testa (botany) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Angiosperm seeds are "enclosed seeds", produced in a hard or fleshy structure called a fruit that encloses them for protection. Some fruits have layers of both hard and fleshy material. In gymnosperms, no special structure develops to enclose the seeds, which begin their development "naked" on the bracts of cones. However, the seeds do become covered by the
Angiosperm seeds are "enclosed seeds", produced in a hard or fleshy structure called a fruit that encloses them for protection. Some fruits have layers of both hard and fleshy material. In gymnosperms, no special structure develops to enclose the seeds, which begin their development "naked" on the bracts of cones. However, the seeds do become covered by the
 After fertilization, the ovules develop into the seeds. The ovule consists of a number of components:
* The funicle (''funiculus, funiculi'') or seed stalk which attaches the ovule to the
After fertilization, the ovules develop into the seeds. The ovule consists of a number of components:
* The funicle (''funiculus, funiculi'') or seed stalk which attaches the ovule to the
 The main components of the embryo are:
* The
The main components of the embryo are:
* The

 A typical seed includes two basic parts:
# an
A typical seed includes two basic parts:
# an

 The seed coat develops from the maternal tissue, the
The seed coat develops from the maternal tissue, the
 Seeds are very diverse in size. The dust-like orchid seeds are the smallest, with about one million seeds per gram; they are often embryonic seeds with immature embryos and no significant energy reserves. Orchids and a few other groups of plants are mycoheterotrophs which depend on
Seeds are very diverse in size. The dust-like orchid seeds are the smallest, with about one million seeds per gram; they are often embryonic seeds with immature embryos and no significant energy reserves. Orchids and a few other groups of plants are mycoheterotrophs which depend on

 * Some seeds (e.g.,
* Some seeds (e.g.,
 Seed germination is a process by which a seed embryo develops into a seedling. It involves the reactivation of the metabolic pathways that lead to growth and the emergence of the radicle or seed root and plumule or shoot. The emergence of the seedling above the soil surface is the next phase of the plant's growth and is called seedling establishment.
Three fundamental conditions must exist before germination can occur. (1) The embryo must be alive, called seed viability. (2) Any dormancy requirements that prevent germination must be overcome. (3) The proper environmental conditions must exist for germination.
Far red light can prevent germination.
Seed viability is the ability of the embryo to germinate and is affected by a number of different conditions. Some plants do not produce seeds that have functional complete embryos, or the seed may have no embryo at all, often called empty seeds. Predators and pathogens can damage or kill the seed while it is still in the fruit or after it is dispersed. Environmental conditions like flooding or heat can kill the seed before or during germination. The age of the seed affects its health and germination ability: since the seed has a living embryo, over time cells die and cannot be replaced. Some seeds can live for a long time before germination, while others can only survive for a short period after dispersal before they die.
Seed vigor is a measure of the quality of seed, and involves the viability of the seed, the germination percentage, germination rate, and the strength of the seedlings produced.
The germination percentage is simply the proportion of seeds that germinate from all seeds subject to the right conditions for growth. The germination rate is the length of time it takes for the seeds to germinate. Germination percentages and rates are affected by seed viability, dormancy and environmental effects that impact on the seed and seedling. In agriculture and horticulture quality seeds have high viability, measured by germination percentage plus the rate of germination. This is given as a percent of germination over a certain amount of time, 90% germination in 20 days, for example. 'Dormancy' is covered above; many plants produce seeds with varying degrees of dormancy, and different seeds from the same fruit can have different degrees of dormancy. It's possible to have seeds with no dormancy if they are dispersed right away and do not dry (if the seeds dry they go into physiological dormancy). There is great variation amongst plants and a dormant seed is still a viable seed even though the germination rate might be very low.
Environmental conditions affecting seed germination include; water, oxygen, temperature and light.
Three distinct phases of seed germination occur: water imbibition; lag phase; and
