|
Ricin
Ricin ( ) is a lectin (a carbohydrate-binding protein) and a highly potent toxin produced in the seeds of the castor oil plant, ''Ricinus communis''. The median lethal dose (LD50) of ricin for mice is around 22 micrograms per kilogram of body weight via intraperitoneal injection. Oral exposure to ricin is far less toxic. An estimated lethal oral dose in humans is approximately one milligram per kilogram of body weight. Ricin is a toxalbumin and was first described by Peter Hermann Stillmark, the founder of lectinology. Ricin is chemically similar to Robin (toxin), robin. Biochemistry Ricin is classified as a type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP). Whereas type 1 RIPs are composed of a single protein chain that possesses catalytic activity, type 2 RIPs, also known as holotoxins, are composed of two different protein chains that form a heterodimeric complex. Type 2 RIPs consist of an A chain that is functionally equivalent to a type 1 RIP, covalently connected by a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castor Oil Plant
''Ricinus communis'', the castor bean or castor oil plant, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus, ''Ricinus'', and subtribe, Ricininae. The evolution of castor and its relation to other species are currently being studied using modern genetic tools. It reproduces with a mixed pollination system which favors selfing by geitonogamy but at the same time can be an out-crosser by anemophily (wind pollination) or entomophily (insect pollination). Its seed is the castor bean, which despite the term is not a bean (as it is not the seed of a member of the family Fabaceae). Castor is indigenous to the southeastern Mediterranean Basin, East Africa, and India, but is widespread throughout tropical regions (and widely grown elsewhere as an ornamental plant). Castor seed is the source of castor oil, which has a wide variety of uses. The seeds contain between 40% and 60% oil that is rich in triglycerides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Hermann Stillmark
Peter Hermann Stillmark (22 July 1860, Penza, Russian Empire – 23 June 1923, Pärnu, Estonia) was a Baltic-German microbiologist. In 1888 at the University in Dorpat, now Tartu in Estonia under Professor Rudolf Kobert's supervision, he completed his doctoral thesis ''Über Ricin, ein giftiges Ferment aus den Samen von ''Ricinus comm.'' L. und einigen anderen Euphorbiaceen'', which is a description of the isolation of ricin, a poisonous protein component from castor beans. That event is internationally recognized as the discovery of a class of carbohydrate-binding proteins called lectins and the birth of a new branch of science called lectinology. In 1988 the University of Tartu crafted a medal to commemorate the centennial of Stillmark’s discovery. It was awarded to Samuel Barondes in September 1990 at the 12th meeting of the International Lectin Society (Interlec-12) in Davis California for his pioneering studies of the multiple biological functions of galectins, a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar Moiety (chemistry), groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination (biology), agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in recognition at the cellular and molecular level and play numerous roles in biological recognition phenomena involving cells, carbohydrates, and proteins. Lectins also mediate attachment and binding of bacteria, viruses, and fungi to their intended targets. Lectins are found in many foods. Some foods, such as beans and grains, need to be cooked, fermented or sprouted to reduce lectin content. Some lectins are beneficial, such as CLEC11A, which promotes bone growth, while others may be powerful toxins such as ricin. Lectins may be disabled by specific monosaccharides, mono- and oligosaccharides, which bind to ingested lectins from grains, legumes, nightshade plants, and dairy; binding can prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxalbumin
Toxalbumins are toxic plant proteins that disable ribosomes and thereby inhibit protein synthesis, producing severe cytotoxic effects in multiple organ systems. They are dimers held together by a disulfide bond and comprise a lectin (carbohydrate-binding protein) part which binds to the cell membrane and enables the toxin part to gain access to the cell contents. Toxalbumins are similar in structure to AB toxins found in cholera, tetanus, diphtheria, botulinum and others; and their physiological and toxic properties are similar to those of viperine snake venom. Description Toxalbumins were first described in about 1890 by Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919) and Sigmund Fraenkel (1868–1939), associates of the organic chemist Eugen Baumann. Brieger first used the term toxin. Toxalbumins notably are present in the plant families Leguminosae and Euphorbiaceae, occurring for instance in ''Robinia pseudoacacia'', '' Abrus precatorius'', '' Jatropha curcas'', '' Croton gratissimus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome-inactivating Protein
A ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) is a protein synthesis inhibitor that acts at the eukaryote, eukaryotic ribosome. This protein family describes a large family of such proteins that work by acting as rRNA N-glycosylase (EC 3.2.2.22). They inactivate 60S ribosomal subunits by an N-glycosidic cleavage, which releases a specific adenine base from the sugar-phosphate backbone of 28S rRNA. RIPs exist in bacteria and plants. Members of the family include shiga toxins, and type I (e.g. trichosanthin and luffin) and type II (e.g. ricin, agglutinin, and abrin) ribosome inactivating proteins (RIPs). All these toxins are structurally related. RIPs have been of considerable interest because of their potential use, conjugated with Monoclonal antibody, monoclonal antibodies, as immunotoxins to treat cancers. Further, trichosanthin has been shown to have potent activity against HIV-1-infected T cells and macrophages. Elucidation of the structure-function relationships of RIPs has therefore b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrin
Abrin is an extremely toxic toxalbumin found in the seeds of the rosary pea (or jequirity pea), '' Abrus precatorius''. It has a median lethal dose of 0.7 micrograms per kilogram of body mass when given to mice intravenously (approximately 3.86 times more toxic than ricin, being 2.7 micrograms per kilogram). The median toxic dose for humans ranges from 10 to 1000 micrograms per kilogram when ingested and is 3.3 micrograms per kilogram when inhaled. Abrin is a ribosome inhibiting protein like ricin, a toxin which can be found in the seeds of the castor oil plant, and pulchellin, a toxin which can be found in the seeds of '' Abrus pulchellus''. Abrin is classed as a " select agent" under U.S. law. Occurrence Abrin is only formed in nature by the rosary pea. The brightly coloured seeds of this plant contain about 0.08% of abrin. The toxin is found within the seeds, and its release is prevented by the seed coat. If the seed coat is injured or destroyed (by chewing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Lethal Dose
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for " lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a given substance. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of higher toxicity. The term LD50 is generally attributed to John William Trevan. The test was created by J. W. Trevan in 1927. The term semilethal dose is occasionally used in the same sense, in particular with translations of foreign language text, but can also refer to a sublethal dose. LD50 is usually determined by tests on animals such as laboratory mice. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved alternative methods to LD50 for testing the cosmetic drug botox without animal tests. Conventions The LD50 is usually expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from '' toxic''. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. They vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Less strict understandings embrace naturally occurring inorganic toxins, such as arsenic. Other understandings embrace synthetic analogs of naturally occurring organic poisons as toxins, and may or may not embrace naturally oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
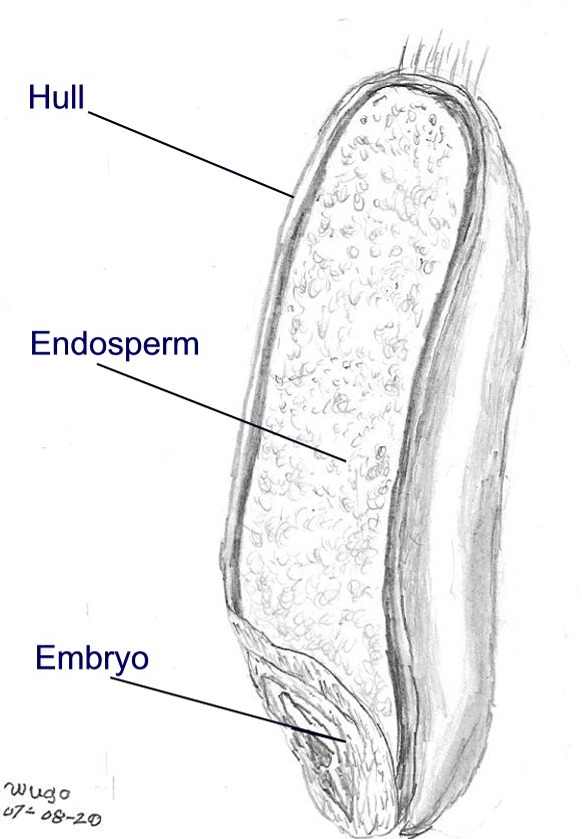
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Quaternary Structure
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also referred to as subunits). Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple dimers to large homooligomers and complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other cofactors. Description and examples Many proteins are actually assemblies of multiple polypeptide chains. The quaternary structure refers to the number and arrangement of the protein subunits w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u, respectively) is a unit of mass defined as of the mass of an Bound state, unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and invariant mass, at rest. It is a Non-SI units mentioned in the SI, non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. The word "unified" emphasizes that the definition was accepted by both IUPAP and IUPAC. The atomic mass constant, denoted , is defined identically. Expressed in terms of , the atomic mass of carbon-12: . Its value in International System of Units, SI units is an experimentally determined quantity. The 2022 CODATA recommended value of the atomic mass constant expressed in the SI base unit kilogram is:This value serves as a Conversion of units, conversion factor of mass from daltons to kilograms, which can easily be converted to Gram, grams and other metric units of mass. The 2019 revision of the SI redefined the kilogram by fixing the value of the Planck constant (), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16–30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus (or occasionally nonclassically at the C-terminus or internally) of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles (the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi or endosomes), secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, most type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide. Function (translocation) Signal peptides function to prompt a cell to transloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |