smaller populations. Panama and Costa Rica have a significantly higher
Economically, Canada and the U.S. are the wealthiest and most developed nations in the continent, followed by Mexico, a newly industrialized country. The countries of Central America and the Caribbean are at various levels of economic and human development. For example, small Caribbean island-nations, such as Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, and Antigua and Barbuda, have a higher GDP (PPP) per capita than Mexico due to their smaller populations. Panama and Costa Rica have a significantly higher Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, Education Index, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the Educational system, education system), ...
and GDP than the rest of the Central American nations. Additionally, despite Greenland's vast resources in oil and minerals, much of them remain untapped, and the island is economically dependent on fishing, tourism, and subsidies from Denmark. Nevertheless, the island is highly developed.
Demographically, North America is ethnically diverse. Its three main groups are Whites, Mestizo
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
s and Blacks. There is a significant minority of Indigenous Americans and Asians among other less numerous groups.
Languages
 The dominant languages in North America are English, Spanish, and French. Danish is prevalent in Greenland alongside Greenlandic, and Dutch is spoken side by side local languages in the
The dominant languages in North America are English, Spanish, and French. Danish is prevalent in Greenland alongside Greenlandic, and Dutch is spoken side by side local languages in the Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-w ...
. The term Anglo-America is used to refer to the anglophone
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest langua ...
countries of the Americas: namely Canada (where English and French are co-official) and the U.S., but also sometimes Belize and parts of the tropics, especially the Commonwealth Caribbean. Latin America refers to the other areas of the Americas (generally south of the U.S.) where the Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language fa ...
s, derived from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
, of Spanish and Portuguese, (but French-speaking countries are not usually included) predominate: the other republics of Central America (but not always Belize), part of the Caribbean (not the Dutch-, English-, or French-speaking areas), Mexico, and most of South America (except Guyana, Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
, French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic ...
rance and the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubou ...
K.
The French language has historically played a significant role in North America and now retains a distinctive presence in some regions. Canada is officially bilingual. French is the official language of the Province of Quebec, where 95% of the people speak it as either their first or second language, and it is co-official with English in the Province of New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic Canad ...
. Other French-speaking locales include the Province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
(the official language is English, but there are an estimated 600,000 Franco-Ontarians), the Province of Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Win ...
(co-official as ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legall ...
'' with English), the French West Indies
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloup ...
and Saint-Pierre et Miquelon, as well as the U.S. state of Louisiana, where French is also an official language. Haiti is included with this group based on historical association but Haitians speak both Creole and French. Similarly, French and French Antillean Creole is spoken in Saint Lucia and the Commonwealth of Dominica alongside English.
A significant number of Indigenous languages are spoken in North America, with 372,000 people in the U.S. speaking an indigenous language at home, about 225,000 in Canada and roughly 6 million in Mexico. In the U.S. and Canada, there are approximately 150 surviving indigenous languages of the 300 spoken prior to European contact.
Religions
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
is the largest religion in the U.S., Canada and Mexico. According to a 2012 Pew Research Center survey, 77% of the population considered themselves Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. Christianity also is the predominant religion in the 23 dependent territories in North America. The U.S. has the largest Christian population in the world, with nearly 247 million Christians (70%), although other countries have higher percentages of Christians among their populations. Mexico has the world's second largest number of Catholics, surpassed only by Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. A 2015 study estimates about 493,000 Christian believers from a Muslim background in North America, most of them belonging to some form of Protestantism.
According to the same study, the religiously unaffiliated (including agnostics and atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
s) make up about 17% of the population of Canada and the U.S. Those with no religious affiliation make up about 24% of the U.S. population, and 24% of Canada's total population.
Canada, the U.S. and Mexico host communities of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
(6 million or about 1.8%), Buddhists (3.8 million or 1.1%) and Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
(3.4 million or 1.0%). The largest number of Jews can be found in the U.S. (5.4 million), Canada (375,000) and Mexico (67,476). The U.S. hosts the largest Muslim population in North America with 2.7 million or 0.9%, While Canada host about one million Muslim or 3.2% of the population. While in Mexico there were 3,700 Muslims in the country. In 2012, '' U-T San Diego'' estimated U.S. practitioners of Buddhism at 1.2 million people, of whom 40% are living in Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban ...