Seed germination is a process by which a seed embryo develops into a seedling. It involves the reactivation of the metabolic pathways that lead to growth and the emergence of the radicle or seed root and plumule or shoot. The emergence of the seedling above the soil surface is the next phase of the plant's growth and is called seedling establishment.
Three fundamental conditions must exist before germination can occur. (1) The embryo must be alive, called seed viability. (2) Any dormancy requirements that prevent germination must be overcome. (3) The proper environmental conditions must exist for germination.
Far red light can prevent germination.
Seed viability is the ability of the embryo to germinate and is affected by a number of different conditions. Some plants do not produce seeds that have functional complete embryos, or the seed may have no embryo at all, often called empty seeds. Predators and pathogens can damage or kill the seed while it is still in the fruit or after it is dispersed. Environmental conditions like flooding or heat can kill the seed before or during germination. The age of the seed affects its health and germination ability: since the seed has a living embryo, over time cells die and cannot be replaced. Some seeds can live for a long time before germination, while others can only survive for a short period after dispersal before they die.
Seed vigor is a measure of the quality of seed, and involves the viability of the seed, the germination percentage, germination rate, and the strength of the seedlings produced.
The germination percentage is simply the proportion of seeds that germinate from all seeds subject to the right conditions for growth. The germination rate is the length of time it takes for the seeds to germinate. Germination percentages and rates are affected by seed viability, dormancy and environmental effects that impact on the seed and seedling. In agriculture and horticulture quality seeds have high viability, measured by germination percentage plus the rate of germination. This is given as a percent of germination over a certain amount of time, 90% germination in 20 days, for example. 'Dormancy' is covered above; many plants produce seeds with varying degrees of dormancy, and different seeds from the same fruit can have different degrees of dormancy. It's possible to have seeds with no dormancy if they are dispersed right away and do not dry (if the seeds dry they go into physiological dormancy). There is great variation amongst plants and a dormant seed is still a viable seed even though the germination rate might be very low.
Environmental conditions affecting seed germination include; water, oxygen, temperature and light.
Three distinct phases of seed germination occur: water imbibition; lag phase; and
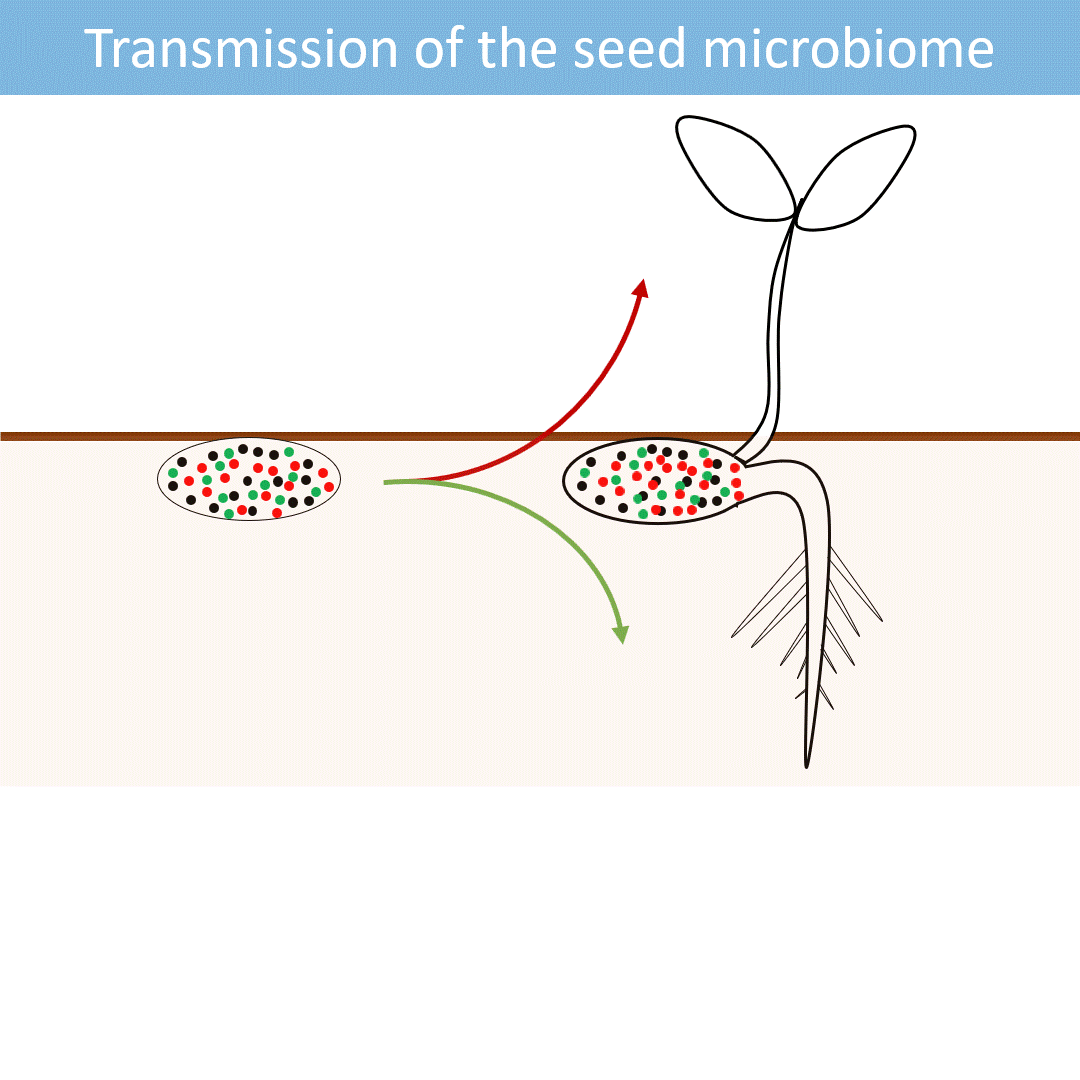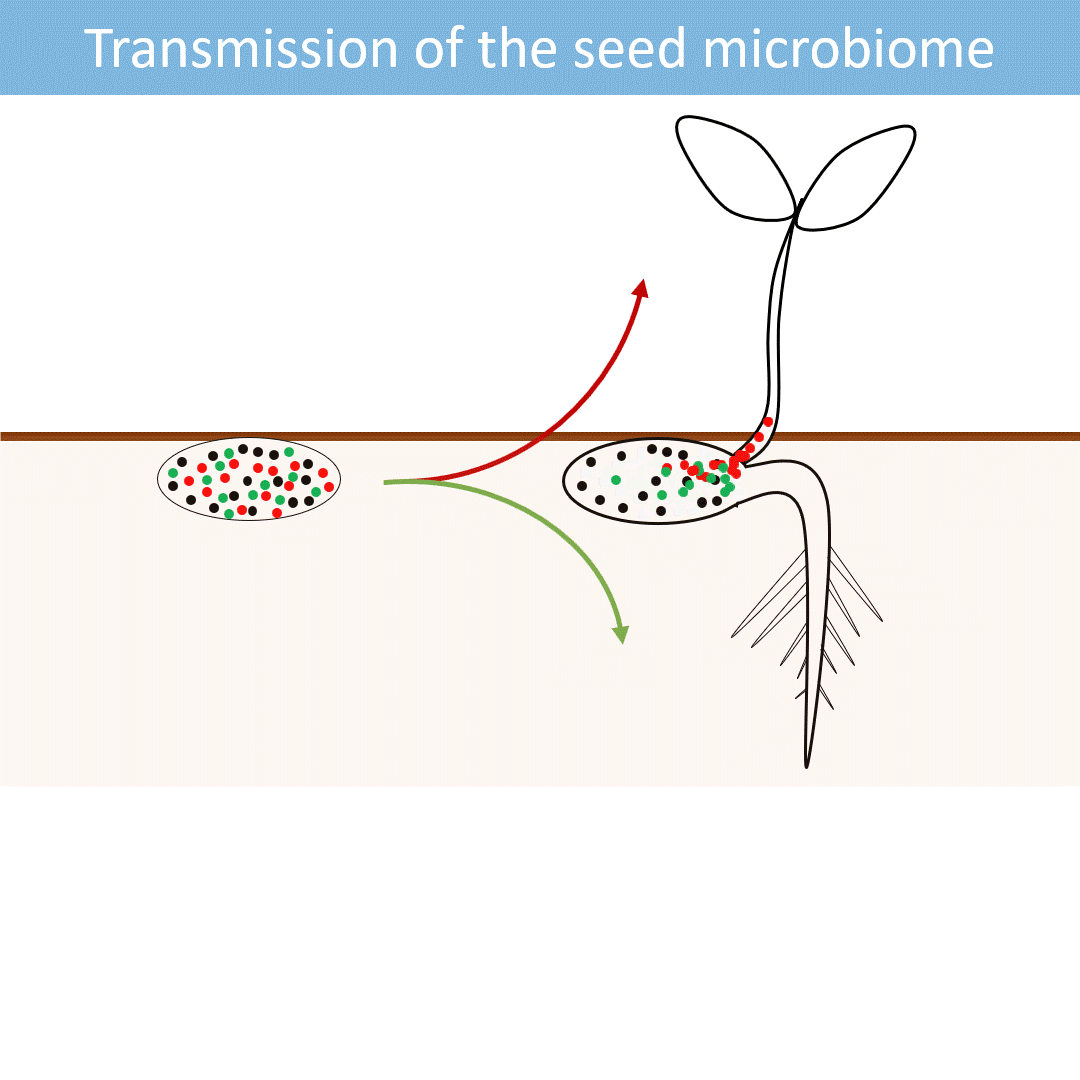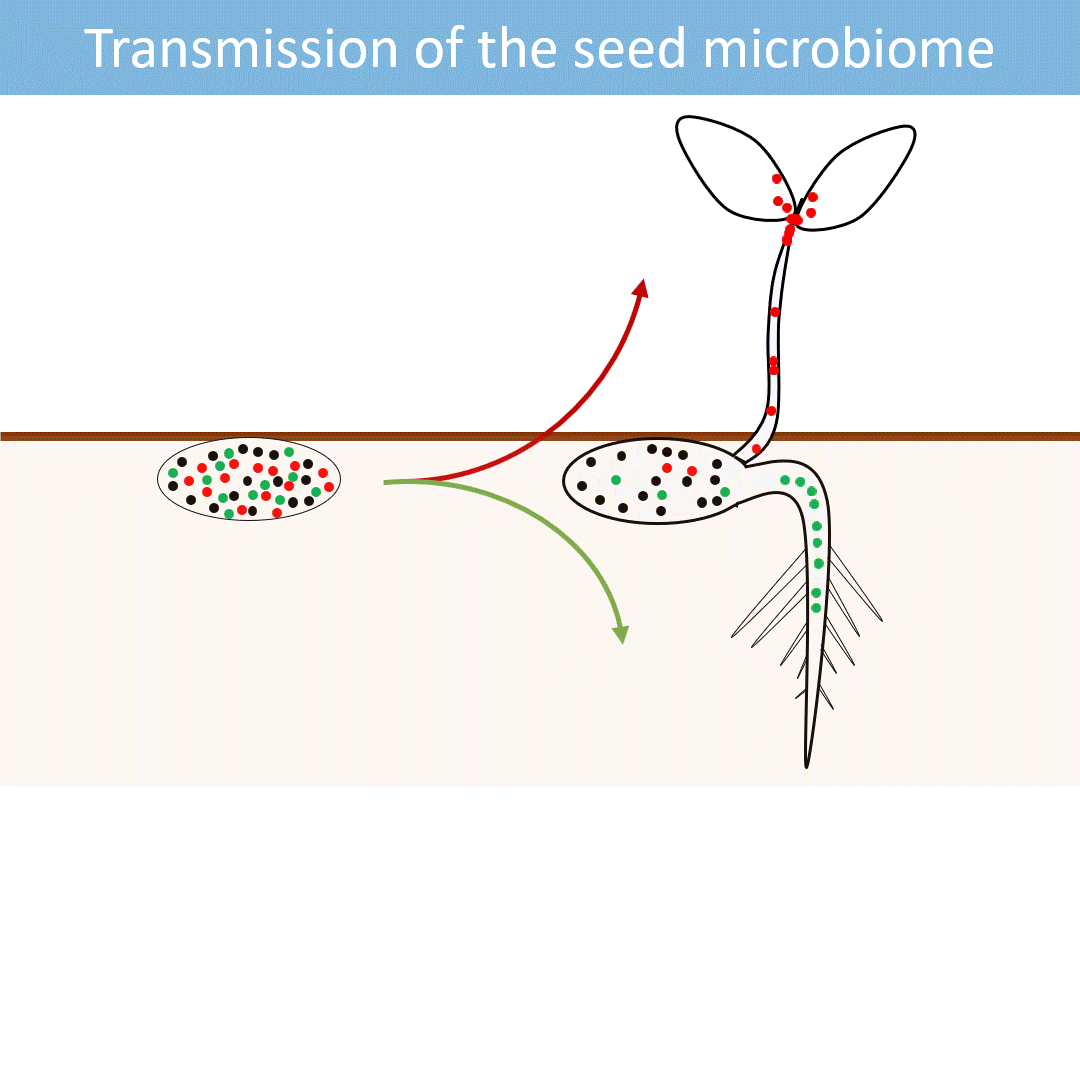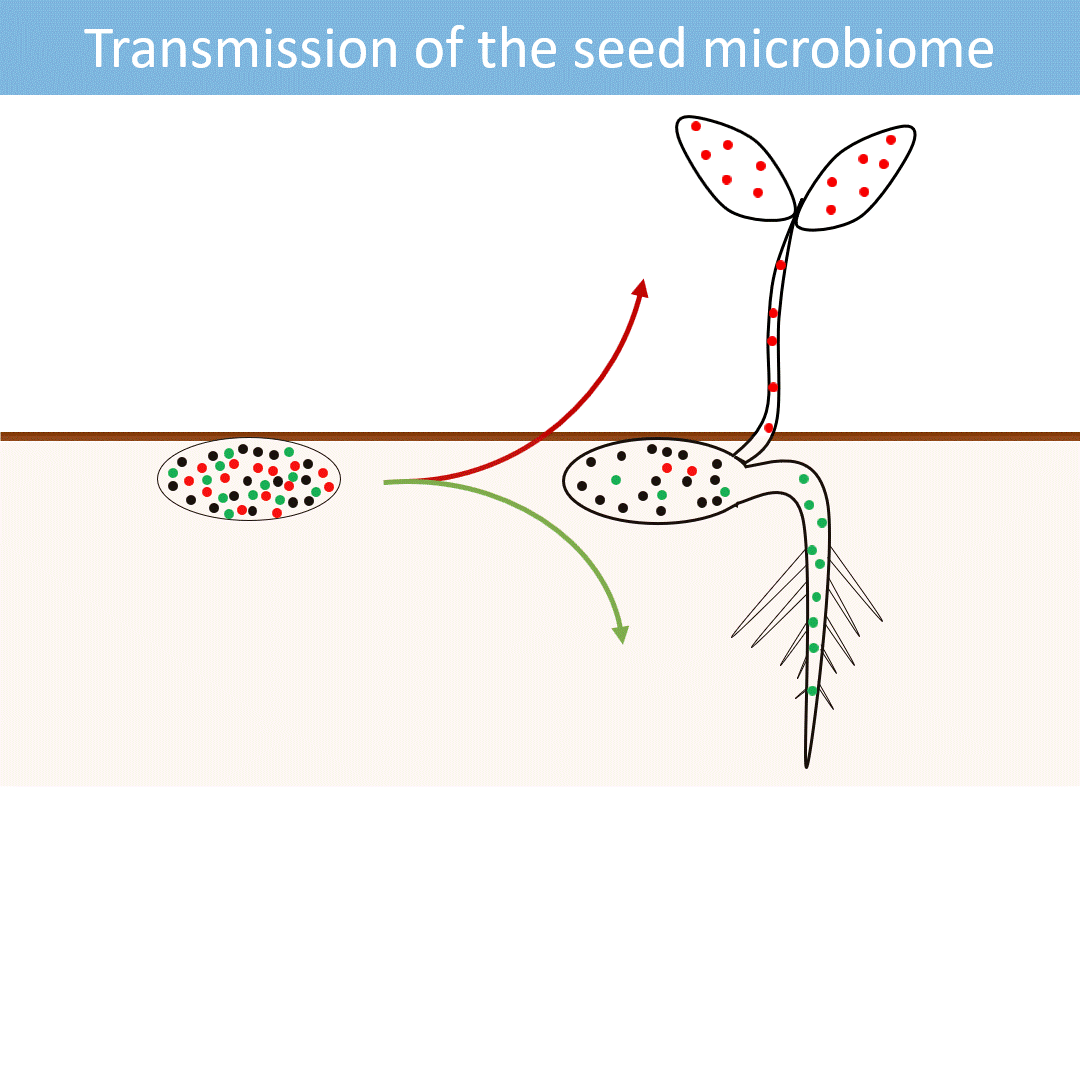 Seeds harbor a diverse microbial community. Most of these microorganisms are transmitted from the seed to the developing seedlings.
Seeds harbor a diverse microbial community. Most of these microorganisms are transmitted from the seed to the developing seedlings.

 * The oldest viable
* The oldest viable
A.C. Martin. The Comparative Internal Morphology of Seeds. American Midland Naturalist Vol. 36, No. 3 (Nov., 1946), pp. 513–660
M.B. McDonald, Francis Y. Kwong (eds.). Flower Seeds: Biology and Technology. CABI, 2005.
Edred John Henry Corner. The Seeds of Dicotyledons. Cambridge University Press, 1976.
United States Forest Service. Woody Plant Seed Manual. 1948
Stuppy, W. Glossary of Seed and Fruit Morphological Terms. Royal botanical gardens, Kew 2004
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070528090503/http://www.kew.org/msbp/ The Millennium Seed Bank ProjectKew Garden's ambitious preservation project
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault
– a backup facility for the world's seed banks
Plant Physiology online: Types of Seed Dormancy and the Roles of Environmental Factors
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20141218084446/http://theseedsite.co.uk/ The Seed Site collecting, storing, sowing, germinating, and exchanging seeds, with pictures of seeds, seedpods and seedlings.
Plant Fix: Check out various plant seeds and learn more information about them
{{Authority control Botany Plant reproduction Plant sexuality
botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be sown, which may include seed and husk
Husk (or hull) in botany is the outer shell or coating of a seed. In the United States, the term husk often refers to the leafy outer covering of an Ear (botany), ear of maize (corn) as it grows on the plant. Literally, a husk or hull includes t ...
or tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure that plants use as storage organs for nutrients, derived from stems or roots. Tubers help plants perennate (survive winter or dry months), provide energy and nutrients, and are a means of asexual reproduc ...
. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the sporangium, megasporangium), ...
