swim bladders on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled

 The swim bladder normally consists of two gas-filled sacs located in the
The swim bladder normally consists of two gas-filled sacs located in the
 Swim bladders are evolutionarily closely related (i.e., homologous) to
Swim bladders are evolutionarily closely related (i.e., homologous) to
File:Melaka-mall-Fish-maw-kiosk-2267.jpg, Swim bladder display in a
"Buoyancy at depth"
In: WS Hoar, DJ Randall and AP Farrell (Eds) ''Deep-Sea Fishes'', pages 195–237, Academic Press. . {{DEFAULTSORT:Swim Bladder Organs (anatomy) Fish anatomy

 The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
in bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
that functions to modulate buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift via swimming, which expends more energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
. Also, the dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
position of the swim bladder means that the expansion of the bladder moves the center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the d ...
downwards, allowing it to act as a stabilizing apparatus. Additionally, the swim bladder functions as a resonating chamber to produce or receive sound.
The swim bladder is evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
arily homologous to the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s of tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s and lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the class Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, inc ...
, and some ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ...
such as bowfins have also evolved similar respiratory functions in their swim bladders. Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
remarked upon this in ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'')The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by M ...
'', and reasoned that the lung in air-breathing vertebrates had derived from a more primitive swim bladder as a specialized form of enteral respiration.
Some species, such as mostly bottom dwellers like the weather fish and redlip blenny, have secondarily lost the swim bladder during the embryonic stage. Other fish, like the opah and the pomfret, use their pectoral fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column ...
s to swim and balance the weight of the head to keep a horizontal position. The normally bottom-dwelling sea robin
Prionotinae is a subfamily of demersal, marine ray-finned fishes, part of the family Triglidae. The fishes in this subfamily are called sea robins and are found in the Western Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans, the other two Triglid subfamili ...
can use their pectoral fins to produce lift while swimming like cartilaginous fish do.
The gas/tissue interface at the swim bladder produces a strong reflection of sound, which is used by sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects o ...
equipment to find fish.
Cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
such as shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s and rays do not have swim bladders, as they belong to a completely different evolutionary clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
. Without swim bladders to modular buoyancy, most cartilaginous fish can only control depth by actively swimming, which produce dynamic lift; others store up lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s with specific density
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nea ...
less than that of seawater
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximat ...
to produce a neutral or near-neutral buoyancy, which cannot be readily changed with depth.
Structure and function

 The swim bladder normally consists of two gas-filled sacs located in the
The swim bladder normally consists of two gas-filled sacs located in the dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
portion of the fish, although in a few primitive species, there is only a single sac. It has flexible walls that contract or expand according to the ambient pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
. The walls of the bladder contain very few blood vessels
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the tissues of a body. They also take waste an ...
and are lined with guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
crystals, which make them impermeable to gases. By adjusting the gas pressurising organ using the gas gland or oval window, the fish can obtain neutral buoyancy and ascend and descend to a large range of depths. Due to the dorsal position it gives the fish lateral stability.
In physostomous swim bladders, a connection is retained between the swim bladder and the gut, the pneumatic duct, allowing the fish to fill up the swim bladder by "gulping" air. Excess gas can be removed in a similar manner.
In more derived varieties of fish (the physoclisti), the connection to the digestive tract is lost. In early life stages, these fish must rise to the surface to fill up their swim bladders; in later stages, the pneumatic duct disappears, and the gas gland has to introduce gas (usually oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
) to the bladder to increase its volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ...
and thus increase buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of t ...