.
The predominant religion in Mexico and Central America is Christianity (96%). Beginning with the Spanish colonization of Mexico in the 16th century, Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
was the only religion permitted by Spanish crown and Catholic church. A vast campaign of religious conversion, the so-called "spiritual conquest", was launched to bring indigenous into the Christian fold. The Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
was established to assure orthodox belief and practice. The Catholic Church remained an important institution, so that even after political independence, Roman Catholicism remained the dominant religion. Since the 1960s, there has been an increase in other Christian groups, particularly Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, as well as other religious organizations, and individuals identifying themselves as having no religion. Also Christianity is the predominant religion in the Caribbean (85%). Other religious groups in the region are Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global po ...
, Islam, Rastafari
Rastafari, sometimes called Rastafarianism, is a religion that developed in Jamaica during the 1930s. It is classified as both a new religious movement and a social movement by scholars of religion. There is no central authority in control ...
(in Jamaica), and Afro-American religions such as Santería
Santería (), also known as Regla de Ocha, Regla Lucumí, or Lucumí, is an African diasporic religion that developed in Cuba during the late 19th century. It arose through a process of syncretism between the traditional Yoruba religion of We ...
and Vodou.
Populace
North America is the fourth most populous continent after Asia, Africa, andEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
. Its most populous country is the U.S. with 329.7 million persons. The second largest country is Mexico with a population of 112.3 million. Canada is the third most populous country with 37.0 million. The majority of Caribbean island-nations have national populations under a million, though Cuba, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Puerto Rico (a territory of the U.S.), Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago each have populations higher than a million. Note: An exchange rate of 1 CUC to US$1.08 was used to convert GDPGreenland has a small population of 55,984 for its massive size (2,166,000 km2 or 836,300 mi2), and therefore, it has the world's lowest population density at 0.026 pop./km2 (0.067 pop./mi2). While the U.S., Canada, and Mexico maintain the largest populations, large city populations are not restricted to those nations. There are also large cities in the Caribbean. The largest cities in North America, by far, are Mexico City and New York. These cities are the only cities on the continent to exceed eight million, and two of three in the Americas. Next in size are Los Angeles,
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most pop ...
, Chicago, Havana, Santo Domingo, and Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
. Cities in the Sun Belt regions of the U.S., such as those in Southern California and Houston
Houston (; ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas, the Southern United States#Major cities, most populous city in the Southern United States, the List of United States cities by population, fourth-most pop ...
, Phoenix, Miami, Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,71 ...
, and Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish language, Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the List of United States cities by population, 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the U.S. state, state of Neva ...
, are experiencing rapid growth. These causes included warm temperatures, retirement of Baby Boomers, large industry, and the influx of immigrants. Cities near the U.S. border, particularly in Mexico, are also experiencing large amounts of growth. Most notable is Tijuana
Tijuana ( ,"Tijuana"
(US) and < ...
, a city bordering San Diego that receives immigrants from all over Latin America and parts of Europe and Asia. Yet as cities grow in these warmer regions of North America, they are increasingly forced to deal with the major issue of water shortages.
Eight of the top ten metropolitan areas are located in the U.S. These metropolitan areas all have a population of above 5.5 million and include the New York City metropolitan area, (US) and < ...
Los Angeles metropolitan area
Greater Los Angeles is the second-largest urban area, metropolitan region in the United States with a population of 18.5 million in 2021, encompassing five counties in Southern California extending from Ventura County in the west to San Ber ...
, Chicago metropolitan area
The Chicago metropolitan area, also colloquially referred to as Chicagoland, is a metropolitan area in the Midwestern United States. Encompassing 10,286 sq mi (28,120 km2), the metropolitan area includes the city of Chicago, its suburbs and hi ...
, and the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex
The Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, officially designated Dallas–Fort Worth–Arlington by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget, is a conurbated metropolitan statistical area in the U.S. state of Texas encompassing 11 counties and ancho ...