, after the embryo sac
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the fe ...
is fertilized
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a zygote and initiate its development into a new individual organism or off ...
by sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
from pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
, forming a zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted.
The formation of the seed is the defining part of the process of reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
in seed plants (spermatophytes
A seed plant or spermatophyte (; New Latin ''spermat-'' and Greek ' (phytón), plant), also known as a phanerogam (taxon Phanerogamae) or a phaenogam (taxon Phaenogamae), is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte (i.e. la ...
). Other plants such as fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s, moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryo ...
es and liverworts
Liverworts are a group of non-vascular plant, non-vascular embryophyte, land plants forming the division Marchantiophyta (). They may also be referred to as hepatics. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in wh ...
, do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological niches on land, from forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
s to grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
s both in hot and cold climates.
In the flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s, the ovary ripens into a fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
which contains the seed and serves to disseminate it. Many structures commonly referred to as "seeds" are actually dry fruits. Sunflower seeds are sometimes sold commercially while still enclosed within the hard wall of the fruit, which must be split open to reach the seed. Different groups of plants have other modifications, the so-called stone fruits (such as the peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
) have a hardened fruit layer (the endocarp
Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits.
Fruitlike structures may develop directly from the seed itself rather th ...
) fused to and surrounding the actual seed. Nuts are the one-seeded, hard-shelled fruit of some plants with an indehiscent
Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that ...
seed, such as an acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
or hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according to ...
.
History
The first land plants evolved around 468 million years ago, and reproduced using spores. The earliest seed bearing plants to appear were thegymnosperms
The gymnosperms ( ; ) are a group of woody, perennial Seed plant, seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetoph ...
, which have no ovaries to contain the seeds. They arose during the late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
period (416 million to 358 million years ago). From these early gymnosperms, seed ferns evolved during the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
period (359 to 299 million years ago); they had ovules that were borne in a cupule, which consisted of groups of enclosing branches likely used to protect the developing seed.
Published literature about seed storage, viability and its hygrometric dependence began in the early 19th century, influential works being:
* 1832 seed storage guide in Augustin Pyramus de Candolle
Augustin Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (, , ; 4 February 17789 September 1841) was a Swiss people, Swiss botany, botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at a herbarium. Within a couple ...
's ''Conservation des Graines'', part of his 3-volume ''Physiologie végétale, ou Exposition des forces et des fonctions vitales des végétaux'' (1832, v. 2, pp. 618–626, Paris); (translated title, "Plant physiology, or Exposition of the vital forces and functions of plants")
* 1846 viability studies by Augustin de Candolle, published in "Sur la durée relative de la faculté de germer des graines appartenant à diverses familles" ('' Annales des Sciences Naturelles; Botanique'', 1846, III 6: 373–382); (translated title, "On the relative duration of the ability to germinate seeds belonging to various families")
* 1897 seed hygrometric studies by Victor Jodin (''Annales Agronomiques'', October 1897)
* 1912's Henry B. Guppy's 528 page "''Studies in Seeds and Fruits- An Investigation with the Balance''" (1912, London, England); subsequently reviewed in ''Science'' (June 1914, Washington, D.C.)
Development
cone
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the '' apex'' or '' vertex''.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines ...
scales as they develop in some species of conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
.
Angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit ...
(flowering plants) seeds consist of three genetically distinct constituents: (1) the embryo formed from the zygote, (2) the endosperm, which is normally triploid, (3) the seed coat from tissue derived from the maternal tissue of the ovule. In angiosperms, the process of seed development begins with double fertilization
Double fertilization or double fertilisation (see spelling differences) is a complex fertilization mechanism of angiosperms. This process involves the fusion of a female gametophyte or megagametophyte, also called the embryonic sac, with two m ...
, which involves the fusion of two male gametes with the egg cell and the central cell to form the primary endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
and the zygote. Right after fertilization, the zygote is mostly inactive, but the primary endosperm divides rapidly to form the endosperm tissue. This tissue becomes the food the young plant will consume until the roots have developed after germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
.
Ovule
placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
and hence ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
or fruit wall, at the pericarp
Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits.
Fruitlike structures may develop directly from the seed itself rather th ...
.
* The nucellus, the remnant of the megasporangium and main region of the ovule where the megagametophyte develops.
* The micropyle, a small pore or opening in the apex of the integument of the ovule where the pollen tube
A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of seed plants when it germinates. Pollen tube elongation is an integral stage in the plant life cycle. The pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells fr ...
usually enters during the process of fertilization.
* The chalaza, the base of the ovule opposite the micropyle, where integument and nucellus are joined.
The shape of the ovules as they develop often affects the final shape of the seeds. Plants generally produce ovules of four shapes: the most common shape is called anatropous, with a curved shape. Orthotropous ovules are straight with all the parts of the ovule lined up in a long row producing an uncurved seed. Campylotropous ovules have a curved megagametophyte often giving the seed a tight "C" shape. The last ovule shape is called amphitropous, where the ovule is partly inverted and turned back 90 degrees on its stalk (the funicle or funiculus).
In the majority of flowering plants, the zygote's first division is transversely oriented in regards to the long axis, and this establishes the polarity of the embryo. The upper or chalazal pole becomes the main area of growth of the embryo, while the lower or micropylar pole produces the stalk-like suspensor that attaches to the micropyle. The suspensor absorbs and manufactures nutrients from the endosperm that are used during the embryo's growth.
Embryo
 The main components of the embryo are:
* The
The main components of the embryo are:
* The cotyledon
A cotyledon ( ; ; "a cavity, small cup, any cup-shaped hollow",
gen. (), ) is a "seed leaf" – a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant – and is formally defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or mor ...
s, the seed leaves, attached to the embryonic axis. There may be one ( Monocotyledons), or two (Dicotyledons
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, ...
). The cotyledons are also the source of nutrients in the non-endospermic dicotyledons, in which case they replace the endosperm, and are thick and leathery. In endospermic seeds, the cotyledons are thin and papery. Dicotyledons have the point of attachment opposite one another on the axis.
* The epicotyl
An epicotyl is important for the beginning stages of a plant's life. It is the region of a seedling stem above the stalks of the seed leaves of an embryo plant. It grows rapidly, showing hypogeal germination, and extends the stem above the soil su ...
, the embryonic axis above the point of attachment of the cotyledon(s).
* The plumule, the tip of the epicotyl, and has a feathery appearance due to the presence of young leaf primordia at the apex, and will become the shoot upon germination.
* The hypocotyl
The hypocotyl (short for "hypocotyledonous stem", meaning "below seed leaf") is the stem of a germinating seedling, found below the cotyledons (seed leaves) and above the radicle (root).
Eudicots
As the plant embryo grows at germination, it send ...
, the embryonic axis below the point of attachment of the cotyledon(s), connecting the epicotyl and the radicle, being the stem-root transition zone.
* The radicle
In botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling (a growing plant embryo) to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil (the shoot emerges from t ...
, the basal tip of the hypocotyl, grows into the primary root.
Monocotyledonous plants have two additional structures in the form of sheaths. The plumule is covered with a coleoptile
Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as grasses in which few leaf primordia and shoot apex of monocot embryo remain enclosed. The coleoptile protects the first leaf as well as the growing ...
that forms the first leaf while the radicle is covered with a coleorhiza that connects to the primary root and adventitious
Important structures in plant development are buds, shoots, roots, leaves, and flowers; plants produce these tissues and structures throughout their life from meristems located at the tips of organs, or between mature tissues. Thus, a living plant ...
roots form the sides. Here the hypocotyl is a rudimentary axis between radicle and plumule. The seeds of corn are constructed with these structures; pericarp, scutellum (single large cotyledon) that absorbs nutrients from the endosperm, plumule, radicle, coleoptile, and coleorhiza – these last two structures are sheath-like and enclose the plumule and radicle, acting as a protective covering.
Seed coat
The maturing ovule undergoes marked changes in the integuments, generally a reduction and disorganization but occasionally a thickening. The seed coat forms from the two integuments or outer layers of cells of the ovule, which derive from tissue from the mother plant, the inner integument forms the tegmen and the outer forms the testa. (The seed coats of some monocotyledon plants, such as the grasses, are not distinct structures, but are fused with the fruit wall to form apericarp
Fruits are the mature ovary or ovaries of one or more flowers. They are found in three main anatomical categories: aggregate fruits, multiple fruits, and simple fruits.
Fruitlike structures may develop directly from the seed itself rather th ...
.) The testae of both monocots and dicots are often marked with patterns and textured markings, or have wings or tufts of hair. When the seed coat forms from only one layer, it is also called the testa, though not all such testae are homologous from one species to the next. The funiculus abscisses (detaches at fixed point – abscission zone), the scar forming an oval depression, the hilum. Anatropous ovules have a portion of the funiculus that is adnate (fused to the seed coat), and which forms a longitudinal ridge, or raphe, just above the hilum. In bitegmic ovules (e.g. ''Gossypium'' described here) both inner and outer integuments contribute to the seed coat formation. With continuing maturation the cells enlarge in the outer integument. While the inner epidermis may remain a single layer, it may also divide to produce two to three layers and accumulates starch, and is referred to as the colourless layer. By contrast, the outer epidermis becomes tanniferous. The inner integument may consist of eight to fifteen layers.
As the cells enlarge, and starch is deposited in the outer layers of the pigmented zone below the outer epidermis, this zone begins to lignify, while the cells of the outer epidermis enlarge radially and their walls thicken, with nucleus and cytoplasm compressed into the outer layer. these cells which are broader on their inner surface are called palisade cells. In the inner epidermis, the cells also enlarge radially with plate like thickening of the walls. The mature inner integument has a palisade layer, a pigmented zone with 15–20 layers, while the innermost layer is known as the fringe layer.
Gymnosperms
In gymnosperms, which do not form ovaries, the ovules and hence the seeds are exposed. This is the basis for their nomenclature – naked seeded plants. Two sperm cells transferred from the pollen do not develop the seed by double fertilization, but one sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus and the other sperm is not used. Sometimes each sperm fertilizes an egg cell and one zygote is then aborted or absorbed during early development. The seed is composed of the embryo (the result of fertilization) and tissue from the mother plant, which also form a cone around the seed in coniferous plants such aspine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
and spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' ...
.