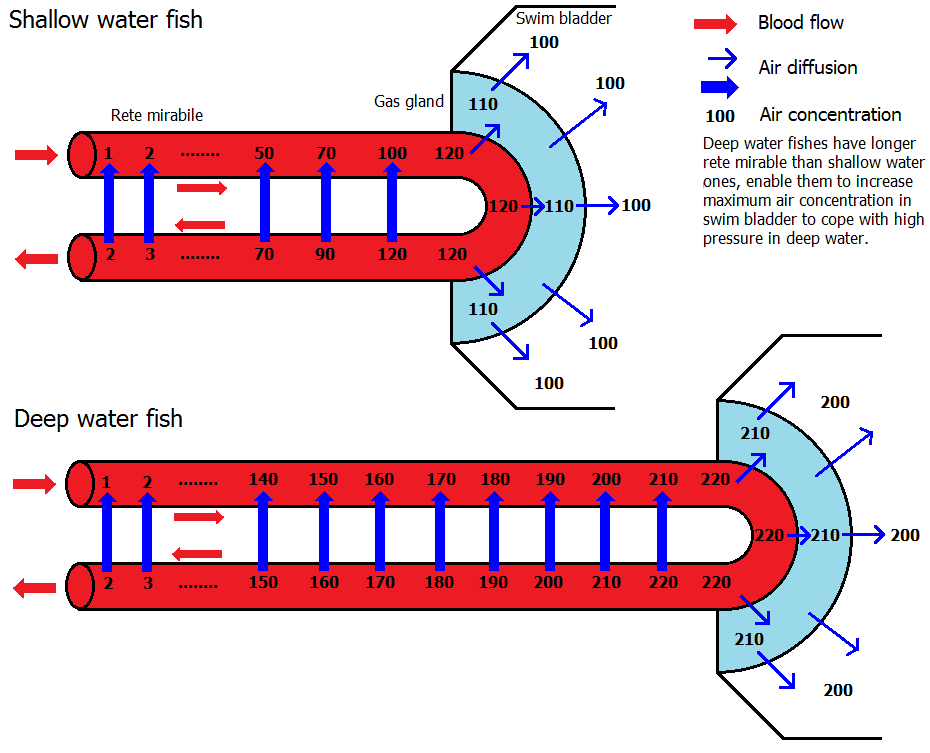
. This process begins with the acidification of the blood in the '' rete mirabile'' when the gas gland excretes lactic acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula C3H6O3. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as wel ...
and produces carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, the latter of which acidifies the blood via the bicarbonate buffer system
The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid-base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid (H2CO3), bicarbonate ion (HCO), and carbon dioxide (CO2) in order to maintain pH in the blood and duodenum, among other tissues, to suppo ...
. The resulting acidity causes the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
of the blood to lose its oxygen ( Root effect) which then diffuses partly into the swim bladder. Before returning to the body, the blood re-enters the ''rete mirabile'', and as a result, virtually all the excess carbon dioxide and oxygen produced in the gas gland diffuses back to the arteries supplying the gas gland via a countercurrent multiplication loop. Thus a very high gas pressure of oxygen can be obtained, which can even account for the presence of gas in the swim bladders of deep sea fish like the eel, requiring a pressure of hundreds of bars. Elsewhere, at a similar structure known as the 'oval window', the bladder is in contact with blood and the oxygen can diffuse back out again. Together with oxygen, other gases are salted out in the swim bladder which accounts for the high pressures of other gases as well.
The combination of gases in the bladder varies. In shallow water fish, the ratios closely approximate that of the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, while deep sea fish tend to have higher percentages of oxygen. For instance, the eel '' Synaphobranchus'' has been observed to have 75.1% oxygen, 20.5% nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, 3.1% carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, and 0.4% argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
in its swim bladder.
Physoclist swim bladders have one important disadvantage: they prohibit fast rising, as the bladder would burst. Physostome
Physostomes are fishes that have a pneumatic duct connecting the gas bladder to the alimentary canal. This allows the gas bladder to be filled or emptied via the mouth. This not only allows the fish to fill their bladder by gulping air, but al ...
s can "burp" out gas, though this complicates the process of re-submergence.
The swim bladder in some species, mainly fresh water fishes (common carp
The common carp (''Cyprinus carpio''), also known as European carp, Eurasian carp, or simply carp, is a widespread freshwater fish of eutrophic waters in lakes and large rivers in Europe and Asia.Fishbase''Cyprinus carpio'' Linnaeus, 1758/ref>Ark ...
, catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order (biology), order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are common name, named for their prominent barbel (anatomy), barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not ...
, bowfin) is interconnected with the inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
of the fish. They are connected by four bones called the Weberian ossicles from the Weberian apparatus. These bones can carry the vibrations to the saccule
The saccule (Latin: sacculus) is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear that detects linear acceleration and head tilting in the vertical plane, and converts these vibrations into electrical impulses to be interpreted by the brain. When the he ...
and the lagena. They are suited for detecting sound and vibrations due to its low density in comparison to the density of the fish's body tissues. This increases the ability of sound detection. The swim bladder can radiate the pressure of sound which help increase its sensitivity and expand its hearing. In some deep sea fishes like the '' Antimora'', the swim bladder maybe also connected to the macula of saccule in order for the inner ear to receive a sensation from the sound pressure.
In red-bellied piranha
The red-bellied piranha, also known as the red piranha (''Pygocentrus nattereri''), is a Type (biology), type of piranha native to South America, found in the Amazon basin, Amazon, Paraguay River, Paraguay, Paraná River, Paraná and Essequibo Ri ...