. Whilst the majority of the largest metropolitan areas are within the U.S., Mexico is host to the largest metropolitan area by population in North America: Greater Mexico City. Canada also breaks into the top ten largest metropolitan areas with the Toronto metropolitan area
The Greater Toronto Area, commonly referred to as the GTA, includes the City of Toronto and the regional municipalities of Durham, Halton, Peel, and York. In total, the region contains 25 urban, suburban, and rural municipalities. The Greater T ...
having six million people. The proximity of cities to each other on the Canada–U.S. border and Mexico–U.S. border has led to the rise of international metropolitan areas. These urban agglomerations
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, t ...
are observed at their largest and most productive in Detroit–Windsor and San Diego–Tijuana and experience large commercial, economic, and cultural activity. The metropolitan areas are responsible for millions of dollars of trade dependent on international freight. In Detroit-Windsor the Border Transportation Partnership study in 2004 concluded US$13 billion was dependent on the Detroit–Windsor international border crossing while in San Diego-Tijuana freight at the Otay Mesa Port of Entry was valued at US$20 billion.
North America has also been witness to the growth of megapolitan areas. In the U.S. exists eleven megaregions that transcend international borders and comprise Canadian and Mexican metropolitan regions. These are the Arizona Sun Corridor, Cascadia, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, a ...
, Front Range
The Front Range is a mountain range of the Southern Rocky Mountains of North America located in the central portion of the U.S. State of Colorado, and southeastern portion of the U.S. State of Wyoming. It is the first mountain range encountere ...
, Great Lakes Megalopolis, Gulf Coast, Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, Northern California
Northern California (colloquially known as NorCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Spanning the state's northernmost 48 counties, its main population centers incl ...
, Piedmont Atlantic, Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban ...
, and the Texas Triangle. Canada and Mexico are also the home of megaregions. These include the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, Golden Horseshoe—both of which are considered part of the Great Lakes Megalopolis—and the Central Mexico megalopolis
The Mexico City megalopolis, also known as the Megalopolis of Central Mexico ( es, link=no, Corona regional del centro de México), is a megalopolis containing Greater Mexico City and surrounding metropolitan areas.
In 1996, the first proposed t ...
. Traditionally the largest megaregion has been considered the Boston-Washington, DC Corridor, or the Northeast, as the region is one massive contiguous area. Yet megaregion criterion have allowed the Great Lakes Megalopolis to maintain status as the most populated region, being home to 53,768,125 people in 2000.Regional Plan Association (2008). ''America 2050: An Infrastructure Vision for 21st Century America''. New York: Regional Plan Association.
The top ten largest North American metropolitan areas by population as of 2013, based on national census numbers from the U.S. and census estimates from Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tota ...
and Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
.
†2011 Census figures
Economy
North America's GDP per capita was evaluated in October 2016 by theInternational Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster gl ...
(IMF) to be $41,830, making it the richest continent in the world, followed by Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
.
Canada, Mexico, and the U.S. have significant and multifaceted economic systems. The U.S. has the largest economy of all three countries and in the world. In 2016, the U.S. had an estimated per capita gross domestic product (PPP) of $57,466 according to the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, and is the most technologically developed economy of the three. The U.S.'s services sector comprises 77% of the country's GDP (estimated in 2010), industry comprises 22% and agriculture comprises 1.2%. The U.S. economy is also the fastest growing economy in North America and the Americas as a whole, with the highest GDP per capita in the Americas as well.
 Canada shows significant growth in the sectors of services, mining and manufacturing. Canada's per capita GDP (PPP) was estimated at $44,656 and it had the 11th largest GDP (nominal) in 2014. Canada's services sector comprises 78% of the country's GDP (estimated in 2010), industry comprises 20% and agriculture comprises 2%. Mexico has a per capita GDP (PPP) of $16,111 and as of 2014 is the 15th largest GDP (nominal) in the world. Being a newly industrialized country, Mexico maintains both modern and outdated industrial and agricultural facilities and operations. Its main sources of income are oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, banking and financial services.
The North American economy is well defined and structured in three main economic areas. These areas are those under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), the
Canada shows significant growth in the sectors of services, mining and manufacturing. Canada's per capita GDP (PPP) was estimated at $44,656 and it had the 11th largest GDP (nominal) in 2014. Canada's services sector comprises 78% of the country's GDP (estimated in 2010), industry comprises 20% and agriculture comprises 2%. Mexico has a per capita GDP (PPP) of $16,111 and as of 2014 is the 15th largest GDP (nominal) in the world. Being a newly industrialized country, Mexico maintains both modern and outdated industrial and agricultural facilities and operations. Its main sources of income are oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, banking and financial services.
The North American economy is well defined and structured in three main economic areas. These areas are those under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), the Caribbean Community and Common Market
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organization that is a political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) throughout the Caribbean. They have primary objectives to promote econom ...
(CARICOM), and the Central American Common Market (CACM). Of these trade blocs, the U.S. takes part in two. In addition to the larger trade blocs there is the Canada-Costa Rica Free Trade Agreement among numerous other free-trade relations, often between the larger, more developed countries and Central American and Caribbean countries.
The NAFTA forms one of the four largest trade blocs in the world. Its implementation in 1994 was designed for economic homogenization with hopes of eliminating barriers of trade and foreign investment between Canada, the U.S. and Mexico. While Canada and the U.S. already conducted the largest bilateral trade relationship—and to present day still do—in the world and Canada–U.S. trade relations already allowed trade without national taxes and tariffs, NAFTA allowed Mexico to experience a similar duty-free trade. The free-trade agreement allowed for the elimination of tariffs that had previously been in place on U.S.–Mexico trade. Trade volume has steadily increased annually and in 2010, surface trade between the three NAFTA nations reached an all-time historical increase of 24.3% or US$791 billion. The NAFTA trade bloc GDP (PPP) is the world's largest with US$17.617 trillion. This is in part attributed to the fact that the economy of the U.S. is the world's largest national economy; the country had a nominal GDP of approximately $14.7 trillion in 2010. The countries of NAFTA are also some of each other's largest trade partners. The U.S. is the largest trade partner of Canada and Mexico, while Canada and Mexico are each other's third largest trade partners. In 2018, the NAFTA was replaced by the U.S.–Mexico–Canada Agreement.
 The Caribbean trade bloc (CARICOM) came into agreement in 1973 when it was signed by 15 Caribbean nations. As of 2000, CARICOM trade volume was US$96 billion. CARICOM also allowed for the creation of a common passport for associated nations. In the past decade the trade bloc focused largely on free-trade agreements and under the CARICOM Office of Trade Negotiations free-trade agreements have been signed into effect.
Integration of Central American economies occurred under the signing of the Central American Common Market agreement in 1961; this was the first attempt to engage the nations of this area into stronger financial cooperation. The 2006 implementation of the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) left the future of the CACM unclear. The Central American Free Trade Agreement was signed by five Central American countries, the Dominican Republic, and the U.S. The focal point of CAFTA is to create a free trade area similar to that of NAFTA. In addition to the U.S., Canada also has relations in Central American trade blocs.
These nations also take part in inter-continental trade blocs. Mexico takes a part in the
The Caribbean trade bloc (CARICOM) came into agreement in 1973 when it was signed by 15 Caribbean nations. As of 2000, CARICOM trade volume was US$96 billion. CARICOM also allowed for the creation of a common passport for associated nations. In the past decade the trade bloc focused largely on free-trade agreements and under the CARICOM Office of Trade Negotiations free-trade agreements have been signed into effect.
Integration of Central American economies occurred under the signing of the Central American Common Market agreement in 1961; this was the first attempt to engage the nations of this area into stronger financial cooperation. The 2006 implementation of the Central American Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) left the future of the CACM unclear. The Central American Free Trade Agreement was signed by five Central American countries, the Dominican Republic, and the U.S. The focal point of CAFTA is to create a free trade area similar to that of NAFTA. In addition to the U.S., Canada also has relations in Central American trade blocs.
These nations also take part in inter-continental trade blocs. Mexico takes a part in the G3 Free Trade Agreement
The G-3 was a free trade agreement between Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela that came into effect on January 1, 1995, which created an extended market of 149 million consumers with a combined GDP (Gross domestic product) of US$486.5 billion. The ag ...
with Colombia and Venezuela and has a trade agreement with the EU. The U.S. has proposed and maintained trade agreements under the Transatlantic Free Trade Area
A Transatlantic Free Trade Agreement (TAFTA) is a proposal to create a free-trade agreement covering Europe and North America, on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Such proposals have been made since the 1990s. Between 2013 and about 2017 an agree ...
between itself and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
; the U.S.–Middle East Free Trade Area between numerous Middle Eastern nations and itself; and the Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership between Southeast Asian nations, Australia, and New Zealand.