Shape and appearance
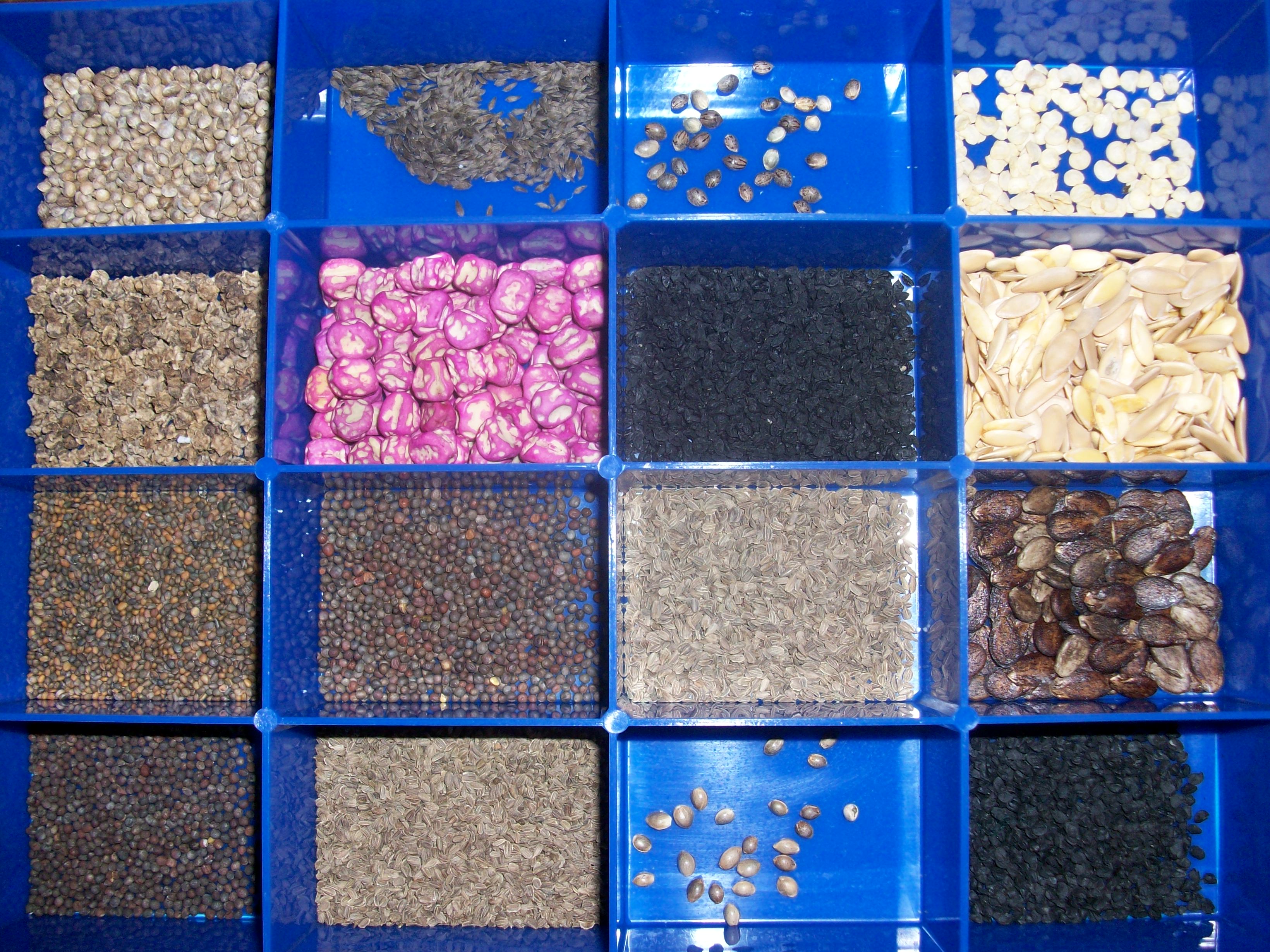
Seeds are very diverse, and as such there are many terms are used to describe them.Terms to describe shape
* Bean-shaped () – resembling a kidney, with lobed ends on either side of the hilum * Square or Oblong – angular, with all sides being either equal, or longer-than-wide * Triangular – three-sided, broadest below the middle * Elliptic or Ovate or Obovate – rounded at both ends, or egg shaped (ovate or obovate, broader at one end), being rounded but either symmetrical about the middle, or broader below the middle, or broader above the middle * Discoid ''–'' resembling a disc or plate, having both thickness and parallel faces and with a rounded margin) * Ellipsoid * Globose – spherical * Subglobose (Inflated, but less than spherical) * Lenticular * Ovoid * Sectoroid * * Other common descriptors for seeds focus on color, texture, and form. Striate seeds are striped with parallel, longitudinal lines or ridges. The most common colours are brown and black, with other colours appearing less frequently. The surface texture varies from highly polished to considerably roughened. The surface may also have a variety of appendages (see Seed coat), and be described by terms such as papillate or digitiform (finger-like). A seed coat with the consistency of cork is referred to as suberose. Other terms include crustaceous (hard, thin or brittle).Structure
embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
;
# a seed coat.
In addition, the endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
forms a supply of nutrients for the embryo in most monocotyledons and the endospermic dicotyledons.
Seed types
Seeds have been considered to occur in many structurally different types (Martin 1946). These are based on a number of criteria, of which the dominant one is the embryo-to-seed size ratio. This reflects the degree to which the developing cotyledons absorb the nutrients of the endosperm, and thus obliterate it. Six types occur amongst the monocotyledons, ten in the dicotyledons, and two in the gymnosperms (linear and spatulate). This classification is based on three characteristics: embryo morphology, amount of endosperm and the position of the embryo relative to the endosperm.Embryo
In endospermic seeds, there are two distinct regions inside the seed coat, an upper and larger endosperm and a lower smaller embryo. Theembryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
is the fertilised ovule, an immature plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
from which a new plant will grow under proper conditions. The embryo has one cotyledon
A cotyledon ( ; ; "a cavity, small cup, any cup-shaped hollow",
gen. (), ) is a "seed leaf" – a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant – and is formally defined as "the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants, one or mor ...
or seed leaf in monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, ( Lilianae '' sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but with various ranks ...
s, two cotyledons in almost all dicotyledon
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, ...
s and two or more in gymnosperms. In the fruit of grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
(caryopses) the single monocotyledon is shield shaped and hence called a scutellum. The scutellum is pressed closely against the endosperm from which it absorbs food and passes it to the growing parts. Embryo descriptors include small, straight, bent, curved, and curled.
Nutrient storage
Within the seed, there usually is a store ofnutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s for the seedling
A seedling is a young sporophyte developing out of a plant embryo from a seed. Seedling development starts with germination of the seed. A typical young seedling consists of three main parts: the radicle (embryonic root), the hypocotyl (embry ...
that will grow from the embryo. The form of the stored nutrition varies depending on the kind of plant. In angiosperms, the stored food begins as a tissue called the endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
, which is derived from the mother plant and the pollen via double fertilization
Double fertilization or double fertilisation (see spelling differences) is a complex fertilization mechanism of angiosperms. This process involves the fusion of a female gametophyte or megagametophyte, also called the embryonic sac, with two m ...
. It is usually triploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one fro ...
, and is rich in oil or starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
. In gymnosperms, such as conifers
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
, the food storage tissue (also called endosperm) is part of the female gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the se ...
, a haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
tissue. The endosperm is surrounded by the aleurone layer (peripheral endosperm), filled with proteinaceous aleurone grains.
Originally, by analogy with the animal ovum
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capa ...
, the outer nucellus layer ( perisperm) was referred to as albumen
Egg white is the clear liquid (also called the albumen or the glair/glaire) contained within an egg. In chickens, it is formed from the layers of secretions of the anterior section of the hen's oviduct during the passage of the egg. It forms aro ...
, and the inner endosperm layer as vitellus. Although misleading, the term began to be applied to all the nutrient matter. This terminology persists in referring to endospermic seeds as "albuminous". The nature of this material is used in both describing and classifying seeds, in addition to the embryo to endosperm size ratio. The endosperm may be considered to be farinaceous (or mealy) in which the cells are filled with starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, as for instance cereal grains, or not (non-farinaceous). The endosperm may also be referred to as "fleshy" or "cartilaginous" with thicker soft cells such as coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
, but may also be oily as in ''Ricinus
''Ricinus communis'', the castor bean or castor oil plant, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus, ''Ricinus'', and subtribe, Ricininae. The evolution of c ...
'' (castor oil), '' Croton'' and Poppy
A poppy is a flowering plant in the subfamily Papaveroideae of the family Papaveraceae. Poppies are herbaceous plants, often grown for their colourful flowers. One species of poppy, '' Papaver somniferum'', is the source of the narcotic drug ...
. The endosperm is called "horny" when the cell walls are thicker such as date and coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
, or "ruminated" if mottled, as in nutmeg
Nutmeg is the seed, or the ground spice derived from the seed, of several tree species of the genus '' Myristica''; fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg ('' M. fragrans'') is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fru ...
, palms and Annonaceae
The Annonaceae are a Family (biology), family of flowering plants consisting of trees, shrubs, or rarely lianas commonly known as the custard apple family or soursop family. With 108 accepted genera and about 2400 known species, it is the largest ...
.
In most monocotyledons (such as grasses and palms) and some (endospermic or albuminous) dicotyledons (such as castor beans) the embryo is embedded in the endosperm (and nucellus), which the seedling will use upon germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
. In the non-endospermic dicotyledons the endosperm is absorbed by the embryo as the latter grows within the developing seed, and the cotyledons of the embryo become filled with stored food. At maturity, seeds of these species have no endosperm and are also referred to as exalbuminous seeds. The exalbuminous seeds include the legumes
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consu ...
(such as bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s and pea
Pea (''pisum'' in Latin) is a pulse or fodder crop, but the word often refers to the seed or sometimes the pod of this flowering plant species. Peas are eaten as a vegetable. Carl Linnaeus gave the species the scientific name ''Pisum sativum' ...
s), trees such as the oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
and walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''. They are accessory fruit because the outer covering of the fruit is technically an i ...
, vegetables such as squash and radish
The radish (''Raphanus sativus'') is a flowering plant in the mustard family, Brassicaceae. Its large taproot is commonly used as a root vegetable, although the entire plant is edible and its leaves are sometimes used as a leaf vegetable. Origina ...
, and sunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a species of large annual forb of the daisy family Asteraceae. The common sunflower is harvested for its edible oily seeds, which are often eaten as a snack food. They are also used in the pr ...
s. According to Bewley and Black (1978), Brazil nut storage is in hypocotyl and this place of storage is uncommon among seeds. All gymnosperm seeds are albuminous.
Seed coat
 The seed coat develops from the maternal tissue, the
The seed coat develops from the maternal tissue, the integument
In biology, an integument is the tissue surrounding an organism's body or an organ within, such as skin, a husk, Exoskeleton, shell, germ or Peel (fruit), rind.
Etymology
The term is derived from ''integumentum'', which is Latin for "a coverin ...
s, originally surrounding the ovule. The seed coat in the mature seed can be a paper-thin layer (e.g. peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
) or something more substantial (e.g. thick and hard in honey locust and coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
), or fleshy as in the sarcotesta
The sarcotesta is a fleshy seedcoat, a type of testa. Examples of seeds with a sarcotesta are pomegranate, ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants, assigned to the gymnosperms. The scientific name is also used as the Eng ...
of pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punica, Punicoideae, that grows between tall. Rich in symbolic and mythological associations in many cultures, it is thought to have o ...
. The seed coat helps protect the embryo from mechanical injury, predators, and drying out. Depending on its development, the seed coat is either bitegmic or unitegmic. Bitegmic seeds form a testa from the outer integument and a tegmen from the inner integument while unitegmic seeds have only one integument. Usually, parts of the testa or tegmen form a hard protective mechanical layer. The mechanical layer may prevent water penetration and germination. Amongst the barriers may be the presence of lignified sclereids.
The outer integument has a number of layers, generally between four and eight organised into three layers: (a) outer epidermis, (b) outer pigmented zone of two to five layers containing tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids. The term ''tannin'' is widel ...
and starch, and (c) inner epidermis. The endotegmen is derived from the inner epidermis of the inner integument, the exotegmen from the outer surface of the inner integument. The endotesta is derived from the inner epidermis of the outer integument, and the outer layer of the testa from the outer surface of the outer integument is referred to as the exotesta. If the exotesta is also the mechanical layer, this is called an exotestal seed, but if the mechanical layer is the endotegmen, then the seed is endotestal. The exotesta may consist of one or more rows of cells that are elongated and pallisade like (e.g. Fabaceae
Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomen ...