, the swim bladder may play an important role in sound production as a resonator. The sounds created by piranhas are generated through rapid contractions of the sonic muscles and is associated with the swim bladder.
Teleost
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of f ...
s are thought to lack a sense of absolute hydrostatic pressure
Hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and "the pressure in a fluid or exerted by a fluid on an immersed body". The word "hydrostatics" is sometimes used to refer specifically to water and o ...
, which could be used to determine absolute depth. However, it has been suggested that teleosts may be able to determine their depth by sensing the rate of change of swim-bladder volume.
Evolution
 Swim bladders are evolutionarily closely related (i.e., homologous) to
Swim bladders are evolutionarily closely related (i.e., homologous) to lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s. The first lungs originated in the last common ancestor of the Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built ...
(ray-finned fish) and Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class (biology), class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. The ...
(lobe-finned fish and the tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s) as expansions of the upper digestive tract which allowed them to gulp air under oxygen-poor conditions. In the Actinopteri (ray-finned fish minus the bichir
Bichirs and the reedfish comprise Polypteridae , a family (biology), family of archaic Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes and the only family in the order (biology), order Polypteriformes .Helfman GS, Collette BB, Facey DE, Bowen BW. 2009. The D ...
s) the lungs evolved into a swim bladder (secondary absent in some lineages), which unlike lungs that bud ventrally, buds dorsally from the anterior foregut. Coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, bi ...
s have a "fatty organ" that have sometimes been referred to as a swim bladder, but is structurally different and have a separate evolutionary history.
In 1997, Farmer proposed that lungs evolved to supply the heart with oxygen. In fish, blood circulates from the gills to the skeletal muscle, and only then to the heart. During intense exercise, the oxygen in the blood gets used by the skeletal muscle before the blood reaches the heart. Primitive lungs gave an advantage by supplying the heart with oxygenated blood via the cardiac shunt. This theory is robustly supported by the fossil record, the ecology of extant air-breathing fishes, and the physiology of extant fishes. In embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
nal development, both lung and swim bladder originate as an outpocketing from the gut; in the case of swim bladders, this connection to the gut continues to exist as the pneumatic duct in the more "primitive" ray-finned fish, and is lost in some of the more derived teleost orders. There are no animals which have both lungs and a swim bladder.
As an adaptation to migrations between the surface and deeper waters, some fish have evolved a swim bladder where the gas is replaced with low-density wax ester
A wax ester (WE) is an ester of a fatty acid and a fatty alcohol. Wax esters are the main components of three commercially important waxes: carnauba wax, candelilla wax, and beeswax..
Wax esters are formed by combining one fatty acid with one ...
s as a way to cope with Boyle's law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an empirical gas laws, gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as:
...
.
The cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
(e.g., sharks and rays) split from the other fishes about 420 million years ago, and lack both lungs and swim bladders, suggesting that these structures evolved after that split. Correspondingly, these fish also have both heterocercal
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
and stiff, wing-like pectoral fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column ...
s which provide the necessary lift needed due to the lack of swim bladders. Teleost fish with swim bladders have neutral buoyancy, and have no need for this lift.
Sonar reflectivity
The swim bladder of a fish can strongly reflect sound of an appropriate frequency. Strong reflection happens if the frequency is tuned to the volume resonance of the swim bladder. This can be calculated by knowing a number of properties of the fish, notably the volume of the swim bladder, although the well-accepted method for doing so requires correction factors for gas-bearing zooplankton where the radius of the swim bladder is less than about 5 cm. This is important, since sonar scattering is used to estimate the biomass of commercially- and environmentally-important fish species.Deep scattering layer
Sonar operators, using the newly developed sonar technology during World War II, were puzzled by what appeared to be a false sea floor 300–500 metres deep at day, and less deep at night. This turned out to be due to millions of marine organisms, most particularly small mesopelagic fish, with swimbladders that reflected the sonar. These organisms migrate up into shallower water at dusk to feed on plankton. The layer is deeper when the moon is out, and can become shallower when clouds obscure the moon. Most mesopelagic fish make daily vertical migrations, moving at night into the epipelagic zone, often following similar migrations of zooplankton, and returning to the depths for safety during the day. These vertical migrations often occur over large vertical distances, and are undertaken with the assistance of a swim bladder. The swim bladder is inflated when the fish wants to move up, and, given the high pressures in the mesopelagic zone, this requires significant energy. As the fish ascends, the pressure in the swimbladder must adjust to prevent it from bursting. When the fish wants to return to the depths, the swimbladder is deflated. Some mesopelagic fishes make daily migrations through thethermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is
a distinct layer based on temperature within a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) with a high gradient of distinct te ...