Transport
ThePan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway (french: (Auto)route panaméricaine/transaméricaine; pt, Rodovia/Auto-estrada Pan-americana; es, Autopista/Carretera/Ruta Panamericana) is a network of roads stretching across the Americas and measuring about in ...
route in the Americas is the portion of a network of roads nearly in length which travels through the mainland nations. No definitive length of the Pan-American Highway exists because the U.S. and Canadian governments have never officially defined any specific routes as being part of the Pan-American Highway, and Mexico officially has many branches connecting to the U.S. border. However, the total length of the portion from Mexico to the northern extremity of the highway is roughly .
 The First Transcontinental Railroad in the U.S. was built in the 1860s, linking the railroad network of the eastern U.S. with California on the Pacific coast. Finished on 10 May 1869 at the famous golden spike event at Promontory Summit, Utah, it created a nationwide mechanized transportation network that revolutionized the population and economy of the
The First Transcontinental Railroad in the U.S. was built in the 1860s, linking the railroad network of the eastern U.S. with California on the Pacific coast. Finished on 10 May 1869 at the famous golden spike event at Promontory Summit, Utah, it created a nationwide mechanized transportation network that revolutionized the population and economy of the American West
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
, catalyzing the transition from the wagon train
''Wagon Train'' is an American Western series that aired 8 seasons: first on the NBC television network (1957–1962), and then on ABC (1962–1965). ''Wagon Train'' debuted on September 18, 1957, and became number one in the Nielsen ratings ...
s of previous decades to a modern transportation system. Although an accomplishment, it achieved the status of first transcontinental railroad by connecting myriad eastern U.S. railroads to the Pacific and was not the largest single railroad system in the world. The Canadian Grand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; french: Grand Tronc) was a railway system that operated in the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the American states of Connecticut, Maine, Michigan, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont. The rai ...
had, by 1867, already accumulated more than of track by connecting Ontario with the Canadian Atlantic provinces west as far as Port Huron, Michigan
Port Huron is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of St. Clair County. The population was 30,184 at the 2010 census. The city is adjacent to Port Huron Township but is administered separately.
Located along the St. Clair ...
, through Sarnia, Ontario.
Communications
A shared telephone system known as theNorth American Numbering Plan
The North American Numbering Plan (NANP) is a telephone numbering plan for twenty-five regions in twenty countries, primarily in North America and the Caribbean. This group is historically known as World Zone 1 and has the international calling ...
(NANP) is an integrated telephone numbering plan
A telephone numbering plan is a type of numbering scheme used in telecommunication to assign telephone numbers to subscriber telephones or other telephony endpoints. Telephone numbers are the addresses of participants in a telephone network, re ...
of 24 countries and territories: the U.S. and its territories, Canada, Bermuda, and 17 Caribbean nations.
Culture
 The cultures of North America are diverse. The .S. and English Canada have many cultural similarities, while French Canada has a distinct culture from Anglophone Canada, which is protected by law. Since the U.S. was formed from portions previously part of the Spanish Empire and then independent Mexico, and there has been considerable and continuing immigration of Spanish speakers from south of the U.S.–Mexico border. In the southwest of the U.S. there are many Hispanic cultural traditions and considerable bilingualism. Mexico and Central America are part of
The cultures of North America are diverse. The .S. and English Canada have many cultural similarities, while French Canada has a distinct culture from Anglophone Canada, which is protected by law. Since the U.S. was formed from portions previously part of the Spanish Empire and then independent Mexico, and there has been considerable and continuing immigration of Spanish speakers from south of the U.S.–Mexico border. In the southwest of the U.S. there are many Hispanic cultural traditions and considerable bilingualism. Mexico and Central America are part of Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
and are culturally distinct from anglophone and francophone North America. However, they share with the United States the establishment of post-independence governments that are federated representative republics with written constitutions dating from their founding as nations. Canada is a federated parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy.