), hence 'palisade exotesta'.
In addition to the three basic seed parts, some seeds have an appendage, an aril
An aril (), also called arillus, is a specialized outgrowth from a seed that partly or completely covers the seed. An arillode, or false aril, is sometimes distinguished: whereas an aril grows from the attachment point of the seed to the ova ...
, a fleshy outgrowth of the funicle ( funiculus), (as in yew and nutmeg
Nutmeg is the seed, or the ground spice derived from the seed, of several tree species of the genus '' Myristica''; fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg ('' M. fragrans'') is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fru ...
) or an oily appendage, an elaiosome
Elaiosomes ( ''élaion'' "oil" + ''sóma'' "body") are fleshy structures that are attached to the seeds of many plant species. The elaiosome is rich in lipids and proteins, and may be variously shaped. Many plants have elaiosomes that attract ...
(as in ''Corydalis
''Corydalis'' (from Greek ''korydalís'' " crested lark") is a genus of about 540 species of annual and perennial herbaceous plants in the family Papaveraceae, native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere and the high mountains of tropical ...
''), or hairs (trichomes). In the latter example these hairs are the source of the textile crop cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
. Other seed appendages include the raphe (a ridge), wings, caruncles (a soft spongy outgrowth from the outer integument in the vicinity of the micropyle), spines, or tubercles.
A scar also may remain on the seed coat, called the hilum, where the seed was attached to the ovary wall by the funicle. Just below it is a small pore, representing the micropyle of the ovule.
Size and seed set
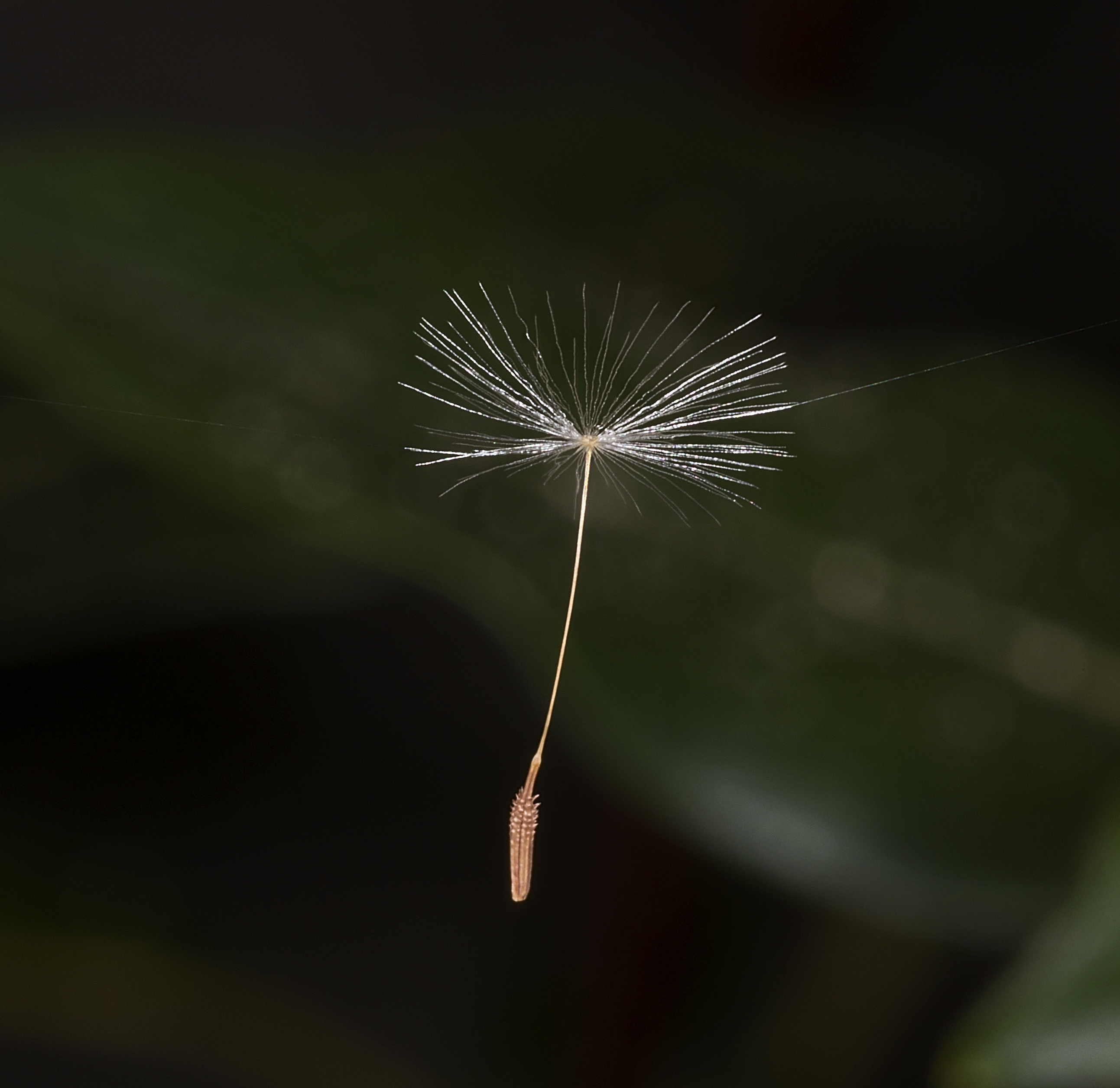
 Seeds are very diverse in size. The dust-like orchid seeds are the smallest, with about one million seeds per gram; they are often embryonic seeds with immature embryos and no significant energy reserves. Orchids and a few other groups of plants are mycoheterotrophs which depend on
Seeds are very diverse in size. The dust-like orchid seeds are the smallest, with about one million seeds per gram; they are often embryonic seeds with immature embryos and no significant energy reserves. Orchids and a few other groups of plants are mycoheterotrophs which depend on mycorrhizal fungi
A mycorrhiza (; , mycorrhiza, or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, the plant root system and its surroundings. Mycorrhizae play ...
for nutrition during germination and the early growth of the seedling. Some terrestrial orchid seedlings, in fact, spend the first few years of their lives deriving energy from the fungi and do not produce green leaves. At up to 55 pounds (25 kilograms) the largest seed is the '' coco de mer''(Lodoicea maldivica). This indicates a 25 Billion fold difference in seed weight. Plants that produce smaller seeds can generate many more seeds per flower, while plants with larger seeds invest more resources into those seeds and normally produce fewer seeds. Small seeds are quicker to ripen and can be dispersed sooner, so autumnal blooming plants often have small seeds. Many annual plants produce great quantities of smaller seeds; this helps to ensure at least a few will end in a favorable place for growth. Herbaceous perennials and woody plants often have larger seeds; they can produce seeds over many years, and larger seeds have more energy reserves for germination and seedling growth and produce larger, more established seedlings after germination.
Functions
Seeds serve several functions for the plants that produce them. Key among these functions are nourishment of theembryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
, dispersal to a new location, and dormancy
Dormancy is a period in an organism's Biological life cycle, life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolism, metabolic activity and therefore helps an organism to conserv ...
during unfavorable conditions. Seeds fundamentally are means of reproduction, and most seeds are the product of sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
which produces a remixing of genetic material and phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
variability on which natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
acts. Plant seeds hold endophytic microorganisms that can perform various functions, the most important of which is protection against disease.
Embryo nourishment
Seeds protect and nourish the embryo or young plant. They usually give a seedling a faster start than a sporeling from a spore, because of the larger food reserves in the seed and the multicellularity of the enclosed embryo.Dispersal
Unlike animals, plants are limited in their ability to seek out favorable conditions for life and growth. As a result, plants have evolved many ways to disperse their offspring by dispersing their seeds (see alsovegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specializ ...
). A seed must somehow "arrive" at a location and be there at a time favorable for germination and growth. When the fruits open and release their seeds in a regular way, it is called dehiscent
Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that op ...
, which is often distinctive for related groups of plants; these fruits include capsules, follicles, legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s, silicles and silique
A silique or siliqua (plural ''siliques'' or ''siliquae'') is a type of fruit (seed capsule) having two fused carpels with the length being more than three times the width. When the length is less than three times the width of the dried fruit ...
s. When fruits do not open and release their seeds in a regular fashion, they are called indehiscent, which include the fruits achene
An achene (; ), also sometimes called akene and occasionally achenium or achenocarp, is a type of simple fruit, simple dry fruits, dry fruit produced by many species of flowering plants. Achenes are monocarpellate (formed from one carpel) and Dehi ...
s, caryopses, nuts, samaras, and utricles.
By wind (anemochory)

 * Some seeds (e.g.,
* Some seeds (e.g., pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
) have a wing that aids in wind dispersal.
* The dustlike seeds of orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Eart ...
s are carried efficiently by the wind.
* Some seeds (e.g. milkweed, poplar) have hairs that aid in wind dispersal.
Other seeds are enclosed in fruit structures that aid wind dispersal in similar ways:
* Dandelion
''Taraxacum'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which consists of species commonly known as dandelions. The scientific and hobby study of the genus is known as taraxacology. The genus has a near-cosmopolitan distribu ...
achenes have hairs.
* Maple
''Acer'' is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the soapberry family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated si ...
samaras have two wings.
By water (hydrochory)
* Some plants, such as ''Mucuna
''Mucuna'' is a genus of around 110 accepted species of vines and shrubs of the Family (biology), family Fabaceae: tribe Phaseoleae, typically found in tropical and subtropical forests in the Americas, sub-Saharan Africa, southern, southeastern, ...
'' and '' Dioclea'', produce buoyant seeds termed sea-beans or drift seeds because they float in rivers to the oceans and wash up on beaches.
By animals (zoochory)
* Seeds ( burrs) with barbs or hooks (e.g. acaena, burdock,dock
The word dock () in American English refers to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore). In British English, the term is not used the same way as in American Engl ...
) which attach to animal fur or feathers, and then drop off later.
* Seeds with a fleshy covering (e.g. apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
, cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet '' Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The na ...
, juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' ( ) of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere as far south ...
) are eaten by animals (bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s, mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
) which then disperse these seeds in their droppings.
* Seeds ( nuts) are attractive long-term storable food resources for animals (e.g. acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s, hazel
Hazels are plants of the genus ''Corylus'' of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family, Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K ...
nut, walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''. They are accessory fruit because the outer covering of the fruit is technically an i ...
); the seeds are stored some distance from the parent plant, and some escape being eaten if the animal forgets them.
Myrmecochory
Myrmecochory ( (sometimes myrmechory); from ("ant") and ''khoreíā'' ("circular dance") is seed dispersal by ants, an ecologically significant Myrmecophily, ant–plant Biological interaction, interaction with worldwide distribution. Most ...
is the dispersal of seeds by ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
s. Foraging ants disperse seeds which have appendages called elaiosome
Elaiosomes ( ''élaion'' "oil" + ''sóma'' "body") are fleshy structures that are attached to the seeds of many plant species. The elaiosome is rich in lipids and proteins, and may be variously shaped. Many plants have elaiosomes that attract ...
s (e.g. bloodroot, trillium
''Trillium'' (trillium, wakerobin, toadshade, tri flower, birthroot, birthwort, and sometimes "wood lily") is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. ''Trillium'' species are native to temperate regions of No ...
s, acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
s, and many species of Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family (biology), family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genus, genera with about 1,660 known species. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentr ...