, where the temperature changes between , thus displaying considerable tolerance for temperature change.
Sampling via deep trawling
Trawling is an industrial method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch di ...
indicates that lanternfish
Lanternfish (or myctophids, from the Greek language, Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family (biology), family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, ...
account for as much as 65% of all deep sea fish biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
. Indeed, lanternfish are among the most widely distributed, populous, and diverse of all vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s, playing an important ecological
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely re ...
role as prey for larger organisms. The estimated global biomass of lanternfish is 550–660 million tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s, several times the annual world fisheries catch. Lanternfish also account for much of the biomass responsible for the deep scattering layer of the world's oceans. Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects o ...
reflects off the millions of lanternfish swim bladders, giving the appearance of a false bottom.
Human uses
In the East Asian culinary sphere, the swim bladders of certain large fishes are considered a food delicacy. In Chinese cuisine, they are known as ''fish maw'', 花膠/鱼鳔, and are served in soups or stews. The vanity price of a vanishing kind of maw is behind the imminent extinction of the vaquita, the world's smallest porpoise species. Found only in Mexico'sGulf of California
The Gulf of California (), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Vermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California peninsula from ...
, the once numerous vaquita are now critically endangered. Vaquita die in gillnets set to catch totoaba (the world's largest drum fish). Totoaba are being hunted to extinction for its maw, which can sell for as much $10,000 per kilogram.
Swim bladders are also used in the food industry as a source of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
. They can be made into a strong, water-resistant glue, or used to make isinglass
Isinglass ( ) is a form of collagen obtained from the dried swim bladders of fish. The English word origin is from the obsolete Dutch ''huizenblaas'' – ''huizen'' is a kind of sturgeon, and ''blaas'' is a bladder, or German ''Hausenblase'', ...
for the clarification of beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
. In earlier times, they were used to make condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
s.
Swim bladder disease
Swim bladder disease is a common ailment in aquarium fish. A fish with swim bladder disorder can float nose down tail up, or can float to the top or sink to the bottom of the aquarium.Johnson, Erik L. and Richard E. Hess (2006) ''Fancy Goldfish: A Complete Guide to Care and Collecting'', Weatherhill, Shambhala Publications, Inc.Risk of injury
Manyanthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
activities, such as pile driving
A pile driver is a heavy-duty tool used to drive piling, piles into soil to build piers, bridges, cofferdams, and other "pole" supported structures, and patterns of pilings as part of permanent deep foundations for buildings or other structures ...
or even seismic waves
A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic wave, acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or generally, a quake (natural phenomenon), quake), types of volcanic eruptions ...
, can create high-intensity sound waves that cause internal injury to fish that possess a gas bladder.
Physoclisti can not expel air quickly enough from the gas bladder, the organ most susceptible to sonic damage, thus making it difficult for them to escape major injury. Physostomes, on the other hand, ''can'' release air from their gas bladder expeditiously enough to protect it; nevertheless, they can not relieve pressure in their other vital organs, and are therefore also vulnerable to injury. Some of the commonly seen injuries include ruptured gas bladder and renal Haemorrhage. These mostly affect the overall health of the fish but not their mortality rate. Investigators employed the High-Intensity-Controlled Impedance-Fluid-Filled (HICI-FT), a stainless-steel wave tube with an electromagnetic shaker. It simulates high-energy sound waves in aquatic far-field, plane-wave acoustic conditions.
Similar structures in other organisms
Siphonophores have a special swim bladder that allows the jellyfish-like colonies to float along the surface of the water while their tentacles trail below. This organ is unrelated to the one in fish.Gallery
Malacca
Malacca (), officially the Historic State of Malacca (), is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the Peninsular Malaysia#Other features, southern region of the Malay Peninsula, facing the Strait of Malacca ...
shopping mall
File:Fish maw soup.jpg, Fish maw soup
File:Goldfish with swim bladder disease.JPG, Swim bladder disease has resulted in this female ryukin goldfish floating upside down
References
Further references
* Bond, Carl E. (1996) ''Biology of Fishes'', 2nd ed., Saunders, pp. 283–290. * Pelster, Bernd (1997"Buoyancy at depth"
In: WS Hoar, DJ Randall and AP Farrell (Eds) ''Deep-Sea Fishes'', pages 195–237, Academic Press. . {{DEFAULTSORT:Swim Bladder Organs (anatomy) Fish anatomy