Canada's constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
dates to 1867, with confederation, in the British North America Act, but not until 1982 did Canada have the power to amend its own constitution. Canada's Francophone heritage has been enshrined in law since the British parliament passed the Quebec Act of 1774. In contrast to largely Protestant Anglo settlers in North America, French-speaking Canadians were Catholic and with the Quebec Act were guaranteed freedom to practice their religion, restored the right of the Catholic Church to impose tithes for its support, and established French civil law in most circumstances.
The distinctiveness of French language and culture has been codified in Canadian law, so that both English and French are designated official languages. The U.S. has no official language, but its national language is English.
The Canadian government took action to protect Canadian culture by limiting non- Canadian content in broadcasting, creating the Canadian Radio and Telecommunications Commission
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC; french: Conseil de la radiodiffusion et des télécommunications canadiennes, links=) is a public organization in Canada with mandate as a regulatory agency for broadcasti ...
to monitor Canadian content. In Quebec, the provincial government established the Quebec Office of the French Language
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen ...
, often called the "language police" by Anglophones, which mandates the use of French terminology and signage in French. Since 1968 the unicameral legislature has been called the Quebec National Assembly. Saint-Jean-Baptiste Day, 24 June, is the national holiday of Quebec and celebrated by francophone Canadians throughout Canada. In Quebec, the school system was divided into Catholic and Protestant, so-called confessional schools. Anglophone education in Quebec has been increasingly undermined.
Latino culture
Latin American culture is the formal or informal expression of the people of Latin America and includes both high culture (literature and high art) and popular culture (music, folk art, and dance), as well as religion and other customary practices. ...
is strong in the southwest of the U.S., as well as Florida, which draws Latin Americans from many countries in the hemisphere. Northern Mexico, particularly in the cities of Monterrey
Monterrey ( , ) is the capital and largest city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León, Mexico, and the third largest city in Mexico behind Guadalajara and Mexico City. Located at the foothills of the Sierra Madre Oriental, the city is ancho ...
, Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, and Mexicali, is strongly influenced by the culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these grou ...
and way of life of the U.S. Monterrey, a modern city with a significant industrial group, has been regarded as the most Americanized city in Mexico. Northern Mexico, the Western U.S. and Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada share a cowboy culture.
The Anglophone Caribbean states have witnessed and participated in the decline of the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
and its influence on the region, and its replacement by the economic influence of Northern America in the Anglophone Caribbean. This is partly due to the relatively small populations of the English-speaking Caribbean countries, and also because many of them now have more people living abroad than those remaining at home.
Greenland has experienced many immigration waves from Northern Canada, e .g. the Thule people. Therefore, Greenland shares some cultural ties with the indigenous peoples of Canada. Greenland is also considered Nordic and has strong Danish ties due to centuries of colonization by Denmark.
Popular culture – sports
The U.S. and Canada have major sports teams that compete against each other, including baseball, basketball, hockey, and soccer/football. Canada, Mexico and the U.S. submitted a joint bid to host the 2026 FIFA World Cup. The following table shows the most prominent sports leagues in North America, in order of average revenue., Guardian.com, 12 March 2014.
Canadian Football League
The Canadian Football League (CFL; french: Ligue canadienne de football—LCF) is a professional sports league in Canada. The CFL is the highest level of competition in Canadian football. The league consists of nine teams, each located in a ...
from the U.S. teams.
The Native American game of lacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensi ...
is considered a national sport in Canada. Curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
is an important winter sport in Canada, and the Winter Olympics includes it in the roster. The English sport of cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
is popular in parts of anglophone Canada and very popular in parts of the former British empire, but in Canada is considered a minor sport. Boxing is also a major sport in some countries, such as Mexico, Panama and Puerto Rico, and it's considered one of the main individual sports in the U.S.
See also
*Flags of North America
This is a gallery of flags of North American countries, territories and their affiliated international organizations.
International organizations
Intercontinental organizations
Intracontinental organizations
Flags of North American sove ...
* List of cities in North America
* North American Union
* Outline of North America
* Table manners in North America
Table manners are the cultural customs and rules of etiquette used while dining. As in other areas of North American etiquette, the rules governing appropriate table manners have changed over time and may differ depending on the setting (e.g. di ...
References
Footnotes
Citations
External links
Houghton Mifflin Company, "North America"
* Interactive SVG version of Non-Native American Nations Control over N America 1750–2008 animation {{Authority control Continents