). Elaiosomes are soft, fleshy structures that contain nutrients for animals that eat them. The ants carry such seeds back to their nest, where the elaiosomes are eaten. The remainder of the seed, which is hard and inedible to the ants, then germinates either within the nest or at a removal site where the seed has been discarded by the ants.Ricklefs, Robert E. (1993) ''The Economy of Nature'', 3rd ed., p. 396. (New York: W.H. Freeman). . This dispersal relationship is an example of mutualism, since the plants depend upon the ants to disperse seeds, while the ants depend upon the plants seeds for food. As a result, a drop in numbers of one partner can reduce success of the other. In South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, the Argentine ant (''Linepithema humile'') has invaded and displaced native species of ants. Unlike the native ant species, Argentine ants do not collect the seeds of '' Mimetes cucullatus'' or eat the elaiosomes. In areas where these ants have invaded, the numbers of ''Mimetes'' seedlings have dropped.
Dormancy
Seed dormancy has two main functions: the first is synchronizing germination with the optimal conditions for survival of the resulting seedling; the second is spreading germination of a batch of seeds over time so a catastrophe (e.g. late frosts, drought,herbivory
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat n ...
) does not result in the death of all offspring of a plant ( bet-hedging). Seed dormancy is defined as a seed failing to germinate under environmental conditions optimal for germination, normally when the environment is at a suitable temperature with proper soil moisture. This true dormancy or innate dormancy is therefore caused by conditions within the seed that prevent germination. Thus dormancy is a state of the seed, not of the environment. Induced dormancy, enforced dormancy or seed quiescence occurs when a seed fails to germinate because the external environmental conditions are inappropriate for germination, mostly in response to conditions being too dark or light, too cold or hot, or too dry.
Seed dormancy is not the same as seed persistence in the soil or on the plant, though even in scientific publications dormancy and persistence are often confused or used as synonyms.
Often, seed dormancy is divided into four major categories: exogenous; endogenous; combinational; and secondary. A more recent system distinguishes five classes: morphological, physiological, morphophysiological, physical, and combinational dormancy.
Exogenous dormancy is caused by conditions outside the embryo, including:
* Physical dormancy or hard seed coats occurs when seeds are impermeable to water. At dormancy break, a specialized structure, the 'water gap', is disrupted in response to environmental cues, especially temperature, so water can enter the seed and germination can occur. Plant families where physical dormancy occurs include Anacardiaceae
The Anacardiaceae, commonly known as the cashew family or sumac family, are a family of flowering plants, including about 83 genera with about 860 known species. Members of the Anacardiaceae bear fruits that are drupes and in some cases produce ...
, Cannaceae, Convulvulaceae, Fabaceae
Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomen ...
and Malvaceae
Malvaceae (), or the mallows, is a family of flowering plants estimated to contain 244 genera with 4225 known species. Well-known members of economic importance include Theobroma cacao, cacao, Cola (plant), cola, cotton, okra, Hibiscus sabdariffa, ...
.
* Chemical dormancy considers species that lack physiological dormancy, but where a chemical prevents germination. This chemical can be leached out of the seed by rainwater or snow melt or be deactivated somehow. Leaching of chemical inhibitors from the seed by rain water is often cited as an important cause of dormancy release in seeds of desert plants, but little evidence exists to support this claim.
Endogenous dormancy is caused by conditions within the embryo itself, including:
* In morphological dormancy, germination is prevented due to morphological characteristics of the embryo. In some species, the embryo is just a mass of cells when seeds are dispersed; it is not differentiated. Before germination can take place, both differentiation and growth of the embryo have to occur. In other species, the embryo is differentiated but not fully grown (underdeveloped) at dispersal, and embryo growth up to a species specific length is required before germination can occur. Examples of plant families where morphological dormancy occurs are Apiaceae
Apiaceae () or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus ''Apium,'' and commonly known as the celery, carrot, or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering p ...
, Cycadaceae, Liliaceae
The lily family, Liliaceae, consists of about 15 genera and 610 species of flowering plants within the order Liliales. They are monocotyledonous, perennial, herbaceous, often bulbous geophytes. Plants in this family have evolved with a fai ...
, Magnoliaceae
The Magnoliaceae () are a flowering plant family, the magnolia family, in the order Magnoliales. It consists of two genera: '' Magnolia'' and ''Liriodendron'' (tulip trees).
Unlike most angiosperms, whose flower parts are in whorls (rings), ...
and Ranunculaceae
Ranunculaceae (, buttercup or crowfoot family; Latin "little frog", from "frog") is a family (biology), family of over 2,000 known species of flowering plants in 43 genera, distributed worldwide.
The largest genera are ''Ranunculus'' (600 spec ...
.Baskin, C.C. and Baskin, J.M. (1998) Seeds: Ecology, biogeography, and evolution of dormancy and germination.San Diego, Academic Press.Baskin, J.M. and Baskin, C.C. (2004) A classification system for seed dormancy. Seed Science Research 14:1–16.
* Morphophysiological dormancy includes seeds with underdeveloped embryos, and also have physiological components to dormancy. These seeds, therefore, require a dormancy-breaking treatments, as well as a period of time to develop fully grown embryos. Plant families where morphophysiological dormancy occurs include Apiaceae
Apiaceae () or Umbelliferae is a family of mostly aromatic flowering plants named after the type genus ''Apium,'' and commonly known as the celery, carrot, or parsley family, or simply as umbellifers. It is the 16th-largest family of flowering p ...
, Aquifoliaceae, Liliaceae
The lily family, Liliaceae, consists of about 15 genera and 610 species of flowering plants within the order Liliales. They are monocotyledonous, perennial, herbaceous, often bulbous geophytes. Plants in this family have evolved with a fai ...
, Magnoliaceae
The Magnoliaceae () are a flowering plant family, the magnolia family, in the order Magnoliales. It consists of two genera: '' Magnolia'' and ''Liriodendron'' (tulip trees).
Unlike most angiosperms, whose flower parts are in whorls (rings), ...
, Papaveraceae
The Papaveraceae, informally known as the poppy family, are an economically important family (biology), family of about 42 genera and approximately 775 known species of flowering plants in the order Ranunculales. The family is cosmopolitan dis ...
and Ranunculaceae
Ranunculaceae (, buttercup or crowfoot family; Latin "little frog", from "frog") is a family (biology), family of over 2,000 known species of flowering plants in 43 genera, distributed worldwide.
The largest genera are ''Ranunculus'' (600 spec ...
. Some plants with morphophysiological dormancy, such as ''Asarum
''Asarum'' is a genus of plants in the birthwort family Aristolochiaceae, commonly known as wild ginger.
''Asarum'' is from Greek ἄσαρον, a name for '' Asarum europaeum''.
Description
''Asarum'' is a genus of low-growing herbs distri ...
'' or ''Trillium
''Trillium'' (trillium, wakerobin, toadshade, tri flower, birthroot, birthwort, and sometimes "wood lily") is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. ''Trillium'' species are native to temperate regions of No ...
'' species, have multiple types of dormancy, one affects radicle (root) growth, while the other affects plumule (shoot) growth. The terms "double dormancy" and "two-year seeds" are used for species whose seeds need two years to complete germination or at least two winters and one summer. Dormancy of the radicle (seedling root) is broken during the first winter after dispersal while dormancy of the shoot bud is broken during the second winter.
* Physiological dormancy means the embryo, due to physiological causes, cannot generate enough power to break through the seed coat, endosperm or other covering structures. Dormancy is typically broken at cool wet, warm wet, or warm dry conditions. Abscisic acid
Abscisic acid (ABA or abscisin II) is a plant hormone. ABA functions in many plant developmental processes, including seed and bud dormancy, the control of organ size and stomatal closure. It is especially important for plants in the response to ...
is usually the growth inhibitor in seeds, and its production can be affected by light.
**Drying, in some plants, including a number of grasses and those from seasonally arid regions, is needed before they will germinate. The seeds are released, but need to have a lower moisture content before germination can begin. If the seeds remain moist after dispersal, germination can be delayed for many months or even years. Many herbaceous plants from temperate climate zones have physiological dormancy that disappears with drying of the seeds. Other species will germinate after dispersal only under very narrow temperature ranges, but as the seeds dry, they are able to germinate over a wider temperature range.
* In seeds with combinational dormancy, the seed or fruit coat is impermeable to water and the embryo has physiological dormancy. Depending on the species, physical dormancy can be broken before or after physiological dormancy is broken.
* Secondary dormancy* is caused by conditions after the seed has been dispersed and occurs in some seeds when nondormant seed is exposed to conditions that are not favorable to germination, very often high temperatures. The mechanisms of secondary dormancy are not yet fully understood, but might involve the loss of sensitivity in receptors in the plasma membrane.
The following types of seed dormancy do not involve seed dormancy, strictly speaking, as lack of germination is prevented by the environment, not by characteristics of the seed itself (see Germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
):
* Photodormancy or light sensitivity affects germination of some seeds. These photoblastic seeds need a period of darkness or light to germinate. In species with thin seed coats, light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
may be able to penetrate into the dormant embryo. The presence of light or the absence of light may trigger the germination process, inhibiting germination in some seeds buried too deeply or in others not buried in the soil.
* Thermodormancy is seed sensitivity to heat or cold. Some seeds, including cocklebur and amaranth, germinate only at high temperatures (30 °C or 86 °F); many plants that have seeds that germinate in early to midsummer have thermodormancy, so germinate only when the soil temperature is warm. Other seeds need cool soils to germinate, while others, such as celery, are inhibited when soil temperatures are too warm. Often, thermodormancy requirements disappear as the seed ages or dries.
Not all seeds undergo a period of dormancy. Seeds of some mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s are viviparous; they begin to germinate while still attached to the parent. The large, heavy root allows the seed to penetrate into the ground when it falls. Many garden plant seeds will germinate readily as soon as they have water and are warm enough; though their wild ancestors may have had dormancy, these cultivated plants lack it. After many generations of selective pressure by plant breeders and gardeners, dormancy has been selected out.
For annuals, seeds are a way for the species to survive dry or cold seasons. Ephemeral plants are usually annuals that can go from seed to seed in as few as six weeks.
Persistence and seed banks
Germination
 Seed germination is a process by which a seed embryo develops into a seedling. It involves the reactivation of the metabolic pathways that lead to growth and the emergence of the radicle or seed root and plumule or shoot. The emergence of the seedling above the soil surface is the next phase of the plant's growth and is called seedling establishment.
Three fundamental conditions must exist before germination can occur. (1) The embryo must be alive, called seed viability. (2) Any dormancy requirements that prevent germination must be overcome. (3) The proper environmental conditions must exist for germination.
Far red light can prevent germination.
Seed viability is the ability of the embryo to germinate and is affected by a number of different conditions. Some plants do not produce seeds that have functional complete embryos, or the seed may have no embryo at all, often called empty seeds. Predators and pathogens can damage or kill the seed while it is still in the fruit or after it is dispersed. Environmental conditions like flooding or heat can kill the seed before or during germination. The age of the seed affects its health and germination ability: since the seed has a living embryo, over time cells die and cannot be replaced. Some seeds can live for a long time before germination, while others can only survive for a short period after dispersal before they die.
Seed vigor is a measure of the quality of seed, and involves the viability of the seed, the germination percentage, germination rate, and the strength of the seedlings produced.
The germination percentage is simply the proportion of seeds that germinate from all seeds subject to the right conditions for growth. The germination rate is the length of time it takes for the seeds to germinate. Germination percentages and rates are affected by seed viability, dormancy and environmental effects that impact on the seed and seedling. In agriculture and horticulture quality seeds have high viability, measured by germination percentage plus the rate of germination. This is given as a percent of germination over a certain amount of time, 90% germination in 20 days, for example. 'Dormancy' is covered above; many plants produce seeds with varying degrees of dormancy, and different seeds from the same fruit can have different degrees of dormancy. It's possible to have seeds with no dormancy if they are dispersed right away and do not dry (if the seeds dry they go into physiological dormancy). There is great variation amongst plants and a dormant seed is still a viable seed even though the germination rate might be very low.
Environmental conditions affecting seed germination include; water, oxygen, temperature and light.
Three distinct phases of seed germination occur: water imbibition; lag phase; and
Seed germination is a process by which a seed embryo develops into a seedling. It involves the reactivation of the metabolic pathways that lead to growth and the emergence of the radicle or seed root and plumule or shoot. The emergence of the seedling above the soil surface is the next phase of the plant's growth and is called seedling establishment.
Three fundamental conditions must exist before germination can occur. (1) The embryo must be alive, called seed viability. (2) Any dormancy requirements that prevent germination must be overcome. (3) The proper environmental conditions must exist for germination.
Far red light can prevent germination.
Seed viability is the ability of the embryo to germinate and is affected by a number of different conditions. Some plants do not produce seeds that have functional complete embryos, or the seed may have no embryo at all, often called empty seeds. Predators and pathogens can damage or kill the seed while it is still in the fruit or after it is dispersed. Environmental conditions like flooding or heat can kill the seed before or during germination. The age of the seed affects its health and germination ability: since the seed has a living embryo, over time cells die and cannot be replaced. Some seeds can live for a long time before germination, while others can only survive for a short period after dispersal before they die.
Seed vigor is a measure of the quality of seed, and involves the viability of the seed, the germination percentage, germination rate, and the strength of the seedlings produced.
The germination percentage is simply the proportion of seeds that germinate from all seeds subject to the right conditions for growth. The germination rate is the length of time it takes for the seeds to germinate. Germination percentages and rates are affected by seed viability, dormancy and environmental effects that impact on the seed and seedling. In agriculture and horticulture quality seeds have high viability, measured by germination percentage plus the rate of germination. This is given as a percent of germination over a certain amount of time, 90% germination in 20 days, for example. 'Dormancy' is covered above; many plants produce seeds with varying degrees of dormancy, and different seeds from the same fruit can have different degrees of dormancy. It's possible to have seeds with no dormancy if they are dispersed right away and do not dry (if the seeds dry they go into physiological dormancy). There is great variation amongst plants and a dormant seed is still a viable seed even though the germination rate might be very low.
Environmental conditions affecting seed germination include; water, oxygen, temperature and light.
Three distinct phases of seed germination occur: water imbibition; lag phase; and radicle
In botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling (a growing plant embryo) to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil (the shoot emerges from t ...
emergence.
In order for the seed coat to split, the embryo must imbibe (soak up water), which causes it to swell, splitting the seed coat. However, the nature of the seed coat determines how rapidly water can penetrate and subsequently initiate germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
. The rate of imbibition is dependent on the permeability of the seed coat, amount of water in the environment and the area of contact the seed has to the source of water. For some seeds, imbibing too much water too quickly can kill the seed. For some seeds, once water is imbibed the germination process cannot be stopped, and drying then becomes fatal. Other seeds can imbibe and lose water a few times without causing ill effects, but drying can cause secondary dormancy.
Repair of DNA damage
During seeddormancy
Dormancy is a period in an organism's Biological life cycle, life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolism, metabolic activity and therefore helps an organism to conserv ...
, often associated with unpredictable and stressful environments, DNA damage accumulates as the seeds age. In rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
seeds, the reduction of DNA integrity due to damage is associated with loss of seed viability during storage. Upon germination, seeds of ''Vicia faba
''Vicia faba'', commonly known as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of vetch, a flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption, and also as a cover crop. Vari ...
'' undergo DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
. A plant DNA ligase
In biochemistry, a ligase is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining ( ligation) of two molecules by forming a new chemical bond. This is typically via hydrolysis of a small pendant chemical group on one of the molecules, typically resulting i ...
that is involved in repair of single- and double-strand breaks during seed germination is an important determinant of seed longevity. Also, in Arabidopsis
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organ ...
seeds, the activities of the DNA repair enzymes Poly ADP ribose polymerases (PARP) are likely needed for successful germination. Thus DNA damages that accumulate during dormancy
Dormancy is a period in an organism's Biological life cycle, life cycle when growth, development, and (in animals) physical activity are temporarily stopped. This minimizes metabolism, metabolic activity and therefore helps an organism to conserv ...
appear to be a problem for seed survival, and the enzymatic repair of DNA damages during germination appears to be important for seed viability.
Inducing germination
A number of different strategies are used by gardeners and horticulturists to breakseed dormancy
Seed dormancy is an evolutionary adaptation that prevents seeds from germinating during unsuitable ecological conditions that would typically lead to a low probability of seedling survival. Dormant seeds do not germinate in a specified period of ...
.
Scarification
Scarification involves scratching, etching, burning/ branding, or superficially cutting designs, pictures, or words into the skin as a permanent body modification or body art. The body modification can take roughly 6–12 months to heal. In t ...
allows water and gases to penetrate into the seed; it includes methods to physically break the hard seed coats or soften them by chemicals, such as soaking in hot water or poking holes in the seed with a pin or rubbing them on sandpaper or cracking with a press or hammer. Sometimes fruits are harvested while the seeds are still immature and the seed coat is not fully developed and sown right away before the seed coat become impermeable. Under natural conditions, seed coats are worn down by rodents chewing on the seed, the seeds rubbing against rocks (seeds are moved by the wind or water currents), by undergoing freezing and thawing of surface water, or passing through an animal's digestive tract. In the latter case, the seed coat protects the seed from digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
, while often weakening the seed coat such that the embryo is ready to sprout when it is deposited, along with a bit of fecal matter that acts as fertilizer, far from the parent plant. Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s are often effective in breaking down hard seed coats and are sometimes used by people as a treatment; the seeds are stored in a moist warm sandy medium for several months under nonsterile conditions.
Stratification, also called moist-chilling, breaks down physiological dormancy, and involves the addition of moisture to the seeds so they absorb water, and they are then subjected to a period of moist chilling to after-ripen the embryo. Sowing in late summer and fall and allowing to overwinter under cool conditions is an effective way to stratify seeds; some seeds respond more favorably to periods of oscillating temperatures which are a part of the natural environment.
Leaching or the soaking in water removes chemical inhibitors in some seeds that prevent germination. Rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
and melting snow
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
naturally accomplish this task. For seeds planted in gardens, running water is best – if soaked in a container, 12 to 24 hours of soaking is sufficient. Soaking longer, especially in stagnant water, can result in oxygen starvation and seed death. Seeds with hard seed coats can be soaked in hot water to break open the impermeable cell layers that prevent water intake.
Other methods used to assist in the germination of seeds that have dormancy include prechilling, predrying, daily alternation of temperature, light exposure, potassium nitrate, the use of plant growth regulators, such as gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, thiourea
Thiourea () is an organosulfur compound with the formula and the structure . It is structurally similar to urea (), with the oxygen atom replaced by sulfur atom (as implied by the '' thio-'' prefix). The properties of urea and thiourea differ s ...
, sodium hypochlorite, and others. Some seeds germinate best after a fire. For some seeds, fire cracks hard seed coats, while in others, chemical dormancy is broken in reaction to the presence of smoke. Liquid smoke is often used by gardeners to assist in the germination of these species.
Sterile seeds
Seeds may be sterile for few reasons: they may have been irradiated, unpollinated, cells lived past expectancy, or bred for the purpose.Evolution and origin of seeds
The issue of the origin of seed plants remains unsolved. However, more and more data tends to place this origin in the middleDevonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
. The description in 2004 of the proto-seed ''Runcaria heinzelinii'' in the Givetian of Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
is an indication of that ancient origin of seed-plants. As with modern ferns, most land plants before this time reproduced by sending into the air spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s that would land and become whole new plants.
Taxonomists have described early "true" seeds from the upper Devonian, which probably became the theater of their true first evolutionary radiation
An evolutionary radiation is an increase in taxonomic diversity that is caused by elevated rates of speciation, that may or may not be associated with an increase in morphological disparity. A significantly large and diverse radiation within ...
. With this radiation came an evolution of seed size, shape, dispersal and eventually the radiation of gymnosperms and angiosperms and monocotyledon
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, ( Lilianae '' sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are flowering plants whose seeds contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. A monocot taxon has been in use for several decades, but with various ranks ...
s and dicotyledon
The dicotyledons, also known as dicots (or, more rarely, dicotyls), are one of the two groups into which all the flowering plants (angiosperms) were formerly divided. The name refers to one of the typical characteristics of the group: namely, ...
s. Seed plants progressively became one of the major elements of nearly all ecosystems.
True to the seed
Also called growing true, refers to plants whose seed will yield the same type of plant as the original plant. Open pollinated plants, which include heirlooms, will almost always grow true to seed if another variety does not cross-pollinate them.Seed microbiome
 Seeds harbor a diverse microbial community. Most of these microorganisms are transmitted from the seed to the developing seedlings.
Seeds harbor a diverse microbial community. Most of these microorganisms are transmitted from the seed to the developing seedlings.
Economic importance

Seed market
In the United States farmers spent $22 billion on seeds in 2018, a 35 percent increase since 2010. DowDuPont andMonsanto
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed ...
account for 72 percent of corn and soybean seed sales in the U.S. with the average price of a bag of GMO corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
seed is priced at $270.
Seed production
Seed production in natural plant populations varies widely from year to year in response to weather variables, insects and diseases, and internal cycles within the plants themselves. Over a 20-year period, for example, forests composed of loblolly pine and shortleaf pine produced from 0 to nearly 5.5 million sound pine seeds per hectare. Over this period, there were six bumper, five poor, and nine good seed crops, when evaluated for production of adequateseedling
A seedling is a young sporophyte developing out of a plant embryo from a seed. Seedling development starts with germination of the seed. A typical young seedling consists of three main parts: the radicle (embryonic root), the hypocotyl (embry ...
s for natural forest reproduction.
Edible seeds
Many seeds are edible and the majority of human calories comes from seeds, especially fromcereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s, legume
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
s and nuts. Seeds also provide most cooking oil
Cooking oil (also known as edible oil) is a plant or animal liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. Oil allows higher cooking temperatures than water, making cooking faster and more flavorful, while likewise distributing h ...
s, many beverage
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothie ...
s and spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
s and some important food additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar ( pickling), salt ( salting), smoke ( smoking) and sugar ( crystallization), have been used f ...
s. In different seeds the seed embryo or the endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
dominates and provides most of the nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s. The storage protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s of the embryo and endosperm differ in their amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
content and physical properties. For example, the gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain Cereal, cereal grains. The term ''gluten'' usually refers to the elastic network of a wheat grain's proteins, gliadin and glutenin primarily, that forms readily with the addition of water ...
of wheat, important in providing the elastic
Elastic is a word often used to describe or identify certain types of elastomer, Elastic (notion), elastic used in garments or stretch fabric, stretchable fabrics.
Elastic may also refer to:
Alternative name
* Rubber band, ring-shaped band of rub ...
property to bread dough
Dough is a malleable, sometimes elastic paste made from flour (which itself is made from grains or from leguminous or chestnut crops). Dough is typically made by mixing flour with a small amount of water or other liquid and sometimes includes ...
is strictly an endosperm protein.
Seeds are used to propagate many crops such as cereals, legumes, forest trees, turfgrasses, and pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing.
Types of pasture
Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, c ...
grasses. Particularly in developing countries, a major constraint faced is the inadequacy of the marketing channels to get the seed to poor farmers. Thus the use of farmer-retained seed remains quite common.
Seeds are also eaten by animals (seed predation
Seed predation, often referred to as granivory, is a type of plant-animal interaction in which granivores (seed predators) feed on the seeds of plants as a main or exclusive food source,Hulme, P.E. and Benkman, C.W. (2002) "Granivory", pp. 13 ...
), and are also fed to livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
or provided as birdseed.
Poison and food safety
While some seeds are edible, others are harmful, poisonous or deadly. Plants and seeds often containchemical compounds
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
to discourage herbivores
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat ...
and seed predators. In some cases, these compounds simply taste bad (such as in mustard), but other compounds are toxic or break down into toxic compounds within the digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
. Children, being smaller than adults, are more susceptible to poisoning by plants and seeds.
A deadly poison, ricin
Ricin ( ) is a lectin (a carbohydrate-binding protein) and a highly potent toxin produced in the seeds of the castor oil plant, ''Ricinus communis''. The median lethal dose (LD50) of ricin for mice is around 22 micrograms per kilogram of body ...
, comes from seeds of the castor bean. Reported lethal doses are anywhere from two to eight seeds,
though only a few deaths have been reported when castor beans have been ingested by animals.
In addition, seeds containing amygdalin
Amygdalin (from Ancient Greek: ' 'almond') is a naturally occurring chemical compound found in many plants, most notably in the seeds (kernels, pips or stones) of apricots, bitter almonds, apples, peaches, cherries and plums, and in the roots ...
– apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
, apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus ''Prunus''.
Usually an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also ...
, bitter almond, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and Agriculture, cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called necta ...
, plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in Prunus subg. Prunus, ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are often called prunes, though in the United States they may be labeled as 'dried plums', especially during the 21st century.
Plums are ...
, cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet '' Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The na ...
, quince
The quince (; ''Cydonia oblonga'') is the sole member of the genus ''Cydonia'' in the Malinae subtribe (which contains apples, pears, and other fruits) of the Rosaceae family. It is a deciduous tree that bears hard, aromatic bright golden-yel ...
, and others – when consumed in sufficient amounts, may cause cyanide poisoning
Cyanide poisoning is poisoning that results from exposure to any of a number of forms of cyanide. Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting. This phase may then be followed by seizures, slo ...
.
Other seeds that contain poisons include annona, cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, custard apple, datura
''Datura'' is a genus of nine species of highly poisonous, Vespertine (biology), vespertine-flowering plants belonging to the nightshade family (Solanaceae). They are commonly known as thornapples or jimsonweeds, but are also known as devil's t ...
, uncooked durian
The durian () is the edible fruit of several tree species belonging to the genus ''Durio''. There are 30 recognized species, at least nine of which produce edible fruit. ''Durio zibethinus'', native to Borneo and Sumatra, is the only species ...
, golden chain, horse-chestnut, larkspur, locoweed, lychee
Lychee ( , ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae.
There are three distinct subspecies of lychee. The most common is the Indochinese lychee found in So ...
, nectarine
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties called nectarines. Peach ...
, rambutan, rosary pea, sour sop, sugar apple, wisteria
''Wisteria'' is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae (Leguminosae). The genus includes four species of woody twining vines that are native to China, Japan, Korea, Vietnam, southern Canada, the Eastern United States, and nor ...
, and yew. The seeds of the strychnine tree are also poisonous, containing the poison strychnine
Strychnine (, , American English, US chiefly ) is a highly toxicity, toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, ...
.
The seeds of many legumes, including the common bean (''Phaseolus vulgaris
''Phaseolus vulgaris'', the common bean,, is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its botanical classification, alo ...
''), contain proteins called lectins
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in r ...
which can cause gastric distress if the beans are eaten without cooking
Cooking, also known as cookery or professionally as the culinary arts, is the art, science and craft of using heat to make food more palatable, digestible, nutritious, or Food safety, safe. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from ...
. The common bean and many others, including the soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
, also contain trypsin inhibitors which interfere with the action of the digestive enzyme trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
. Normal cooking processes degrade lectins and trypsin inhibitors to harmless forms.
Other uses
Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
grows attached to cotton plant seeds. Other seed fibers are from kapok and milkweed.
Many important nonfood oils are extracted from seeds. Linseed oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colorless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by ...
is used in paints. Oil from jojoba and crambe are similar to whale oil
Whale oil is oil obtained from the blubber of whales. Oil from the bowhead whale was sometimes known as train-oil, which comes from the Dutch word ''traan'' ("tear drop").
Sperm oil, a special kind of oil used in the cavities of sperm whales, ...
.
Seeds are the source of some medicines including castor oil
Castor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans, the seeds of the plant ''Ricinus communis''. The seeds are 40 to 60 percent oil. It is a colourless or pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is and its den ...
, tea tree oil
Tea tree oil, also known as melaleuca oil, is an essential oil with a fresh, camphoraceous odour and a colour that ranges from pale yellow to nearly colourless and clear. It is derived from the leaves of the tea tree, '' Melaleuca alternif ...
and the quack cancer drug Laetrile.
Many seeds have been used as bead
A bead is a small, decorative object that is formed in a variety of shapes and sizes of a material such as stone, bone, shell, glass, plastic, wood, or pearl and with a small hole for threading or stringing. Beads range in size from under 1 ...
s in necklaces and rosaries including Job's tears, Chinaberry, rosary pea, and castor bean. However, the latter three are also poisonous.
Other seed uses include:
* Seeds once used as weights for balances.
* Seeds used as toys by children, such as for the game Conkers
Conkers is a List of traditional children's games, traditional children's game in Great Britain and Ireland played using the seeds of Aesculus hippocastanum, horse chestnut trees—the name 'conker' is also applied to the seed and to the tree i ...
.
* Resin from '' Clusia rosea'' seeds used to caulk boats.
* Nematicide from milkweed seeds.
* Cottonseed meal used as animal feed and fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
.
Seed records
 * The oldest viable
* The oldest viable carbon-14
Carbon-14, C-14, C or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic matter is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and coll ...
-dated seed that has grown into a plant was a Judean date palm seed about 2,000 years old, recovered from excavations at Herod the Great
Herod I or Herod the Great () was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman Jewish client king of the Herodian kingdom of Judea. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea. Among these works are the rebuilding of the ...
's palace on Masada
Masada ( ', 'fortress'; ) is a mountain-top fortress complex in the Judaean Desert, overlooking the western shore of the Dead Sea in southeastern Israel. The fort, built in the first century BCE, was constructed atop a natural plateau rising ov ...
in Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
. It was germinated in 2005. (A reported regeneration of '' Silene stenophylla'' (narrow-leafed campion) from material preserved for 31,800 years in the Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
n permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
was achieved using fruit tissue, not seed.)
* The largest seed is produced by the coco de mer, or "double coconut palm", ''Lodoicea maldivica''. The entire fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
may weigh up to 23 kilograms (50 pounds) and usually contains a single seed.
* The smallest seeds are produced by epiphytic orchids
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth ...
. They are only 85 micrometers long, and weigh 0.81 micrograms. They have no endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Pla ...
and contain underdeveloped embryos.
* The earliest fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
seeds are around 365 million years old from the Late
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Groh ...
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
of West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
. The seeds are preserved immature ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the sporangium, megasporangium), ...
s of the plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
'' Elkinsia polymorpha''.
In religion
TheBook of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek language, Greek ; ; ) is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its incipit, first word, (In the beginning (phrase), 'In the beginning'). Genesis purpor ...
in the Old Testament begins with an explanation of how all plant forms began:
And God said, Let the earth bring forth grass, the herb yielding seed, and the fruit tree yielding fruit after his kind, whose seed is in itself, upon the earth: and it was so. And the earth brought forth grass, and herb yielding seed after its kind, and the tree yielding fruit, whose seed was in itself, after its kind: and God saw that it was good. And the evening and the morning were the third day.The
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
speaks of seed germination thus:
It isAllah Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...Who causeth the seed-grain and the date-stone to split and sprout. He causeth the living to issue from the dead, and He is the one to cause the dead to issue from the living. That is Allah: then how are ye deluded away from the truth?Quran, Translation: Abdullah Yusuf Ali, Al-An'aam 95:6
See also
*Biological dispersal
Biological dispersal refers to both the movement of individuals (animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, etc.) from their birth site to their breeding site ('natal dispersal') and the movement from one breeding site to another ('breeding dispersal' ...
* Carpology
* Genetically modified crops
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of '' Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of ...
* List of world's largest seeds
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
* Recalcitrant seed
* Seed company
Seed companies produce and sell seeds for flowers, Fruit, fruits and vegetables to commercial growers and amateur gardener, gardeners. The production of seed is a multibillion-dollar global business, which uses growing facilities and growing loca ...
* Seed enhancement
* Seed library
* Seed orchard
A seed orchard is an intensively-managed plantation of specifically arranged trees for the mass production of genetically improved seeds to create plants, or seeds for the establishment of new forests.
General
Seed orchards are a common method of ...
* Seed paper
* Seed saving
In agriculture and gardening, seed saving (sometimes known as brown bagging) is the practice of saving seeds or other reproductive material (e.g. tubers, Grafting, scions, Cutting (plant), cuttings) from vegetables, grain, herbs, and flowers for u ...
* Seed testing
* Seed trap
* Seedbed
* Soil seed bank
* Selective embryo abortion
References
Bibliography
* *A.C. Martin. The Comparative Internal Morphology of Seeds. American Midland Naturalist Vol. 36, No. 3 (Nov., 1946), pp. 513–660
M.B. McDonald, Francis Y. Kwong (eds.). Flower Seeds: Biology and Technology. CABI, 2005.
Edred John Henry Corner. The Seeds of Dicotyledons. Cambridge University Press, 1976.
United States Forest Service. Woody Plant Seed Manual. 1948
Stuppy, W. Glossary of Seed and Fruit Morphological Terms. Royal botanical gardens, Kew 2004
External links
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20070528090503/http://www.kew.org/msbp/ The Millennium Seed Bank ProjectKew Garden's ambitious preservation project
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault
– a backup facility for the world's seed banks
Plant Physiology online: Types of Seed Dormancy and the Roles of Environmental Factors
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20141218084446/http://theseedsite.co.uk/ The Seed Site collecting, storing, sowing, germinating, and exchanging seeds, with pictures of seeds, seedpods and seedlings.
Plant Fix: Check out various plant seeds and learn more information about them
{{Authority control Botany Plant reproduction Plant sexuality